Unique visualization of the wealth gap shows what your salary looks like stacked in $5 bills
This eye-opening visualization makes income inequality impossible to ignore.
These stacks are easy enough to grasp, but the two in the back will blow your mind.
There comes a point in many conversations when numbers all just start to lose meaning. The nearest star is, however, many gazillion miles away. The national debt is, however, many tens of trillions of dollars. None of it really makes sense.
We can't really understand numbers at this scale, which is a problem because numbers matter when it comes to things like policy decisions and economic justice. If we can't truly understand the scale of an issue like income inequality, how can we even begin to address it? And income inequality is an issue that needs to be addressed.
The value of a stack of fives

A five-dollar bill is still enough to buy a cup of coffee in most places. Stack 200 of them together, and you have a thousand dollars, which is just under an inch tall. That will be our basic unit of measurement as we climb the economic ladder. It's something tangible that we can understand easily.
Minimum wage: barely scraping by
The federal minimum wage in early 2025 is $7.25 an hour. Someone working full-time at this rate earns $15,080 a year—a stack of fives about 13 inches tall. This number hasn't changed since 2009, and in inflation-adjusted buying power, it's the lowest it has been in 66 years.
The wealth gap visualized in stacks of $5 bills Greg Sullivan/Upworthy
A two-adult household working full-time at minimum wage earns $30,160, which is just above the poverty line of $24,860—a stack of about 21 inches. People living at this level will struggle to get the basic necessities of life, and even a minor setback can be devastating.
The median full-time worker: financial stability with limits

The median annual income in the united states was, as of 2024, about $57,000. This translates to a stack of five-dollar bills just over four feet tall. Depending on where a person lives, they can get by pretty comfortably, but things are still financially precarious. Good luck saving up or surviving a layoff.
Interestingly, this stack of fives is tall enough that, according to OSHA guidelines, you should wear safety gear when working here.
High earners: entering serious money
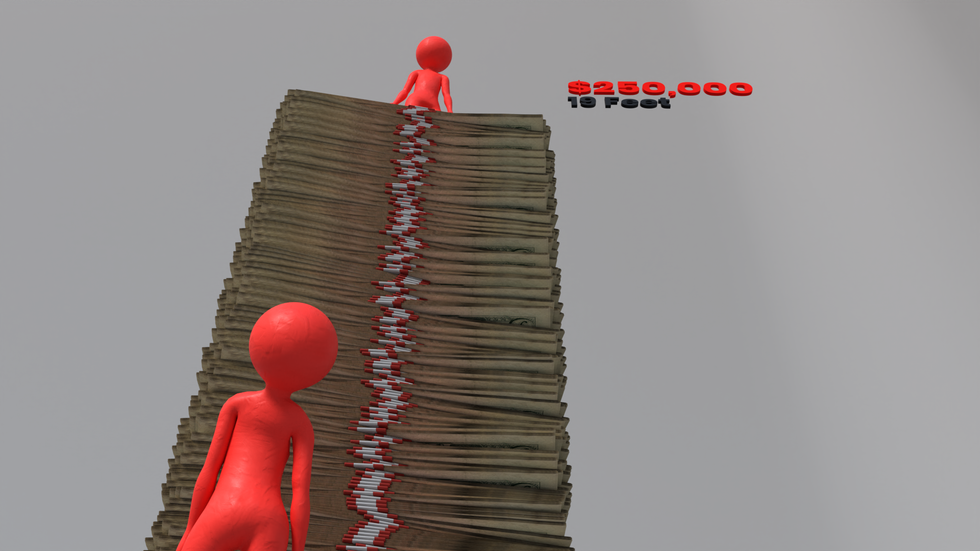

Hitting an annual income of $250,000 puts you in the “high earner” category. That’s an 18-foot stack of fives—taller than a two-story house.
Among the fun ways you might get yourself a stack like this are being a drone light-show operator, a high-end stylist, or maybe playing on an NFL team’s practice squad. That’s right… the practice squad will get you about $250,000 a year. Nice work if you can get it!
A millionaire’s earnings: wealth that withstands crises
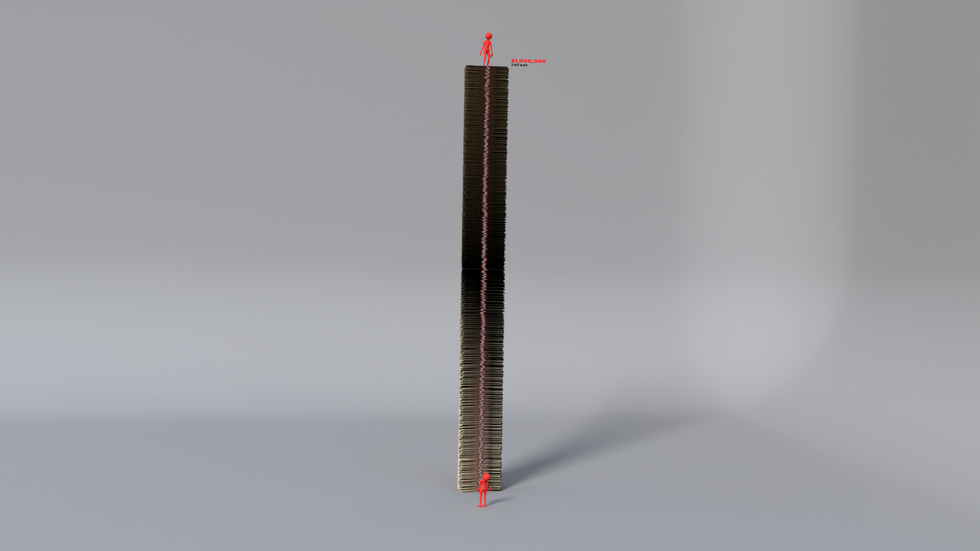
A quarter-million dollars is a lot of money, but it's never been the ultimate dream. After all, the show wasn't called Who Wants to Be a Quarter Millionaire. For generations, a million dollars has held a mythical status. But if you had won that prize on Who Wants to Be a Millionaire’s first season in 1999, today it would be worth only about $550,000 after adjusting for inflation.
A million dollars in five-dollar bills would stack up to about 72 feet. At this level, financial setbacks aren’t life-ruining. If you're taking home this much money a year, inflation or not, you probably live a very enviable life.
A billionaire: money beyond comprehension
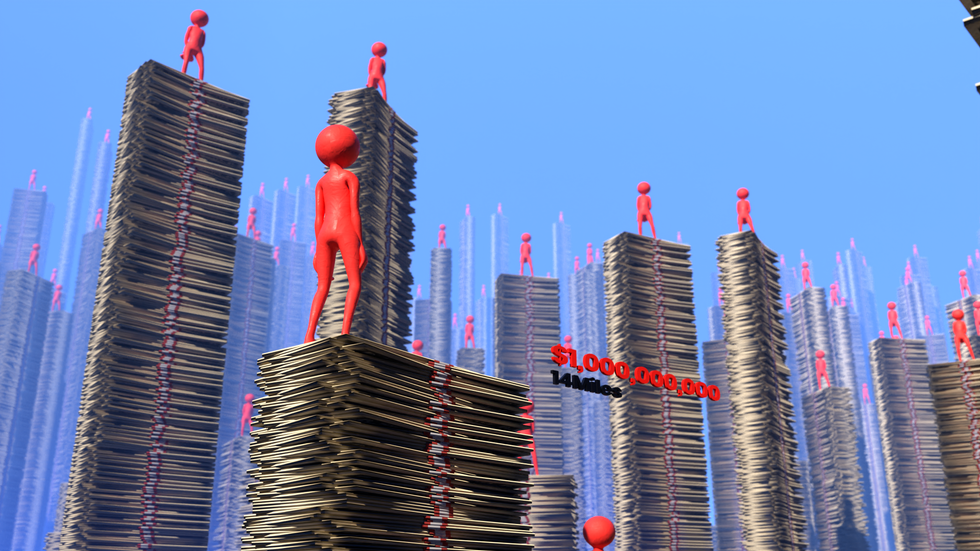

A new class of Americans is emerging, and people are starting to take notice. These individuals haven’t just achieved the American Dream of a million dollars, they’ve surpassed it by over a thousand times.
A billion dollars stacked in $5 bills would reach 13.5 miles into the sky, towering higher than Mt. Everest.
In 1916, John D. Rockefeller became the first billionaire in U.S. history. Today, there are 737 billionaires in the country. In the past four years alone, 123 more have joined their ranks, that’s one every 12 days.
Elon Musk: wealth at an astronomical scale
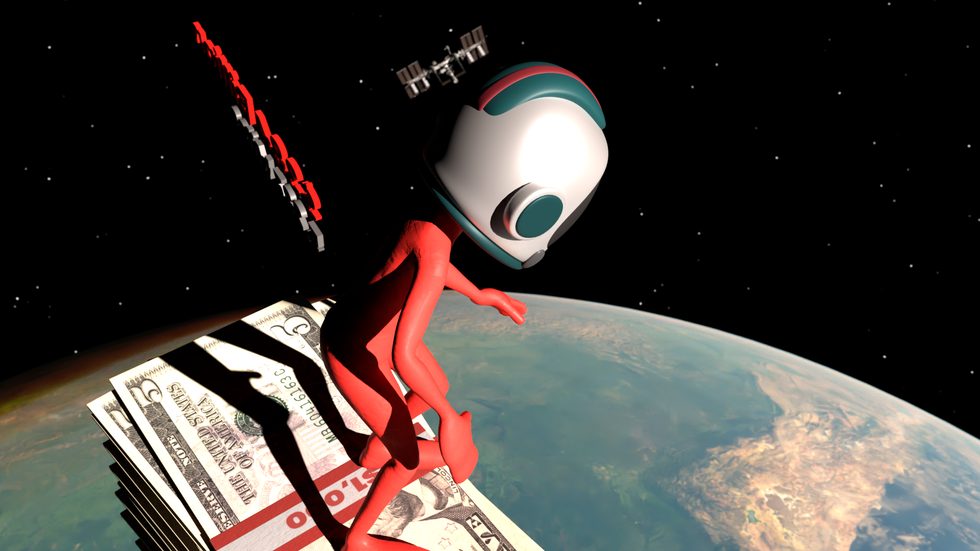

Elon Musk is the richest man in the U.S., with a net worth of about $384 billion as of March 2025—though that number fluctuates depending on when and how you measure it. Stacked in $5 bills, his fortune would soar more than 5,220 miles into the sky. To put that in perspective, his net worth has almost certainly shifted by more than you'll earn in a lifetime in just the time it took you to read this sentence.
If he jumped from the top of his theoretical money stack, he’d fall past the entire GDP of Vermont in just three minutes—assuming he didn’t burn up on reentry or drift into orbit. His fortune towers so high that the International Space Station would orbit far below him. Only the Apollo astronauts have ever been higher.
Why these numbers matter
These towering stacks of money are just a visualization, but they highlight the extreme differences in wealth. When the gap is this wide, it affects everything—economic policy, opportunity, and quality of life for millions.
If we want to address inequality, we first need to understand its scale. Because only when we see the differences clearly can we even begin to close the gap.
- A 'Daily Show' correspondent asks a millionaire about inequality and gets an unexpected response. ›
- NFL star Malcolm Jenkins is working to bridge the ethnic wealth gap by giving kids real money to invest ›
- A guy and his friends shared their travel plans. The results perfectly explain the wealth gap. ›




