A school in Northern Ireland banned smartphones and the impact was tremendous
The "buzz" is back at Lisneal College.
Students are Lisneal College in Northern Ireland.
The world has hit an interesting turning point regarding young people and smartphone use, especially in schools. After 15-plus years of letting young people have smartphones on them all day long, we’re beginning to learn that they pose a serious threat to their mental health, social development, and academics.
The most startling research shows that right around 2012, when young people started using smartphones, the U.S. and other developed nations saw an astronomical spike in mental health problems among young people, including self-harm, suicide, psychological distress, anxiety, and depression. The change in behavior among students inspired Lisneal College in Northern Ireland to become the first school in the country to be phone-free. Lisneal College is a co-educational all-ability school for 11 to 18-year-olds.
"Since the introduction of smartphones, our concerns have gradually increased," Craig Johnson, VP for Pastoral Affairs at Lisneal, told Smartphone Free Childhood Northern Ireland. “For me, I'll never forget a clear turning point, where I walked into our school canteen one day, and we had all these students sitting in round tables with their friends and every one of them on their phone, canteen nearly deathly quiet. It was just this moment of reflection and going ‘We have to do something about this and we have to start somewhere.’"
The school administration contacted the students' parents, who shared the same concerns. However, the parents didn’t know how to address the problem.
In 2023, the school implemented a phone-free program for students from years 8 to 12 (grades 7 to 12 in America). Students place their phones in lock boxes upon arrival and cannot access them during the rest of the school day. At the end of the day, they can pick up their phones before they go home. After trying the program for one term, the parents were happy and even saw changes in their kids' attitudes towards technology at home.
What are the benefits of smartphone-free schools?
The large school has had very few concerns after implementing the policy besides some grumbling from older students. One of the older kids at the school, who gave administrators some of the most pushback, later changed their mind after one month. "I'll never forget one of our pupils who had given some of the most pushback said to me after a month, 'Sir, that's been a really good thing for me,'" Johnson said.
The teachers at the school love the policy as well. "Staff were immediately seeing a difference in their classrooms. They were immediately feeding back, 'This was a really good thing,'" Johnson said.
"Pupils are definitely more present in the classroom. They are more prepared and engaged to learn. They don't feel that they are the odd man out if they don't have a mobile phone. For any other schools looking to implement this policy, I say, 'Go for it.' It was a way forward for us, and I feel that it has been real positive. It has definitely benefitted myself, as a teacher, and it has benefitted pupils,” Emma Harper, a teacher at the school, told Smartphone Free Childhood Northern Ireland.
If half your day is spent using screens that gives you continuous rounds of stimulus-response-reward, your brain will adapt and the other half of your day will become more boring. This may be why boredom is rising among Gen Z, and test scores are fallinghttps://t.co/PW7HugD60k
— Jonathan Haidt (@JonHaidt) January 30, 2025
Principal Michael Allen says smartphones are a massive distraction for students, even in their pockets or purses. “If you can imagine sitting in a classroom with a mobile phone in your pocket, even if that phone is never out, and that mobile phone buzzes, rings, chimes,” he told the BBC. "No matter how focused you are as a student, whether you decide to take that phone out and look which some pupils may do, or even if you don’t, you spend the next two or three minutes thinking, ‘Who was that? I wonder who wants me?’"
Johnson says that since the ban, children are talking more to one another and that there is a positive "buzz" and energy at the school now. Gabriella, a year 11 student at the school, says there is much less bullying now that the phones are gone. "You're building better friendships and you're learning how to not be reliable on a phone to start a conversation. So it's a better way to socialize," she said.
"[Before the ban], people would have just stayed on their phones all day, and I know that happens in other schools as well. But here, since we've got the phones took away, people engage with the classes more and they engage with each other," Luke, a year-11 student, added.
Lisneal College’s bold move to ban smartphones has proven to be a huge win for students, teachers, administrators, and parents. Who doesn't want to go to a school where students focus on their teachers, lessons, and each other rather than on their phones? As other schools consider similar rules, Lisneal’s success shows that phone-free may be the best way forward.





 A couple glued to their phones.via
A couple glued to their phones.via  A family glued to their phones.via
A family glued to their phones.via 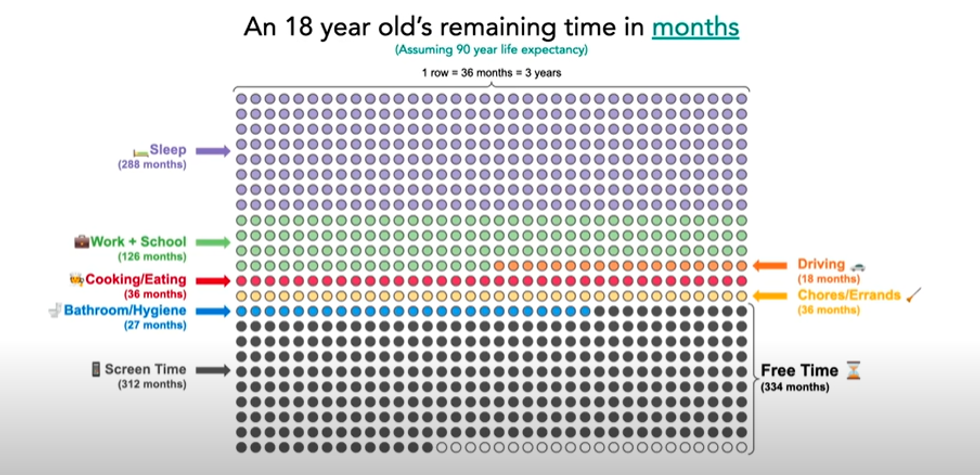 An 18-year-olds remaining time, in months. via TEDx
An 18-year-olds remaining time, in months. via TEDx Dino AMbrosi speaks at Berkeley.via Dino Ambrosi (used with permission)
Dino AMbrosi speaks at Berkeley.via Dino Ambrosi (used with permission) Smartphones are bad for focus.via
Smartphones are bad for focus.via 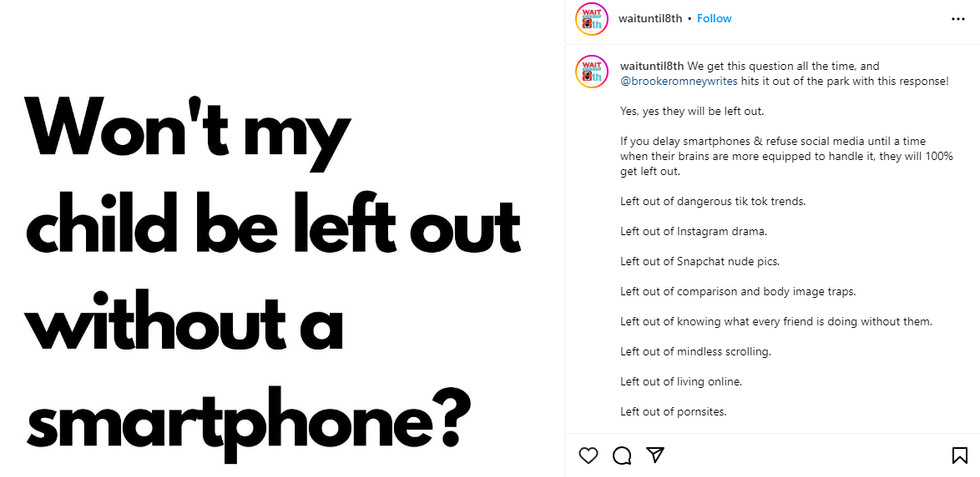 Won't my child be left out without a smartphone?via
Won't my child be left out without a smartphone?via  Boys sitting down and staring at their phones.via
Boys sitting down and staring at their phones.via