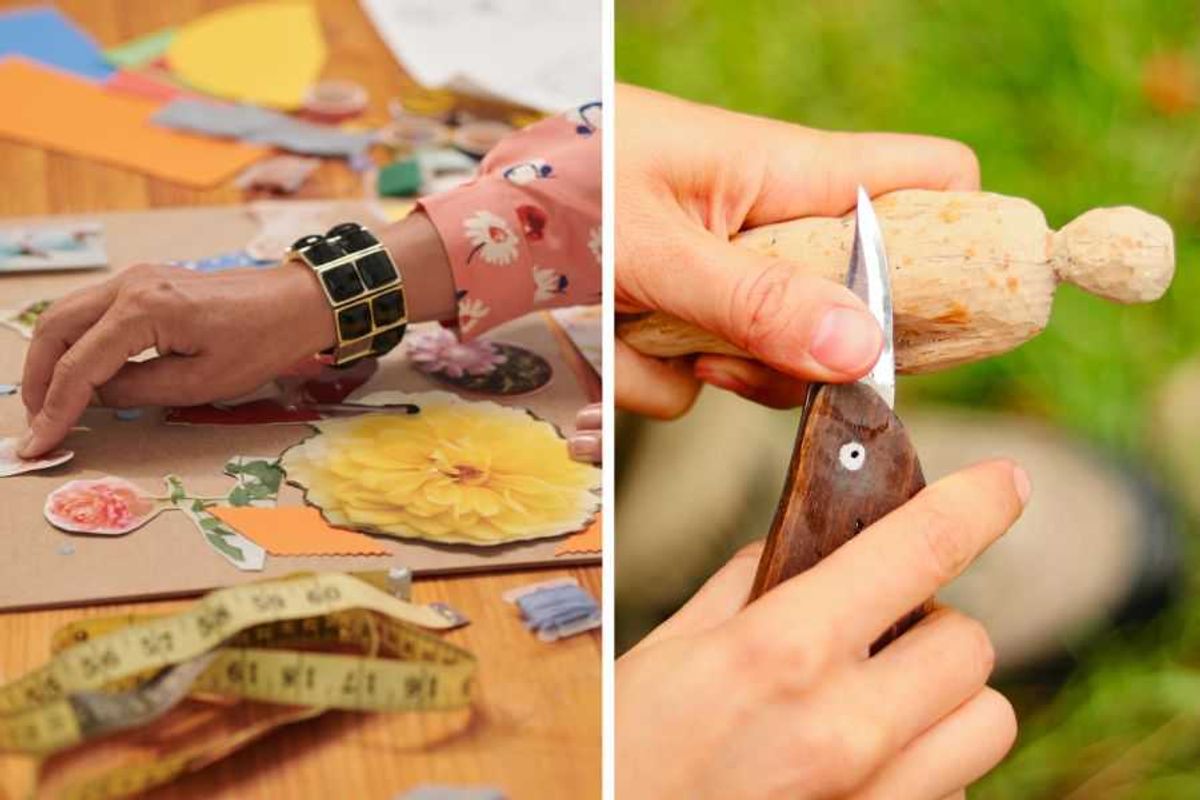
People share their favorite 'non-tech' hobbies that keep them sane in a digital world
Some inspo for those craving a bit of simplicity and a break from the screens.
Working with your hands is medicine for the soul.
Digital fatigue is brutal. It robs us of our focus, productivity, and most importantly, our joy. Thankfully, there is a way to escape the never-ending flurry of notifications, emails, and pings and reclaim our inner peace in a way that’s not only effective but fun as well.
Cue: analog hobbies.
The health benefits of analog hobbies are well-documented. Whether they be artistic pursuits like painting or drawing, which help ease racing thoughts and anxiety, or physical activities like gardening or dancing, which get us more active, or some combination of both, like cooking or woodworking, which enlists both the practical and creative sides of our brains.
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, many of us found out firsthand just how soothing tech-free hobbies could be. According to one survey, nearly two-thirds of Americans picked up a new hobby during this time. And even though we are more or less back to the regular hustle and bustle of pre-COVID times, the need to unplug is just as important now as ever.
If you’re looking for inspiration for your next low-to-no tech hobby, keep reading.
Recently, a Reddit user shared that they had been “craving a bit of simplicity and a break from screens,” and in the process rediscovered former analog passions like sketching and playing vinyl records.
“Personally, I’ve found that stepping away from tech even for just an hour or two really helps with mental clarity and stress relief," they wrote. "Also, there’s something so satisfying about making something with your hands, right?"
“It made me wonder: what non-tech hobbies have you all picked up or returned to recently?" they added. "Whether it’s knitting, gardening, brewing your own coffee, or something else that doesn’t require a charger or Wifi.”
Boy, did people respond in kind. Be it with classics like cross-stitching, or some out-of-the-box ideas like sending postcards to German princes (more on that later). Many even shared samples of their WIPS (works in progress), which was doubly inspiring.
Take a look at some of our favorites:
“Fused glass is my current hobby. I just enjoy doing it and don't look at my phone for hours when I'm cutting glass. Unfortunately, I do have a lot of cuts on my hands.”

“Solo board games. There are tons of different mechanics, difficulties and themes…My favorites are Tiny Epic Dungeons, Nemo’s War, Zombicide Black Plague, Threetale, Grove, Valor and Villainy, Ludwig’s Labyrinth.”
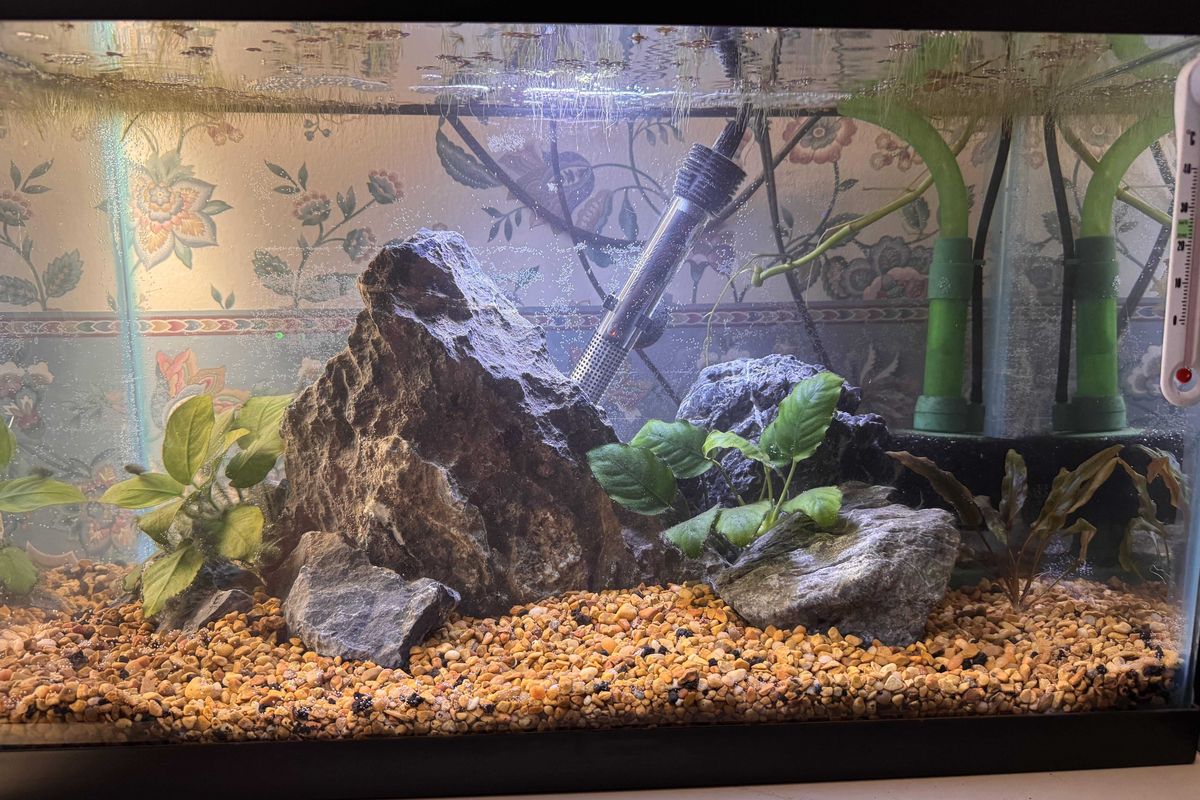
“Aquascaping is such a good break from tech. I have all the time I spend fiddling with rocks and plants, and once that’s done and I stock the tank with fish and shrimp and whatever else, I have a living piece of art that is 100% custom and always changing.”

“Volunteering at the animal shelter.”
“Journaling! My thoughts feel so much clearer after writing everything down. :-)”
“I've fallen in love with whittling.”
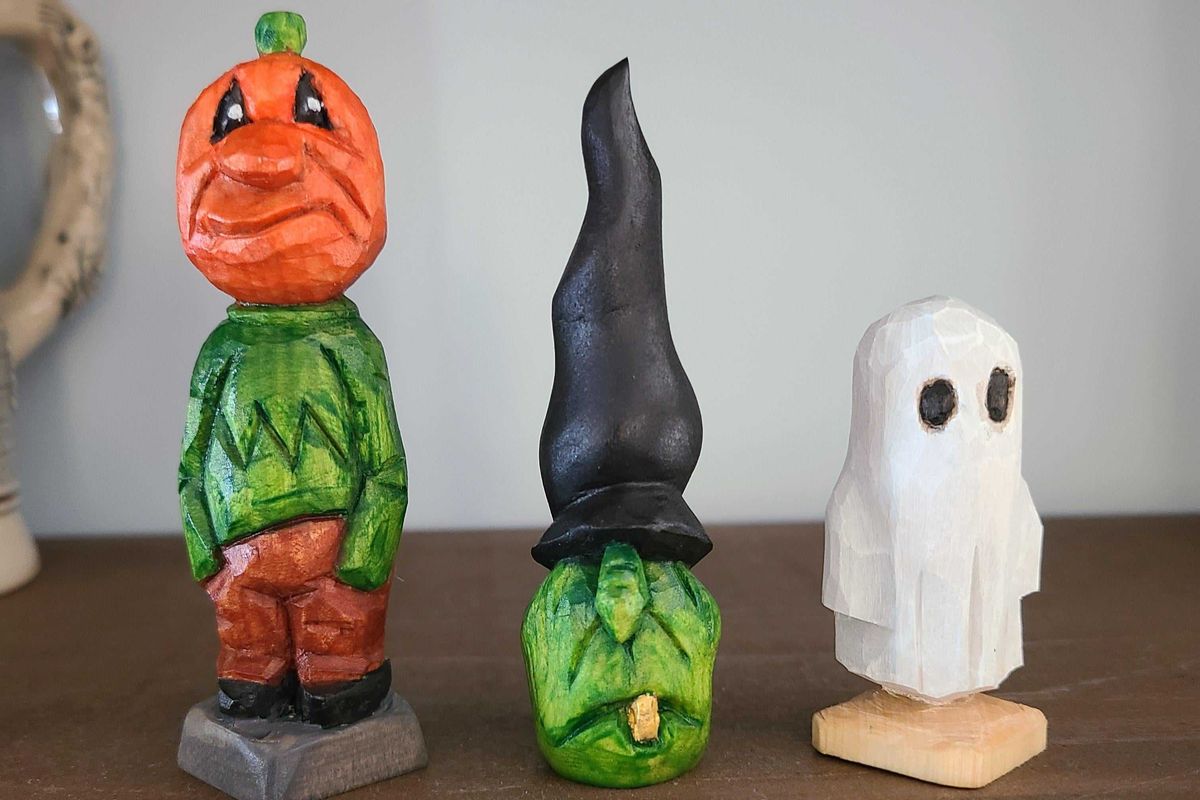

“Gardening has probably become the one that’s changed my life the most, it gets me more active, I spend and enjoy hours outside now. It’s taken a big bite out of my grocery bill, it also forces me to cook more. I extend the season by growing cool season crops, keeping a small hydro grow indoors and starting seeds in March. I also vermicompost indoors which is oddly fun and comforting — digging in dirt in the middle of winter and anticipating spring. I find having year round gardening activities helps with SAD and it’s done a ton for my overall mental health and sense of wellbeing.”
“Water coloring bookmarks.”

“I’ve been doing film photography since 1973 and am still at it in my home darkroom.”
“Repairing old electric toy trains. I find myself looking forward to unplugging and taking these things apart to fix or replace a part or two and bring them back to life. The smell of oil, soldering a wire or two, working through a fairly simple mechanical problem - these are the only things keeping me sane these days!”
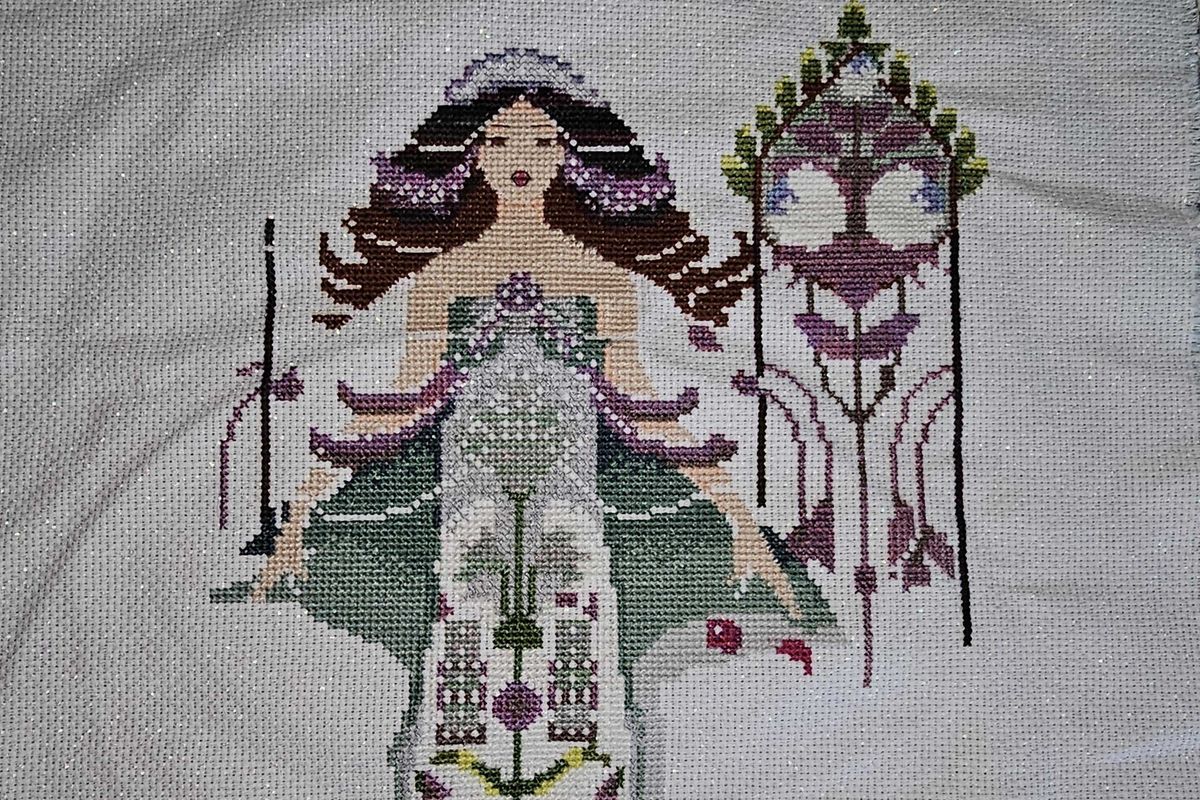
“Counted cross-stitch work in progress”

“I have gotten back into writing letters to pen pals but most of them are what I call fictional pen pals. That's where I create a character and that character writes a pen pal letter to another created character. It's a lot of fun and makes me slow down to actually write a letter and I can live a more exciting life through my character.”
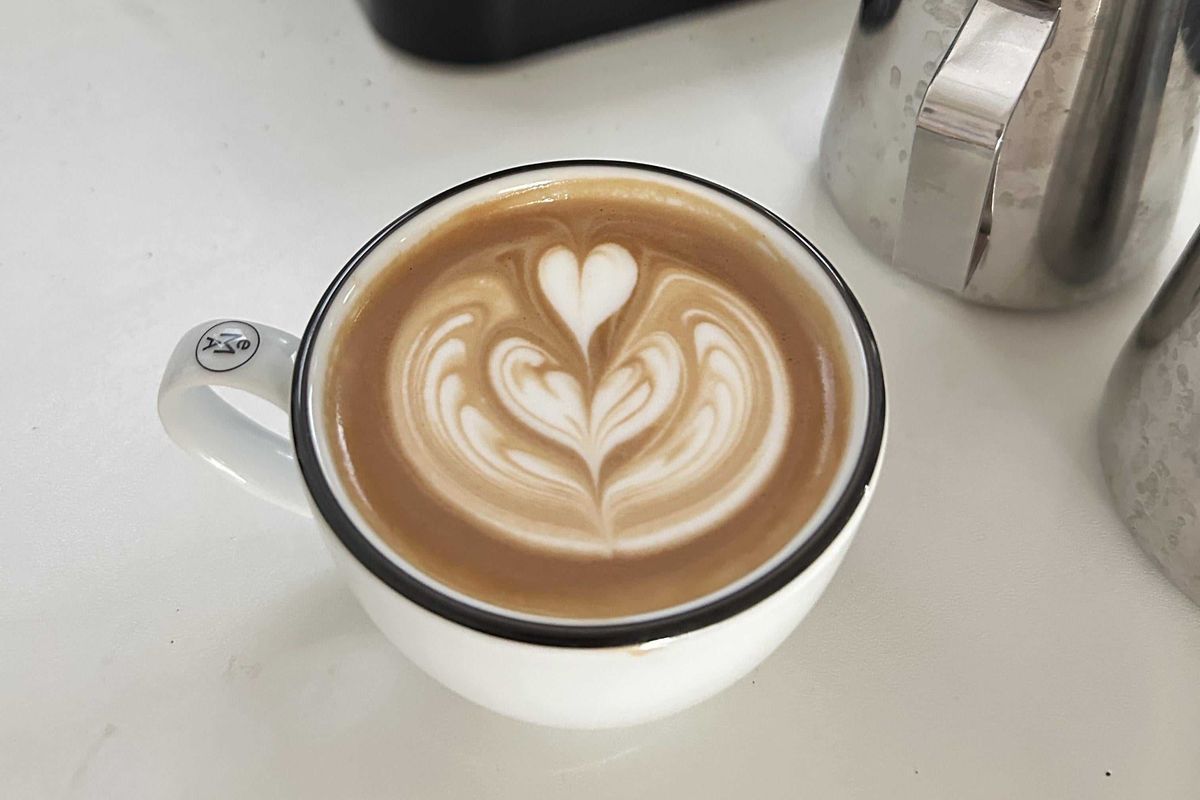
“Latte-art for me :)”

“I write letters to royals and nobles world wide and collect their responses. It makes going to the mailbox a lot of fun! I always send birthday, anniversary, and coronation day greetings. Other times it might be commenting on an event they attended or appearance they made. Other times letters of condolence if they've experienced a recent death of a loved one. You'd be surprised how many respond personally, particularly minor royals or nobles (the German princes have been particularly gracious with their time to write back).”
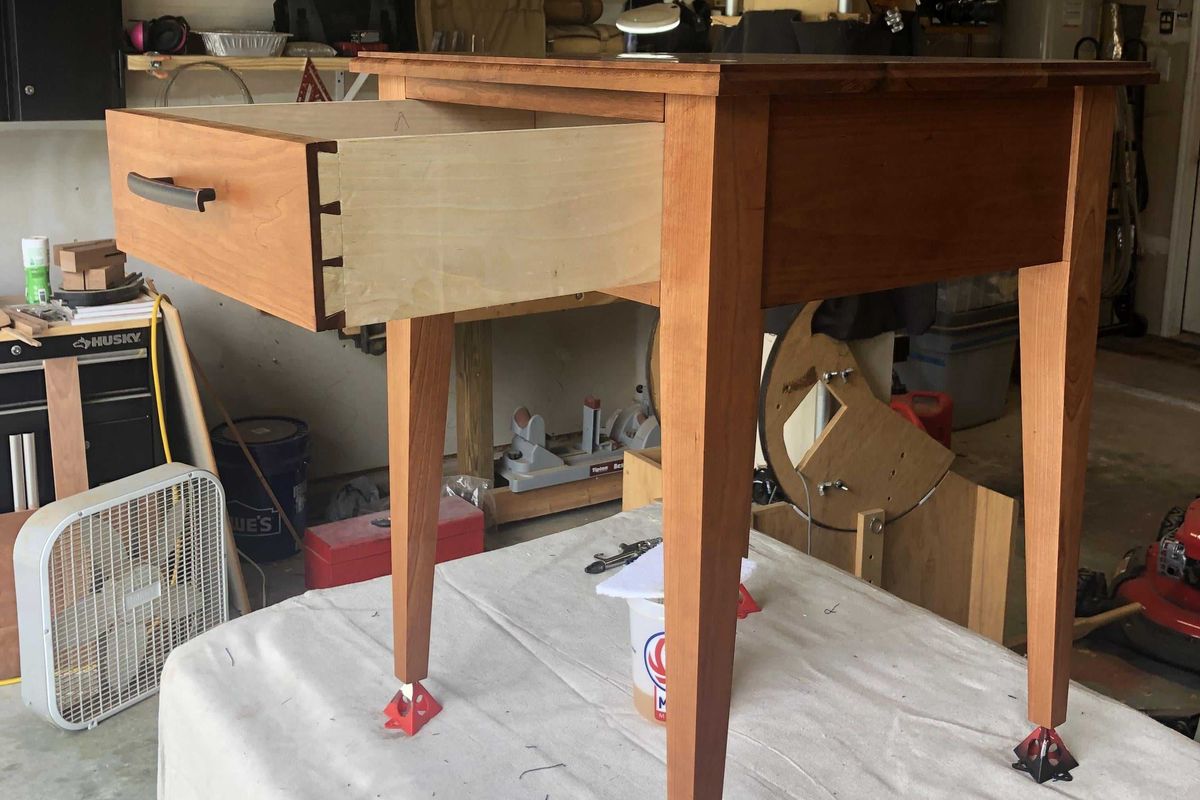
“Been a woodworker since I was a wee lad. It’s just super relaxing and mentally rewarding to dive into a project… Here's one of my latest…Most of the work was done with muscle powered hand tools…”

“Making collages from old magazines. It’s somewhat mindless and cheap to get started. People give away free old magazines on Facebook marketplace or you can buy cheap ones on eBay.”
“Making my own stencils from cardboard and using them on my gelli plate. I’m into surface design at the moment.”

“I’m getting back into art welding. Last week, I found myself in a flow state and forgot to eat. I’m also stunned at how encouraging different old dudes have been to me at supply shops. It was not like that 13 years ago when I learned.”
“Knitting socks.”
“Dollhouse miniature modeling.”
“Getting back into pottery. I get into my zen zone when my hands get dirty.”
“After dabbling before, I’m now taking up bookbinding! Despite the latest trend in doing up fancy versions of paperbacks, you can actually start with stuff you have at home and would otherwise throw away. The first book we’re making in my coptic class uses cardboard packaging and regular printer paper.”
“Camping and backpacking are the most fulfilling for me. I enjoy hiking, birding, tying knots, chilling in a hammock, reading, and photography. I get to do all those things in one hobby.”
“Mandolin and tenor guitar.”
“I paint portraits in oils - mostly of family, or pets. Here is my latest piece. It’s a very rewarding hobby and I’ve met some amazing people along the way.”

“My all-time favourite analog hobbies are dirt biking, snowmobiling, skiing at 2-3 years old, and they certainly do not need WiFi. Why are they such a great escape from the digital world? Cause you literally leave your home, go where theres no cell service, and you only focus on the machine/skis and never the phone while doing them. Perfect, best escape from the digital world.”
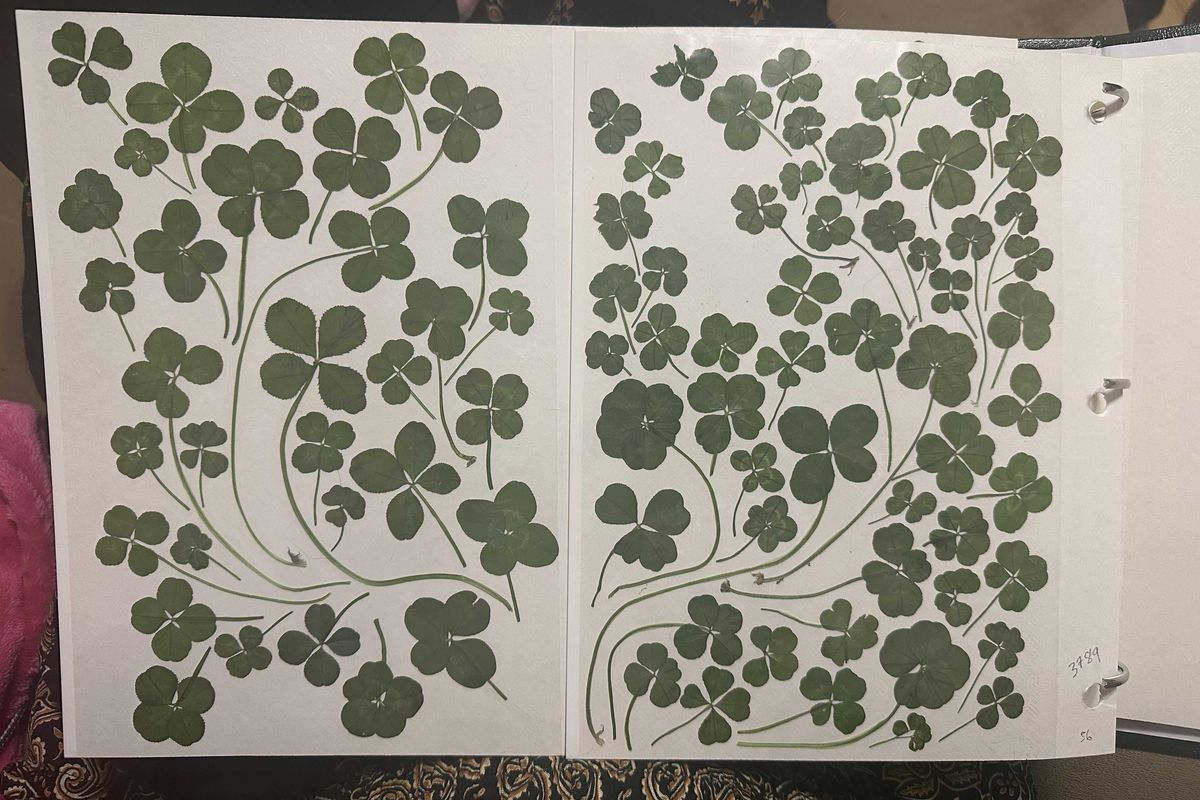
“I go on walks looking for 4 leaf clovers and lay them out in a photo album and think of it kind of like art meets meditation meets scavenger hunting.”

“Penmanship. Specifically: writing cursive with a fountain pen. I've started collecting some pens, improved my handwriting, started journaling a little, and even ground some of my own nibs.”
“Public lectures, author meet-and-greets, book clubs, meetups in general- local colleges often have special interest groups open to the public, public libraries usually have some event going on, farmer's markets and local festivals frequently have interesting people who love to talk about what they do.”
“I love air dry clay, particularly the brand Das.”

“Rockhounding, because it literally gets me out of the house and going places.”
For those wondering, rockhounding is searching for and collecting rocks, minerals, fossils, gems, etc. Some folks get specific on what types of colors or shapes they aim to find. And while rockhounding itself involves no tech, you might need to hop online to make sure you're allowed to take items from the spot you're in.
“I love fishing! It's so peaceful!”
“I danced as a kid and recently got back into it through a dance fitness class. Now I'm choreographing my own dances. It's fun, active, and creative.”
Let this be your sign to carve out some time for joy today, in whatever way feels best. Your mind, body, and spirit will thank you for it.
This article originally appeared last year.
- Doctor shares her new favorite hobby: Hyping up NICU babies ›
- A 12-year-old was told his woodworking hobby wasn't cool. One tweet changed everything. ›
- Does everyone think your hobby should be a side hustle? Here's why they're probably wrong. ›
- Woman shares what she keeps in her 'analog bag,' and it starts an offline movement - Upworthy ›
- Why Millennials are going 'chronically offline' and back to analog - Upworthy ›
- 22 hobbies folks claim are surefire ways to meet super-friendly people in real life - Upworthy ›

