A guy went viral for tracking the taste of his own urine. Doctors used to do it all the time.
"I am equally impressed and disgusted by this."
A guy says he can tell when he's getting sick based on the taste of his pee. Ancient doctors would probably agree.
A recent Super Bowl ad by the hydration brand Liquid IV urges viewers, with an assist from Phil Collins, to "take a look" at their urine as the color could be a warning sign of dehydration. It's long been known that lighter pee often means you've been drinking more water and other fluids. Darker yellow or amber pee can mean you're not well-hydrated, which forces the kidneys to concentrate the urine, leading to darker colors and a more powerful odor. Crucially, striving for pee that is completely clear isn't ideal.
In short, there's a lot you can learn from pee without any complicated lab tests. But some people take this pee science more seriously than others. A user on Reddit recently went viral for confessing that he's been not only tracking the color and clarity of his own pee for four years, he's been tasting it as well.
- YouTube www.youtube.com
"Every morning for the past four years, I've tasted my own urine. Approximately 5ml, enough for proper palate evaluation," he wrote in a post.
Again, don't try this at home.
"I've developed what I call the Golden Index, a standardized evaluation framework with six primary metrics," he explained, going on to list how he evaluates his urine's color, clarity, sweetness, salinity, bitterness, and mouthfeel each on a five-point scale each morning.
Naturally, the jokes practically wrote themselves over the course of several hundred comments:
"'Hi Mr. Johnson, just wanted to call in sick for my shift on the 19th…' ... 'But it’s only the 16th' swishes profusely around mouth 'Trust me sir, you’re gonna want to find coverage'”
"Please tell me stool isn’t your next experiment"
"I am equally impressed and disgusted by this"And OP was kind enough to answer the question on everyone's mind: "My wife believes I simply 'take a long time' in the bathroom each morning. She's not aware of the research."
We don't know for sure who this anonymous, and brave, Internet data-nerd is, but modern doctors advise that you should never drink, or even taste, your own urine. But he's not wrong about one thing: Medical professionals used to taste pee all the time.
It's hard to stomach, but the tasting of pee proved to be a crucial step forward in the diagnosing of some illnesses, especially diabetes.
Diabetes was, if not discovered, then at least noticed by the ancient Egyptians as far back as around 1550 BCE. Papers discovered from the time recommended an antiquated treatment for "excessive urination" involving a concoction of pond water, elderberry, milk, and more. A few hundred years later, ancient Indian physicians noted that the urine of people who were sick with this mysterious affliction attracted ants.
It wasn't until 1674 that a doctor named Thomas Willis tasted diabetic urine and couldn't help but notice how sweet it was. "Wonderfully sweet as if it were imbued with honey or sugar," were his exact words. Further experiments would eventually prove that the pee was full of sugar. It took centuries, but, in 1921, the very beginnings of an effective treatment for diabetes began to pop up. The discovery of sugar in urine was an incredible key to understanding the disease.
Doctors had been tasting and visually analyzing urine for centuries in order to detect illnesses. They even had complex charts correlating different colors with potential diagnoses. It was a practice called uroscopy.
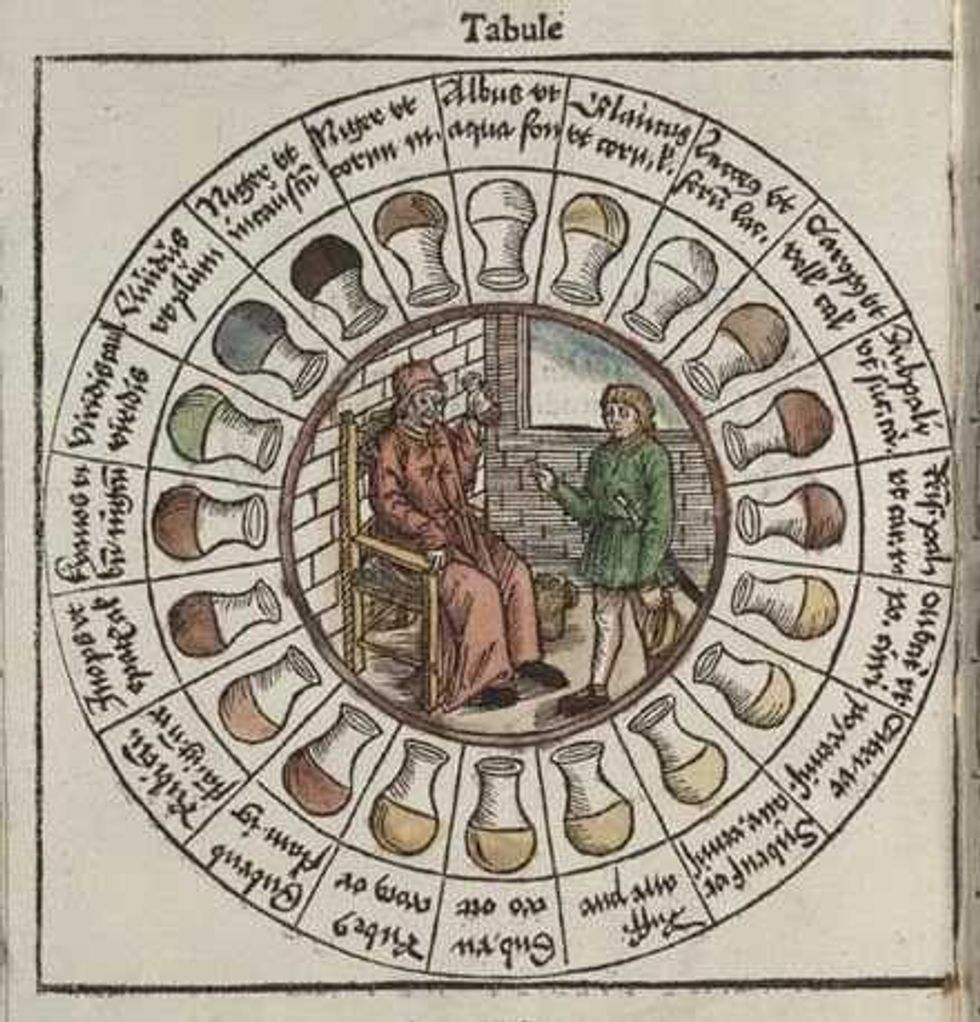
Most of it was, respectfully, bunk, and uroscopy became mostly extinct not long after Thomas Wills' discovery. But some elements of it persist today.
Signs of ailments like urinary tract infections, liver failure, and certain kidney issues can be outwardly visible in urine samples upon visual inspection. Doctors will still look for color, clarity, and thickness in their visual exams. But most of the rest of urinalysis is best performed in a lab, where accurate readings on pH levels, protein, glucose, nitrites, and more can tell them far better information.
But as gross as it is, not to mention unsanitary and potentially unsafe, there are crazier ideas out there than the concept that tasting your own pee could alert you to a brewing illness. Ancient Indian and Egyptian doctors would probably agree with this guy.

