The QAnon cult: What it is, how it works, and how to help deprogram your loved ones
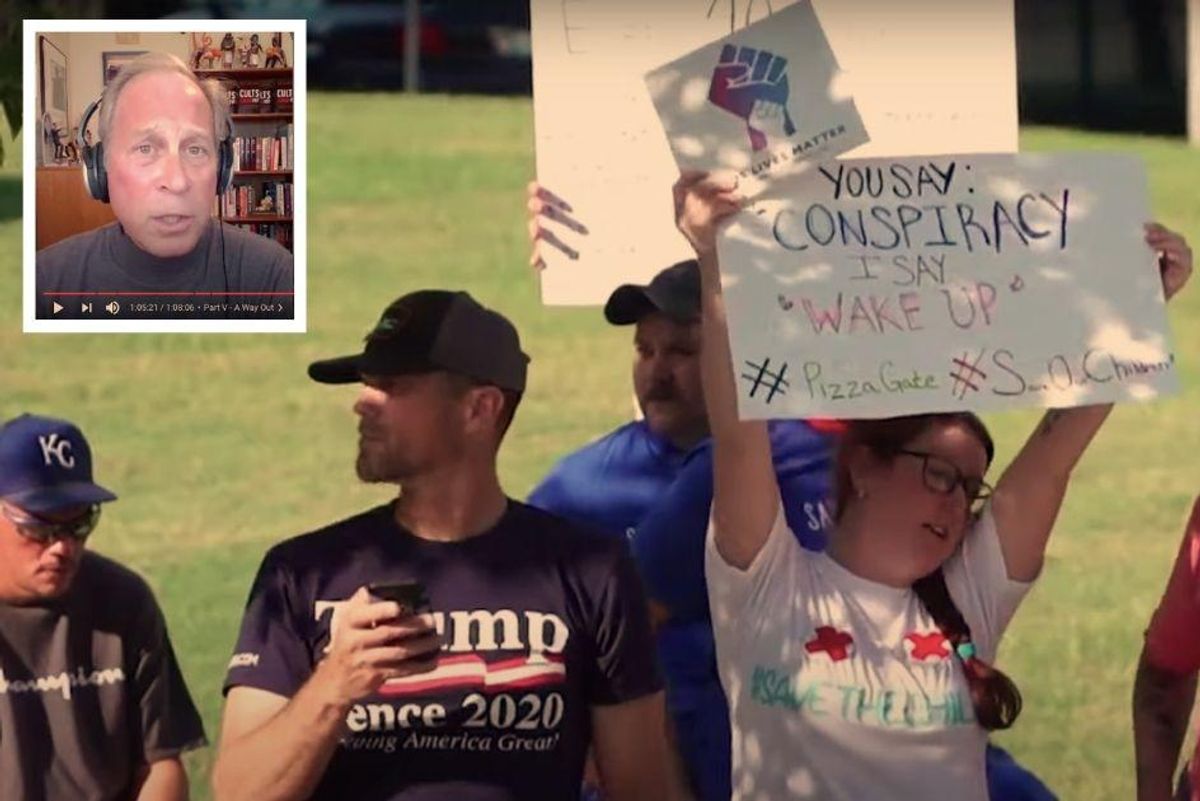
Two weeks ago, we watched a pro-Trump mob storm the U.S. Capitol in an attempt to overthrow the results of a U.S. election and keep Donald Trump in power. And among those insurrectionists were well-known adherents of QAnon, nearly every image of the crowd shows people wearing Q gear or carrying Q flags, and some of the more frightening elements we saw tie directly into QAnon beliefs.
Since hints of it first started showing up in social media comments several years ago, I've been intrigued—and endlessly frustrated—by the phenomenon of QAnon. At first, it was just a few fringey whacko conspiracy theorists I could easily roll my eyes at and ignore, but as I started seeing elements of it show up more and more frequently from more and more people, alarm bells started ringing.
Holy crap, there are a lot of people who actually believe this stuff.
Eventually, it got personal. A QAnon adherent on Twitter kept commenting on my tweets, pushing bizarro Q ideas on many of my posts. The account didn't use a real name, but the profile was classic QAnon, complete with the #WWG1WGA. ("Where we go one, we go all"—a QAnon rallying cry.) I thought it might be a bot, so I blocked them. Later, I discovered that it was actually one of my own extended family members.
Holy crap, I actually know people who actually believe this stuff.
I've written articles about how QAnon's pedophilia-obsessed mythology does real harm to actual anti-child trafficking organizations. After the "Save the Children" hashtag started going viral based on (false) messages and memes about hundreds of thousands of children going missing every year as part of a Democrat-and-celebrity-run pedophile cabal, I interviewed international organizations that truly battle child sex trafficking. I shared their plea to stop pushing QAnon lies.
That brought to my inbox QAnoners accusing me of being a pedophile and part of "the Deep State." And now we've watched some of these folks stage a violent attack on our government.
Holy crap, this stuff actually has serious, real-world consequences.
At this point, it's not overstating to all QAnon a destructive cult. And it's likely that we all know someone who have been sucked into it. I know people who have lost friends and family members to this stuff, as reasoning with them goes nowhere and their constant conspiracy talk becomes unbearable.
That's where deprogramming comes in.
I've followed the QAnon saga for a long time, and it's a little tricky to know where to start if you're trying to make sense of it. (Trying to make sense of something that inherently doesn't make sense is always fun.) This documentary that was recently posted from a YouTuber called Infranaut is the best comprehensive overview of QAnon—and what to do about it on an individual level—that I've seen yet. If you want to understand what QAnon is, how it works, why it draws people in, and how to help loved ones get out, this video covers it all succinctly.
In addition to his own explanations, Infranaut interviews professional cult deprogrammer and founder of the nonprofit Cult Education Institute, Rick A. Ross, who shares steps families can take to help extract their loved ones from the QAnon cult.
I'm going to summarize some of the main points below the video but I highly recommend you go ahead and watch the whole thing. It's well worth it. If you want to skip to specific sections, here's a handy guide the creator shared.
0:00 Introduction
7:21 Part I - Defining "Q"
10:01 Part II - Becoming a Believer
20:39 Compliance Interlude
22:44 Part III - Staying a Believer
36:45 Capitol Interlude
39:14 Part IV - The Future of Q
53:28 Part V - A Way Out
1:05:52 Outro
Q's Going Nowhere: Cults and Conspiracies in the Online Erayoutu.be
The video starts by describing a bit about how cult thinking works and giving an example of a doomsday cult from the 1950s called "The Seekers," which serves as a comparative example throughout the video.
Then Infranaut gives a brief definition of what QAnon is:
"QAnon refers to the belief that the United States government, if not the entire world, is secretly run by the "Deep State," a shadowy organization that exists above and behind the current government as we understand it," he says. "While the exact size and goals of the Deep State are ambiguous, it's taken that their ranks include several figures in the public eye, that they are largely pedophiles, and depending on who you ask, also Satanists."
QAnon believes Trump ran for president in 2016 in order to expose and dismantle the Deep State. "Q" is a nameless someone who claims to be a high-ranking ally of Trump, working alongside him to defeat this Deep State, and who posts cryptic messages on anonymous online boards with information about how that fight is going and what's coming next. Many of these messages, or "Q drops" make reference to The Great Awakening or The Storm—the big finale when Trump and his allies will arrest prominent members of the Deep State and expose them in public.
Here's where it gets tricky, though. The QAnon world contains a mind-bogglingly large and complex set of beliefs, so it's a bit difficult to synopsize. The basic details above are pretty much agreed upon by all, but beyond that, it's an octopus with tentacles all over the place, and some beliefs contradict one other. For example, some believe Mike Pence is helping Trump fight the Deep State; some believe Mike Pence is a part of the Deep State. But no one seems to care about those inconsistencies much.
In fact, these various, inconsistent tentacles are part of what makes QAnon so strong. If you point to one super out-there belief (as if it's not all super out-there, but we'll hold that thought for a minute) there will always be a bunch of people who can say, "That's fake news. We don't believe that. You're just trying to make us look bad." If you get five different QAnon adherents together, you'll get five different explanations of what QAnon is.
That's because it's less of a defined set of beliefs, Infranaut explains, than "an explanation for why the world feels dark, confusing, and wrong."
And there are a dozen doorways to get into it. Some come through classic conspiracy thinking (JFK, Jr. is still alive, for example), some through bigotry (there's anti-Semitism in some core elements of QAnon belief), and some through a righteous desire to rid the world of evil.
The whole child trafficking/pedophilia thing has proven to be a big draw. After all, there is a grain of truth, in that those things actually do exist in the world (just not the way QAnon paints it). And is there anything worse than child sacrifice and sex slavery? No, there's not. Fighting to save children from such a horrific fate is an "inarguable moral good." If you truly believe that Democrats and celebrities are trafficking hundreds of thousands of children for heinous purposes, it would actually be wrong not to be part of a movement against it.
Infranaut and Ross explore a bit about how Christianity has overlapped with QAnon iconography, which Ross says is common in cults as people come up with ways to market the belief system and make it more palatable.
When you just look at one tentacle, you can see how people get pulled in. And then once you're in, the other beliefs become easier to accept.
It would be easy to call people who fall down the rabbit hole stupid because the entire thing sounds so ridiculous, but as Ross explains, it's not that simple. "I've seen people that are highly educated, very sophisticated people. I've done five interventions with medical doctors. One was an orthopedic surgeon, another an anesthesiologist. One woman that I worked with was a clinical psychologist, and she was, in my opinion, totally brainwashed. So very sophisticated, highly educated people can succumb to this kind of manipulation, and it behooves us to understand all the tricks and the methods that can be used to gain undue influence over us. And that's the inoculation. That's the vaccine, if you will."
None of us want to admit that we are vulnerable to such persuasion, but Ross points out that the world of advertising wouldn't exist if we weren't.
One of the tricks of QAnon is the central tenet of the Deep State and also "false flags"—the idea that the Deep State will do things that make QAnon look crazy or throw Q adherents off track. So when facts fly in the face of the belief, or when something that was supposed to happen doesn't, or when something that wasn't supposed to happen does, you can immediately blame the Deep State and dismiss it.
For example, when QAnoners do something violent or dangerous, that's the Deep State planting a false flag. We see a similar narrative in the "Antifa did it!" response to the Capitol riots. It doesn't matter that the FBI or the DOJ say that they don't have evidence of Antifa involvement—that's all part of the Deep State.
Trump hasn't helped any of this, of course. He has never denounced QAnon ideology. In fact, he's said he doesn't know much about it but they seem like people who love America. And his claims of election rigging have been fuel for QAnon belief; that's totally something the Deep State would do.
It doesn't matter that specific Q prophecies don't come true. Adherents just keep saying, "Trust the plan," even though the plan isn't clear. It's a test of faith. They also come up with ways to explain away facts that counter the belief.
This is what's the most bafflingly frustrating thing about trying to reason with a QAnoner. You just can't. It doesn't matter how many facts you bring in or logical inconsistencies you point out. "The lengths to which a true believer will contort the truth or manufacture evidence really can't be overstated," say Infranaut.
Rick Ross explains that people often follow QAnon in a cult-like way, gradually alienating or cutting themselves off from their families and social circles, making the QAnon world their primary community. The cult becomes the social circle, and that's an incredibly powerful pull for people.
No one knows what's going to become of QAnon after Trump is out of office, but there's very little chance of it going away. Most cults die out when a leader dies or goes to jail (though there are always believers who maintain loyalty no matter what). But barring those things happening to Trump, the QAnon movement will continue in ways we probably can't even imagine at this point.
So how do we get people out? The key hurdle is people's inability to accept and admit that they were wrong. Infranaut calls "the beating heart" of the QAnon movement is the idea of "I didn't get duped." No one wants to believe they voted for a conman, or that they supported a sexual predator, or that they are still waiting around for him to save the world.
Ross offers some hope for families, though. If done effectively, a deprogramming intervention process can extract around 70% of people who have been taken by a cult. For some who aren't as deep into the movement, it might not be as hard as for the long-timers, but the key to both is having the intervention come from people they are close to.
Unfortunately, it also entails a bit of what will feel like coddling. Some of us just want to confront them with the truth, to somehow shake them out of their brainwashed stupor, to scream, "How can you believe something so outrageously stupid!" But Ross says not to be confrontational or judgmental, but to keep the line of communication going to see how deep they are into the brainwashing.
Ross says if a family decides to stage an official intervention, it takes three or four days of dialogue in which loved ones supply support and love as they go step by step through the process.
Those basic steps of dialogue look like this:
1. How do you define a destructive cult? (Walk them through a different cult. Ross uses Scientology as an example.)
2. How does that cult gain influence over a person? (General methodology for brainwashing and manipulation the cult uses.)
3. What problems are you not aware of related to your group? (How those methods are used in your group, even if you don't think it's a cult.)
4. Why is your family so worried about you? (There's obviously a reason for this intervention. Each person explains what their concerns are, hoping the person will stay and listen because they care about the people intervening.)
Ross offers more details about how to go about that process on the Cult Education Institute website and he also recommended some books to read, which you can find around the 1:03:45 mark.
I wish I could say that QAnon will just fade away, but it does not appear likely that it will. It's endlessly annoying and clearly dangerous, but it's where we are. Hopefully, people can help their loved ones climb back out of the rabbit hole and rejoin us in reality.
- Kooky conspiracy theories are detracting from the very real issue of ... ›
- If you really want to #SaveTheChildren, stop sharing QAnon ... ›
- Child sex trafficking organizations set the record straight on QAnon ... ›
- A former QAnon believer answers all your questions about how the cult really works - Upworthy ›
- Are cults amking a comeback? Twitter says so. ›
- Parents won't let daughter attend Taylor Swift birthday party - Upworthy ›





 Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via
Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via  Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.
Turbulent flow illustrated and animated. Animation of art referencing science.
Animation of art referencing science. Animated Starry Night
Animated Starry Night An animated depiction of The Scream.
An animated depiction of The Scream. People clinking their glasses of red wine for a cheers.
Photo by
People clinking their glasses of red wine for a cheers.
Photo by  I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN
I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN "Love you!" Oops.
"Love you!" Oops. Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show
Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor
Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor gorilla hurrying GIF
gorilla hurrying GIF Gorillas are generally pretty chill.
Gorillas are generally pretty chill. A court reporter taking notes.via
A court reporter taking notes.via Depiction of Jesus Christ in Heaven.via
Depiction of Jesus Christ in Heaven.via A photo of Santa Claus.via
A photo of Santa Claus.via