Sometimes the smallest interactions parents have with their kids can have the biggest impact. For parents looking to pass down the positive things their parents did raising them to their kids, they shared their experiences and ideas with others.
"I’d love to know positive memories from your childhood that standout to you. Could be small things your parents said or did to make you feel safe and loved, family trips you may have taken, traditions, or little things you did with your parents," the parent wrote on Reddit. "I want to be intentional with my children and give them a childhood that feels warm and happy and memorable. And I’d just love to hear others positive experiences."
Other parents did not hold back opening up about the meaningful memories. Twenty parents share how their parents made them feel loved and seen, and how they plan to do the same with their kids and generations after to build better relationships.
1. "My dad was never afraid to apologize. When I was about 8, I remember getting Big Red all over his car because I was pouring it out the window and watching it fly. I didn't realize it was getting all over the car (and probably other cars). We had just left the car wash. When we got home he freaked out and yelled and screamed. I got the car wash stuff out of the garage and just sat and cried for a bit. Then he came out and sat with me and said that dad's mess up too sometimes. He said he understood I was just being curious and did not mean it and he wished he had explained his frustration in a calmer way. He hugged me and helped me wash the car again. I remember that he said mean things, but not what he said before the apology. I remember just about every word of that apology though. I think that one sticks out because that was the maddest he had been at me up to that point...maybe ever. There a few other stand out ones, some were even funny, but he always used them as a time to reconnect and really make sure we knew he loved us and respected us." – sstr677
2. "My dad showed up to everything. Every. Single. Thing. Spelling bee, Girl Scouts, cheerleading. When my cheer games overlapped with Buckeye games, he brought his Walkman to listen to the game while he watched me cheer. He did the Girl Scout camp outs with us. I’m 33 and I know that if I called him right this second to say I needed him, he’d be here immediately." – books-and-baking-
 clapping father wild GIFGiphy
clapping father wild GIFGiphy
3. "My granny would always feed me unprompted. I would be relaxing watching TV and here she came with fresh cut fruit or a glass of sweet tea. It felt good knowing she was thinking of me. She also would always say “Penny for your thoughts” and I always felt open to sharing with her.. I miss her so much nobody ever loved me like Geneva." – AquafinaRaeGina
4. "We had movie nights on Fridays. We were pretty poor but every Friday, we’d go to little Cesar’s down the road and get a $5 pizza. Then we’d go to the dollar store and get to pick out our favorite $1 candy. We’d go home, watch the movie with our pizza and candy, and then have a camp out in the living room. My brothers and I would fight over who got the couch and who got the hand-me-down recliners haha. We’d also drag out all of our mattresses and sleep in the living room on Christmas Eve. My dad made sure to read us a story every night for years. We’d ride our bikes to the library on Saturday afternoons if he wasn’t working and pick our bedtime stories for the week." – Prize_Common_8875
5. "Either one of my parents tucked me into bed every single night and told me they love me, until I was a teen. Meant the world to me now I think back. Will definitely be doing this when my little one goes into his own room." – hainii
 bart simpson sleeping GIFGiphy
bart simpson sleeping GIFGiphy
6. "One that sticks with me was my dad saying this to me over the years: “No matter where you are or what happens, if you need me, call me and nothing will keep me away.” He kept his promise till the day he died, and I miss him every day." – Baaaaaah-baaaaaah
7. "For me it was going to sporting events with my Dad. It doesn’t have to be even a professional game. I went to multiple games of mid tier college basketball locally with my Dad starting at 5. We would watch the game, hang out with his friends after, get popcorn and a soda, talk about the game on the drive back. It made me feel like I was not only his son but also a buddy that he wanted to talk to and hang out with. I do the same thing with my boys now. I don’t think it has to be sports. Whether it be going to the movies, concerts, plays, whatever including them on events you enjoy is a great way to bond and show love." – HangmanHummel
8. "My mom would leave sweet notes in our lunches. Not every day but I remember oftentimes getting “Happy Friday!” or “Good luck on your game today!” type of notes. I’m tearing up just thinking about it…" – JustAnotherPoster_
 lunch i love you note GIF by eviteGiphy
lunch i love you note GIF by eviteGiphy
9. "When I was a preteen/teenager, my dad would let me play whatever CD I wanted in his truck. I was an emo/goth/alternative kind of girl so music was important to me, and still is. He actually would give the music a chance and we ended up bonding over a bunch of bands you wouldn't guess he would even like, but it was so nice." – lisa_rae_makes
10. "Honestly as an adult, my mom went to therapy when I asked her to. She made significant growth over the last few ways and it’s allowed us to repair and deepen our relationship in a way I would have never imagined. It shows so much love and effort that at 60 she has learned how to take accountability and change how she treats us. It is my ongoing goal to always be willing to apologize to/listen to my kids." – hfdxbop
11. "Spaghetti was ready to serve with table set, right as I got home from track practice. The sunsetting rays would come through the windows and I could see the steam coming off food, table set beautifully. This was such a treat as a young teenager, I can replay this scene in my head clear as day. The feeling of emptiness being filled with that warm homemade, healthy meal - yeah, that's love." – NocturneGrind_739
 Michelle Tanner Pasta GIFGiphy
Michelle Tanner Pasta GIFGiphy
12. "My dad has always randomly given me a hug and a kiss, followed by an 'I love you'—and he still does it, even now that I'm 38 years old. I'll be working at my desk, and he'll come over, give me a hug and a kiss, and say, 'I love you.'" – repderp
13. "As I was falling asleep, my mom would get up to leave and I’d reach out the her… she always quietly sat back down and continued waiting. It made me feel loved and safe. She died when I was young. Just knowing she always chose me was a gift. She also was always the first person to tell me happy birthday first thing in the morning before anyone else." – FoodisLifePhD
14. "My mom was at EVERY game, recital, musical, or other event I was a part of. She volunteered in our classrooms at school, on field trips, or behind the scenes in the productions I was in. She was always working too, but she did everything she could to be there for my extracurriculars and that meant so much." – savsheaxo
 deandre jordan love GIF by NBAGiphy
deandre jordan love GIF by NBAGiphy
15. "My dad would just hug me while I fell apart & cried. He did it until I’d stop. Happy to do the same with my kiddos." – offensivecaramel29
16. "Ever since I could remember, my dad told me beautiful bedtime stories where I was the main character, and he prompted me to add to the story, keeping things interesting. It helped build our communication and grow my imagination. ❤️" – JeremeysHotCNA
17. "Had room on their lap for me. Read books to me. Asked me what I thought or what I thought something was in nature? I was raised by hippies who did build me up to be smart and forever willing to learn from new things." – Spiritual_Lemonade
 Is There Life Out There GIF by Reba McEntireGiphy
Is There Life Out There GIF by Reba McEntireGiphy
18. "When I started driving and borrowing my mom's car to go to parties, she told me, 'If you ever can't drive for any reason, including drinking, call me; I don't care how late it is. I won't give you a hard time when I come get you, and we can talk about whatever it is later. But I'd much rather you be safe and alive than feel like you have to hide something from me and do something dangerous.' I actually never ended up needing the offer, but I definitely felt much safer knowing I had an ace in my pocket." – Dowager-queen-beagle
19. "My parents were not perfect by any means but they were intentionally present in our lives and remain so to this day and I'm now 57. They show up, they respect our free will and support us even when they don't agree with us. They have independent relationships with their grandchildren. Their actions match their words and their actions are driven by their love for us." – DbleDelight
20. "One simple thing was whenever my dad ordered food, like from a fast food restaurant, he would always give them my name for the order. I felt so special and grown up to have my name called for the food." – Appropriate_Ad_6997







 Buddy Holly was 20 years old in this photo.
Buddy Holly was 20 years old in this photo.  30 going on 60…
30 going on 60… season 6 episode 23 GIF
season 6 episode 23 GIF French Yes GIF by Robert E Blackmon
French Yes GIF by Robert E Blackmon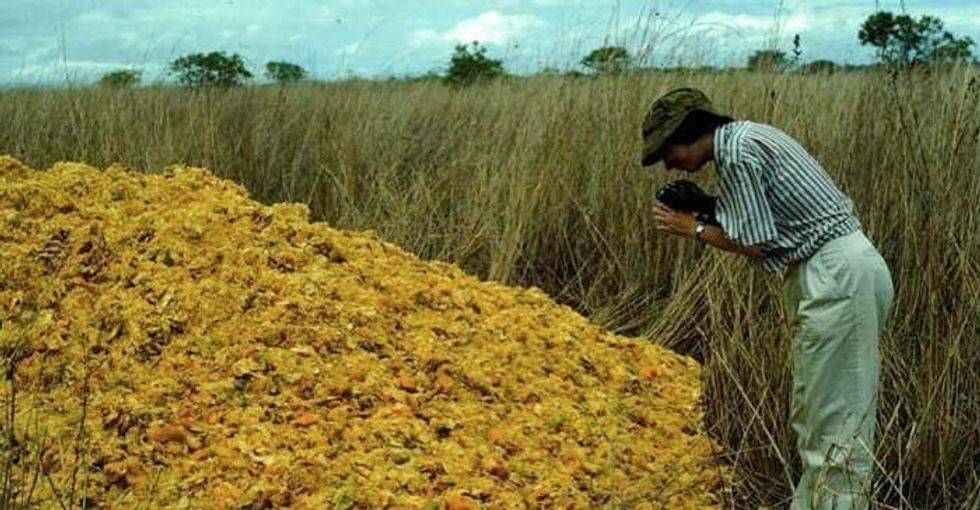 The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.
The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.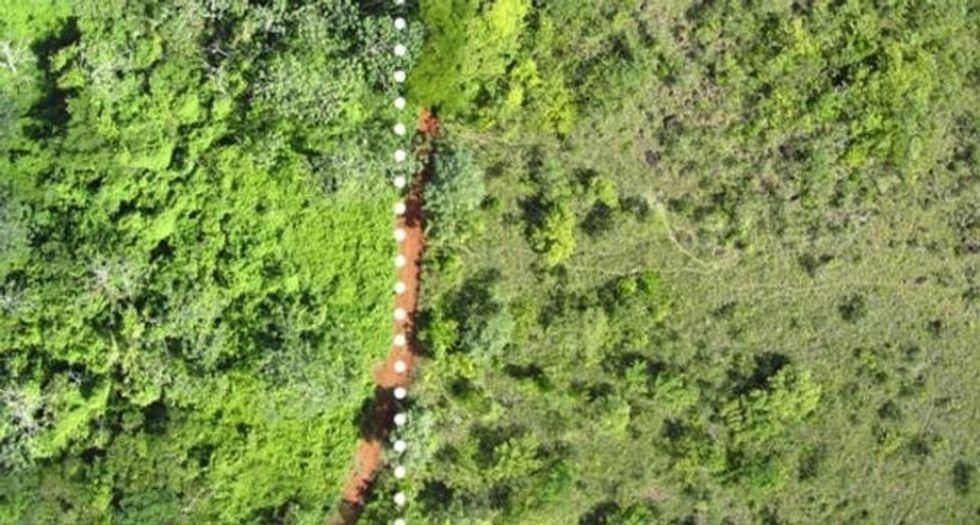 The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R).
The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R). Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.
Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.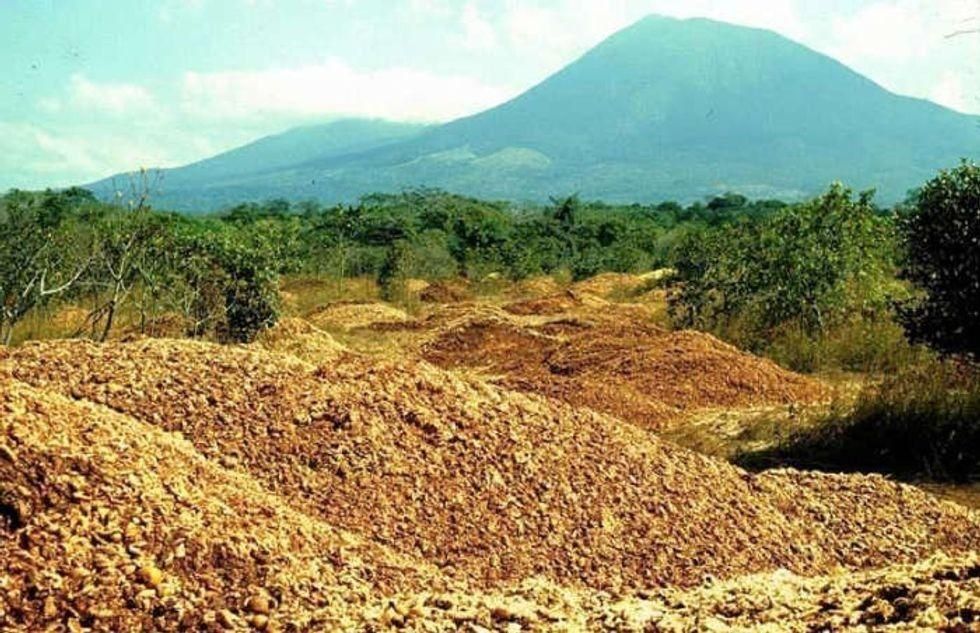 The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998.
The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998. The sign after clearing away the vines.
The sign after clearing away the vines. clapping father wild GIF
clapping father wild GIF bart simpson sleeping GIF
bart simpson sleeping GIF lunch i love you note GIF by evite
lunch i love you note GIF by evite Michelle Tanner Pasta GIF
Michelle Tanner Pasta GIF deandre jordan love GIF by NBA
deandre jordan love GIF by NBA Is There Life Out There GIF by Reba McEntire
Is There Life Out There GIF by Reba McEntire Helping kids become resilient is an ongoing process.
Helping kids become resilient is an ongoing process. "I believe you" is a simple but powerful phrase.
"I believe you" is a simple but powerful phrase.