The fascinating reason people looked much older in the past than they do today
Why did teenagers look like they were in their mid-30s?
Norm was only in his 30s?
Ever look at your parents' high school yearbooks and think people looked so much older back then? All of the teenagers look like they’re in their mid-30s and the teachers who are 50 look like they’re 80. When we watch older movies, even those from the 1980s, the teenagers appear to be a lot older as well. Why is it that they looked so much older? Was life harder? Did people act more mature? Did they spend more time outdoors and less time playing video games? Is it their sense of fashion? Were they all smokers?
Educator Michael Stevens, who runs the super-popular Vsauce YouTube channel, explains the phenomenon in a video called, “Did people used to look older?” In it, he explains that people in the past appear a lot older due to retrospective aging.
This is how it works: when we see people in the past, they are wearing outdated styles that we associate with older people; therefore, we think they have aged rapidly. For example, a teenager in the 1950s may have been in fashion while wearing thick Buddy Holly-style glasses.
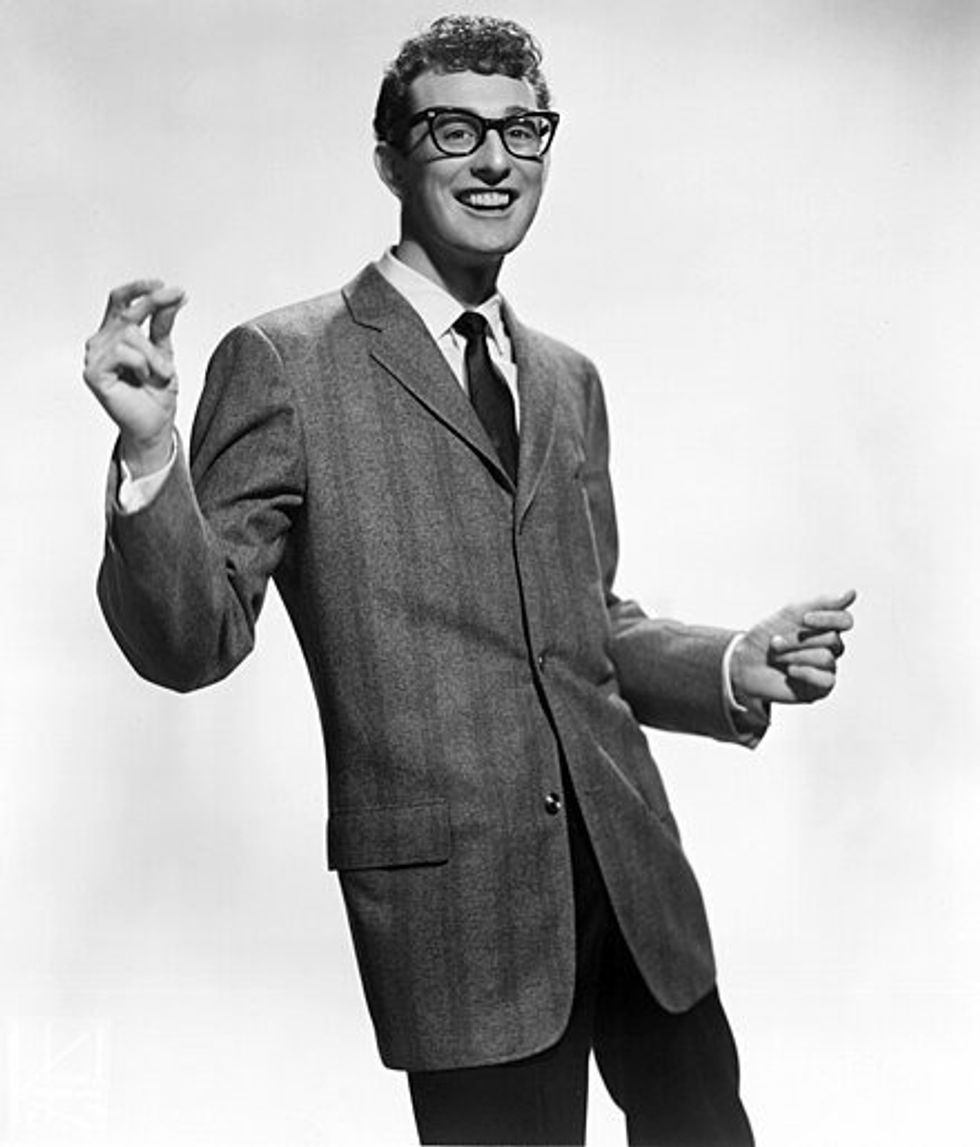

But as people age, they tend to cling to the fashion of their youth. So many people of that generation continued to wear the Buddy Holly-style glasses into their 50s. So when younger people see those glasses they see them as old people's glasses and not a hip kid from the '50s.
So in the photo from the '50s, the teen appears to look a lot older because our perspective has been tainted by time.

But it isn’t all just an illusion. Stevens also points out that people did age faster back in the day due to differences in nutrition, lifestyle and medicine. In addition, he also does a deep dive on how a person's name can affect their appearance, referencing the Dorian Gray effect, which theorizes that cultural stereotypes linked to a name come to be written on the faces of their bearers, as well as the name matching effect, in which people whose faces "match" their names tend to be better perceived.
Basically, this 22-minute video is chalked full of fascinating tidbits. Give it a watch below.
- YouTubewww.youtube.com
It might be worth noting that, in addition to healthier lifestyle options, younger generations have more access to anti-aging procedures than ever before. "Tweakments," like fillers and botox, are less expensive and more readily available than ever—not to mention every anti-aging cream, serum, and cleanser known to man. And many millennials and Gen Zers take advantage of that, whether prompted by selfie anxiety, a growing obsession with youth, or some other motivation.
Plus, millennial and Gen Z fashion often honors their inner child. Nostalgic cartoon tees, colorful prints, cutesy accessories, etc. Granted, under the retrospective aging theory, even those styles could one day look dated, but they are so youthful that it's hard to imagine that being the case. That said, can't wait to see bunch of geezers sporting those broccoli haircuts.
This article originally appeared three years ago.





 luxo jr lamp GIF by Disney Pixar
luxo jr lamp GIF by Disney Pixar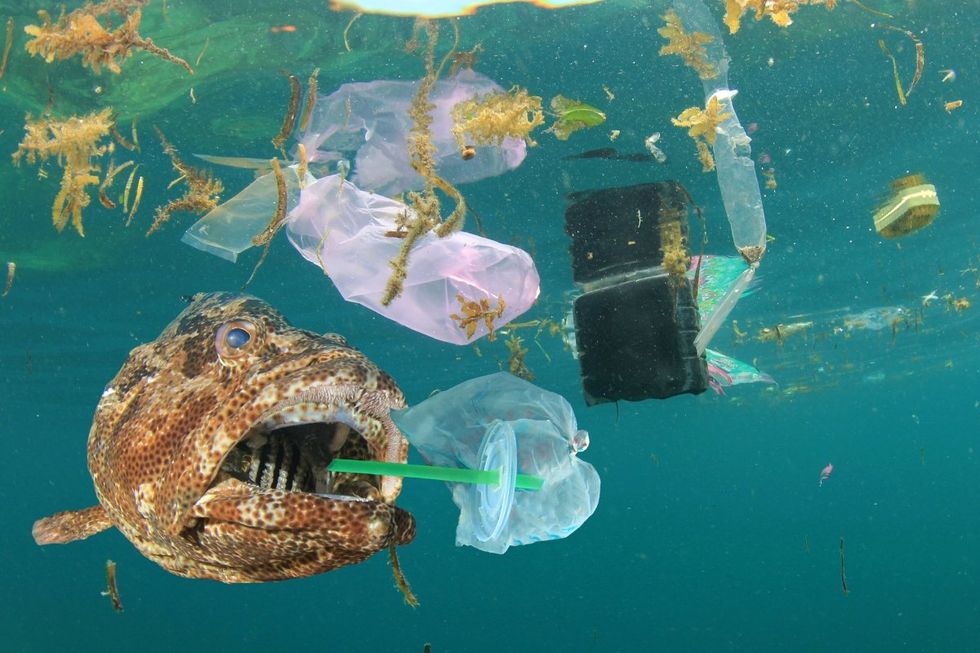 Plastic doesn't belong in the ocean.
Plastic doesn't belong in the ocean.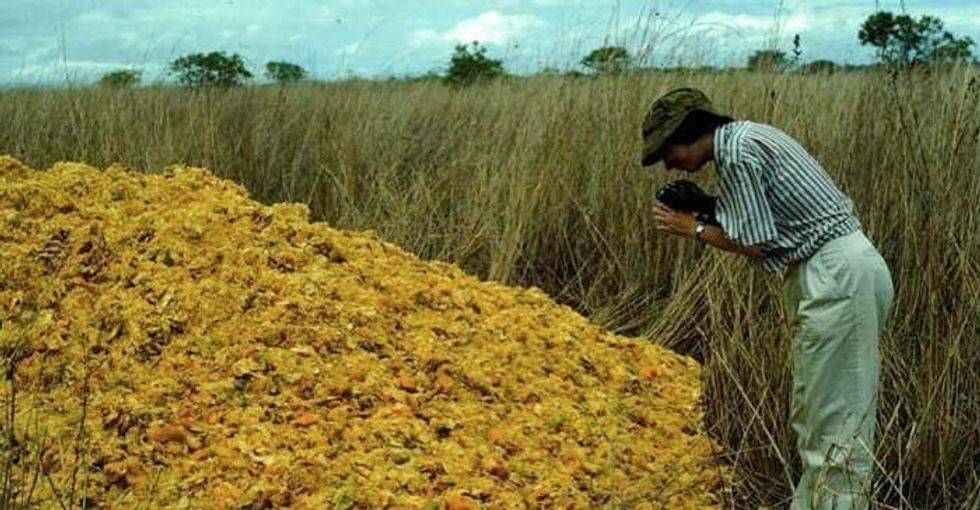 The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.
The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.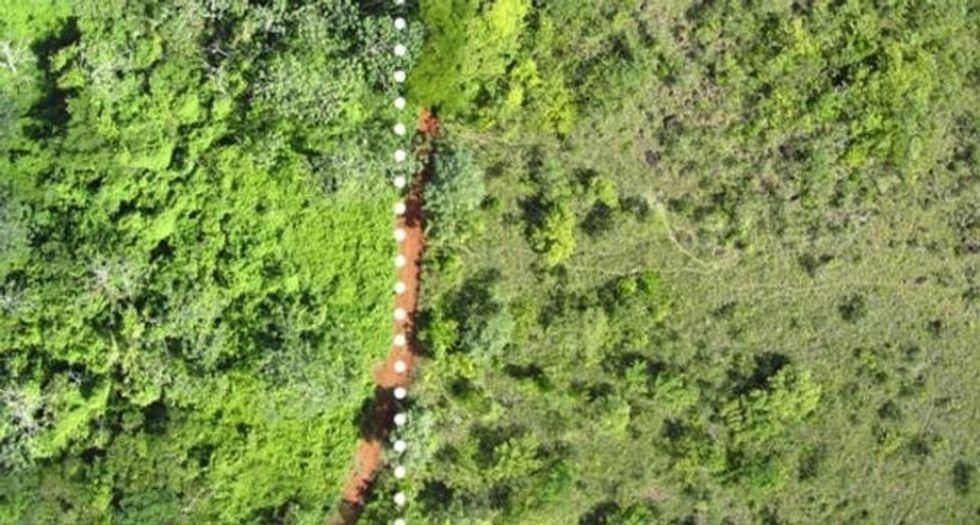 The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R).
The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R). Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.
Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.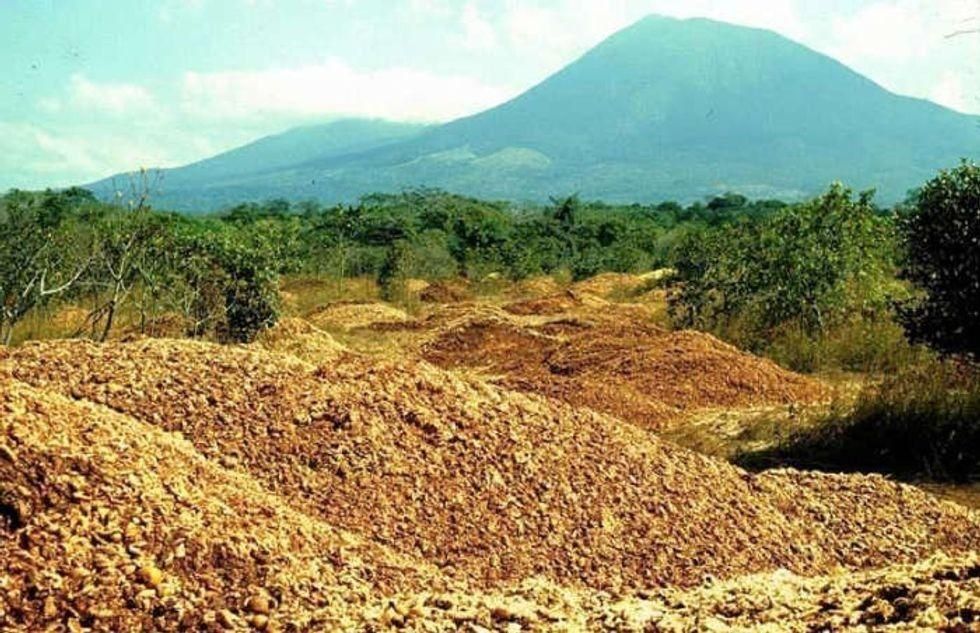 The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998.
The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998. The sign after clearing away the vines.
The sign after clearing away the vines. These moments may be harder to remember. Image via Canva
These moments may be harder to remember. Image via Canva You'll probably forget the stress of these days too. Image via Canva.
You'll probably forget the stress of these days too. Image via Canva.
Men try to read the most disturbing comments women get online back to them.
If you wouldn't say it to their faces, don't type it.
This isn’t comfortable to talk about.
Trigger warning for discussion of sexual assault and violence.
in 2016, a video by Just Not Sports took two prominent female sportswriters and had regular guys* read the awful abuse they receive online aloud.
Sportswriters Sarah Spain and Julie DiCaro sat by as men read some of the most vile tweets they receive on a daily basis. See how long you can last watching it.
*(Note: The men reading them did not write these comments; they're just being helpful volunteers to prove a point.)
It starts out kind of jokey but eventually devolves into messages like this:
Awful.
All images and GIFs from Just Not Sports/YouTube.
These types of messages come in response to one thing: The women were doing their jobs.
Those wishes that DiCaro would die by hockey stick and get raped? Those were the result of her simply reporting on the National Hockey League's most disturbing ordeal: the Patrick Kane rape case, in which one of the league's top players was accused of rape.
DiCaro wasn't writing opinion pieces. She was simply reporting things like what the police said, statements from lawyers, and just general everyday work reporters do. In response, she received a deluge of death threats. Her male colleagues didn't receive nearly the same amount of abuse.
It got to the point where she and her employer thought it best for her to stay home for a day or two for her own physical safety.
The men in the video seemed absolutely shocked that real live human beings would attack someone simply for doing their job.
Not saying it.
All images and GIFs from Just Not Sports/YouTube.
Most found themselves speechless or, at very least, struggling to read the words being presented.
It evoked shame and sympathy.
All images and GIFs from Just Not Sports/YouTube.
Think this is all just anecdotal? There's evidence to the contrary.
The Guardian did a study to find out how bad this problem really is. They combed through more than 70 million comments that have been posted on their site since 2006 and counted the number of comments that violated their comment policy and were blocked.
The stats were staggering.
From their comprehensive and disturbing article:
If you can’t say it to their face... don’t type it.
All images and GIFs from Just Not Sports/YouTube.
So, what can people do about this kind of harassment once they know it exists?
There are no easy answers. But the more people who know this behavior exists, the more people there will be to tell others it's not OK to talk to anyone like that.
Watch the whole video below:
This article originally appeared nine years ago.