Nómade the elephant was born without tusks. Now her mutation is mainstream.
Evolution could help defend elephants from poachers — but that might not be a good thing.
Growing up in war-torn Mozambique wasn't easy for Nómade the elephant.
Mozambique, a southeastern African nation, gained its independence from Portugal in 1975. Then two years later, the Cold War found its way onto Mozambican soil in a bloody conflict that lasted until the mid-1990s and claimed up to a million human lives and displacing even more.
When the human forces weren't directly at each other's throats, they scavenged the savannah for animals they could kill for meat and ivory to trade for weapons or cash. But Nómade survived, along with 11 of her sisters, thanks in part to a miracle mutation that left them without tusks.
Nómade and her family. Photo provided by Joyce Poole/ElephantVoices, used with permission.
By the end of the war, the African elephant population in the Mozambique park where Nómade lived had been reduced by more than 90%.
Half of the females left alive were tuskless, just like Nómade.
Tusks are a crucial survival tool for elephants and, unfortunately, one of the main reasons why people try to kill them. While those lengthy incisors obviously make great weapons, elephants also rely on them for foraging in the dirt for minerals or food as well as scraping bark off trees or bending down branches to reach tasty goods. They're handy as a place to rest those big, heavy trunks on, too.
In typical animal fashion, however, males tend to have the mightier tusks, which they rely on to show off their elephant sexiness. It also means that they get poached in much higher numbers. As a result, the tusklessness gene has only really passed down the maternal side of the African elephant family tree, to elephants like Nómade.
This is the epitome of evolution in action: a rare mutation that grows more common over several generations when it turns out to be a blessing for survival.
Back in the 1930s, tusklessness was estimated to affect about 1% of both African elephant genders; today, there are parts of the continent where 98% of the females are born without tusks. 'Cause who's gonna hunt 'em if there isn't ivory to sell?
Average male tusk sizes in Africa are actually shrinking. But totally tuskless males are still rare, seeing as — erm — lady elephants are less inclined to breed with them. Sorry, fellas. Photo by Alexander Joe/AFP/Getty Images.
It turns out the same tusklessness that saved these females' lives might also be leaving a lasting impact on the whole of African elephant society.
Elephants are, of course, incredibly smart and social creatures. "But the scars of poaching last a very long time," according to Joyce Poole, Ph.D., co-founder and co-director of the ElephantVoices, a conservation group that works with Gorongosa National Park in Mozambique, where Nómade and her family roam.
Having lived under the threat of violence for so long has left many elephants with the equivalent of a broken home, Poole explains. "When a family loses a matriarch, the possibility of calf survival drops because there's no one to take care of the young." For example, the first few times she encountered Nómade, she says, "she was in a different group. A similar configuration of animals, but a different configuration every time." (That's also how she got her name — "nomad" in Portuguese).
To make matters worse, many of the females that do survive past childhood don't even reach full sexual maturity — both from increased stress levels and the fact that, well, there just aren't enough males left to go around, which means they probably aren't going to get pregnant. As a result, the rate of tuskless elephants just keeps going up because the males with tusks are dying out faster than they can be replaced.
Photo by Anna Zieminski/AFP/Getty Images.
"There's also pervasive myth — I'd call it an old wives' tale — that tuskless females are more aggressive than elephants with tusks," Poole says.
To be fair, there are some aggressive tuskless females, particularly in Nómade's family. In another early encounter at Gorongosa, one of Nómade's sisters led a massive mob of more than 30 elephants straight at Poole's safari truck, a move which earned her the name Corajosa, or "Courageous One."
But that behavior wasn't because of her tusklessness, Poole explains. "These are some of the most aggressive elephants in Africa because of what they've been through, and they pass that behavior down from one generation to the next."
Fortunately, Corajosa, Nómade, and the rest of their kin have warmed up to Poole over time. They also have another tool to make up for their lack of tusks: their trunks. "They're such smart animals and the trunk is such a magnificent organ that they are able to compensate," Poole says. "It can push over a tree or caress a baby … it's a magnificent thing to have."
HOORAY, WE STILL HAVE TRUNKS! Photo by Simon Maina/AFP/Getty Images.
On one hand, these African "tusklesses" are proof of evolution in progress.
On the other hand, it's also a frightening example of the damage that human intervention can really do. What was once a genetic survival advantage has now become the exact opposite — and it's likely that that trend will continue.
"If we're able to bring poaching and the illegal trade, then over generations, the tusklessness will decline," says Poole. "But that's going to take a long, long time."
There is a silver lining, however. While half of the females who lived through the war in Mozambique are tuskless, only about a third of the elephants born since then have the same condition. And the fact that they can live for upwards of 70 years means that, if things do improve, we'll actually be able to observe the difference across generations. It's one thing to know that nature always finds a way; it's another thing entirely to see that change in action.
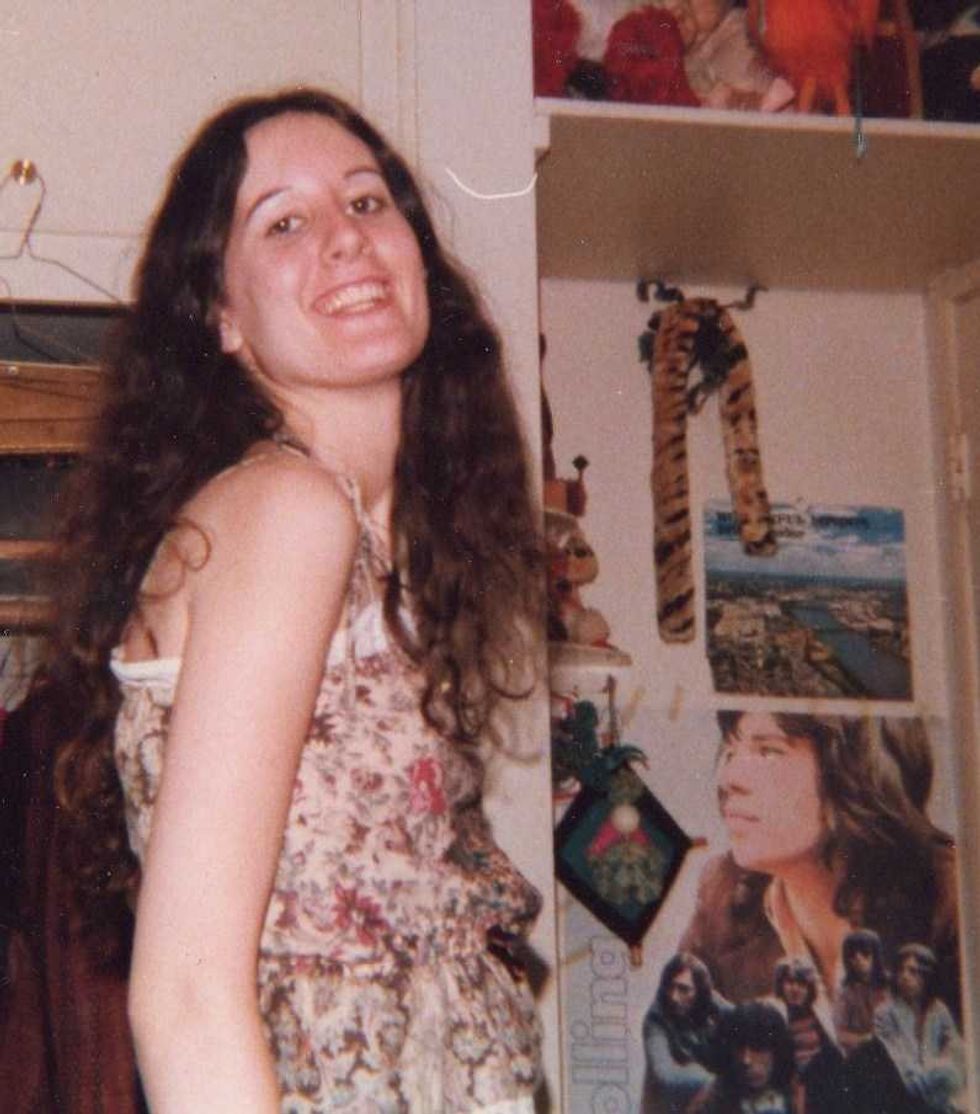

 A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
 An office kitchen.via
An office kitchen.via  An angry man eating spaghetti.via
An angry man eating spaghetti.via 
 Gif of baby being baptized
Gif of baby being baptized Woman gives toddler a bath Canva
Woman gives toddler a bath Canva


An Irish woman went to the doctor for a routine eye exam. She left with bright neon green eyes.
It's not easy seeing green.
Did she get superpowers?
Going to the eye doctor can be a hassle and a pain. It's not just the routine issues and inconveniences that come along when making a doctor appointment, but sometimes the various devices being used to check your eyes' health feel invasive and uncomfortable. But at least at the end of the appointment, most of us don't look like we're turning into The Incredible Hulk. That wasn't the case for one Irish woman.
Photographer Margerita B. Wargola was just going in for a routine eye exam at the hospital but ended up leaving with her eyes a shocking, bright neon green.
At the doctor's office, the nurse practitioner was prepping Wargola for a test with a machine that Wargola had experienced before. Before the test started, Wargola presumed the nurse had dropped some saline into her eyes, as they were feeling dry. After she blinked, everything went yellow.
Wargola and the nurse initially panicked. Neither knew what was going on as Wargola suddenly had yellow vision and radioactive-looking green eyes. After the initial shock, both realized the issue: the nurse forgot to ask Wargola to remove her contact lenses before putting contrast drops in her eyes for the exam. Wargola and the nurse quickly removed the lenses from her eyes and washed them thoroughly with saline. Fortunately, Wargola's eyes were unharmed. Unfortunately, her contacts were permanently stained and she didn't bring a spare pair.
- YouTube youtube.com
Since she has poor vision, Wargola was forced to drive herself home after the eye exam wearing the neon-green contact lenses that make her look like a member of the Green Lantern Corps. She couldn't help but laugh at her predicament and recorded a video explaining it all on social media. Since then, her video has sparked a couple Reddit threads and collected a bunch of comments on Instagram:
“But the REAL question is: do you now have X-Ray vision?”
“You can just say you're a superhero.”
“I would make a few stops on the way home just to freak some people out!”
“I would have lived it up! Grab a coffee, do grocery shopping, walk around a shopping center.”
“This one would pair well with that girl who ate something with turmeric with her invisalign on and walked around Paris smiling at people with seemingly BRIGHT YELLOW TEETH.”
“I would save those for fancy special occasions! WOW!”
“Every time I'd stop I'd turn slowly and stare at the person in the car next to me.”
“Keep them. Tell people what to do. They’ll do your bidding.”
In a follow-up Instagram video, Wargola showed her followers that she was safe at home with normal eyes, showing that the damaged contact lenses were so stained that they turned the saline solution in her contacts case into a bright Gatorade yellow. She wasn't mad at the nurse and, in fact, plans on keeping the lenses to wear on St. Patrick's Day or some other special occasion.
While no harm was done and a good laugh was had, it's still best for doctors, nurses, and patients alike to double-check and ask or tell if contact lenses are being worn before each eye test. If not, there might be more than ultra-green eyes to worry about.