Health experts created a patch that can repair damaged hearts
German scientists found a way to fix a broken heart—literally
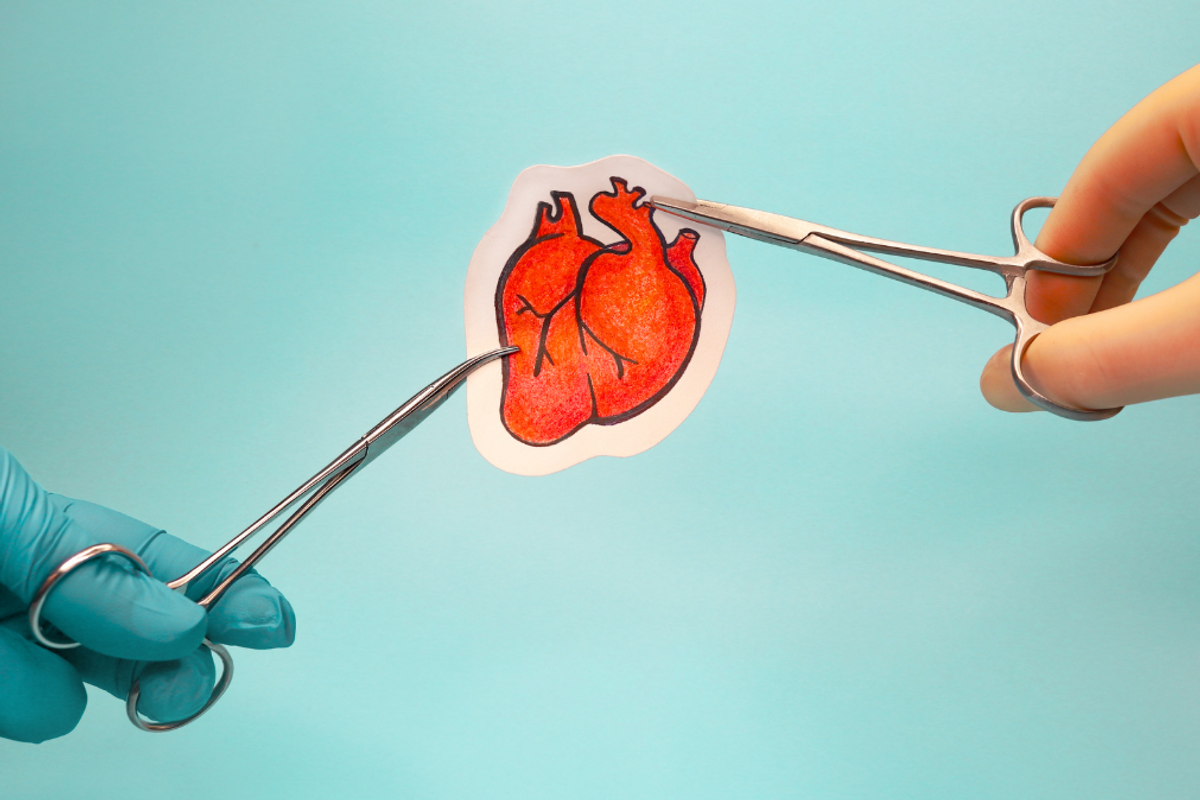
A new patch made of human cells could help repair damage from heart failure.
Scientists at the University Medical Center Göttingen in Germany have found a way to mend hearts. Not the metaphorical version, but literal flesh-and-blood hearts! Through cell manipulation they have successfully tested a patch that can strengthen heart tissue for those with heart disease and advanced heart failure.
“We now have, for the first time, a laboratory grown biological transplant available, which has the potential to stabilize and strengthen the heart muscle,” said co-author of the study, Prof. Ingo Kutschka to The Guardian.
In this study, the researchers took blood cells from a donor and “reprogrammed” them into mimicking stem cells. This allowed those cells to further change into heart muscle cells and connective tissue cells. After combining these cells with collagen, the scientists were able to create a graftable patch that could be implanted onto a damaged area of the heart to increase its strength. In fact, the completed heart muscle patches have the characteristics of a heart that is only four to eight years old.
The reason for this experiment was two-fold. First, it was done to explore other health care options for people who need a donated heart, which is typically a very long waitlist. Secondly, because previous methods of injecting heart muscle cells into the heart have led to patients experiencing tumors or an irregular heartbeat, both of which could be fatal.
Initial trials of this heart patch have been promising. After successful trials with macaque monkeys, the researchers approached a 46-year-old woman with advanced heart failure to treat her with patches made with human cells after a minimally invasive procedure. Three months afterward, the patient received a transplant and the scientists were able to study her discarded heart that they had patched to see how effective their treatment was. They found that not only did the patches survive but they had developed their own blood supply.
While this is definitely great news for heart patients, there still needs to be further testing. As of now, it takes three to six months for these patches to fully benefit the patient, meaning that transplants would be prioritized for patients that urgently need a new heart. However, fifteen patients have been approved for the procedure and are currently being monitored with their new heart patches.

While advances in heart medicine are great news overall, further research is needed to make sure this and other advances are viable in the long term. In the meantime, it’s best for everyone to take steps to ensure maximum heart health. This may sound like an afterschool special or a basic lesson in health class, but according to American Heart Association nearly half of American adults have a cardiovascular issue, so it might be good to have a refresher.

Make sure your diet is rich with heart-healthy foods like vegetables and fish, with little to no added fat, sugar, or salt. Exercise at least 150 minutes per week to keep your heart rate strong. Visit your doctor with regular check-ups to keep track of your overall health, so you can both create a treatment plan if something comes up.
Over time, more and more medical breakthroughs will occur, but it’ll be better to do what you can to ensure you’ll be around to see them.





 The more passionate you are about your goals, the more secretive you should be.
The more passionate you are about your goals, the more secretive you should be.  Potted plants and herbs can thrive in a container garden.
Potted plants and herbs can thrive in a container garden. Freshly harvested potatoes are so satisfying.
Freshly harvested potatoes are so satisfying. Do you see a box or do you see a planter?
Do you see a box or do you see a planter? Kamikatusu's recycling techniques are well worth the effort.
Kamikatusu's recycling techniques are well worth the effort.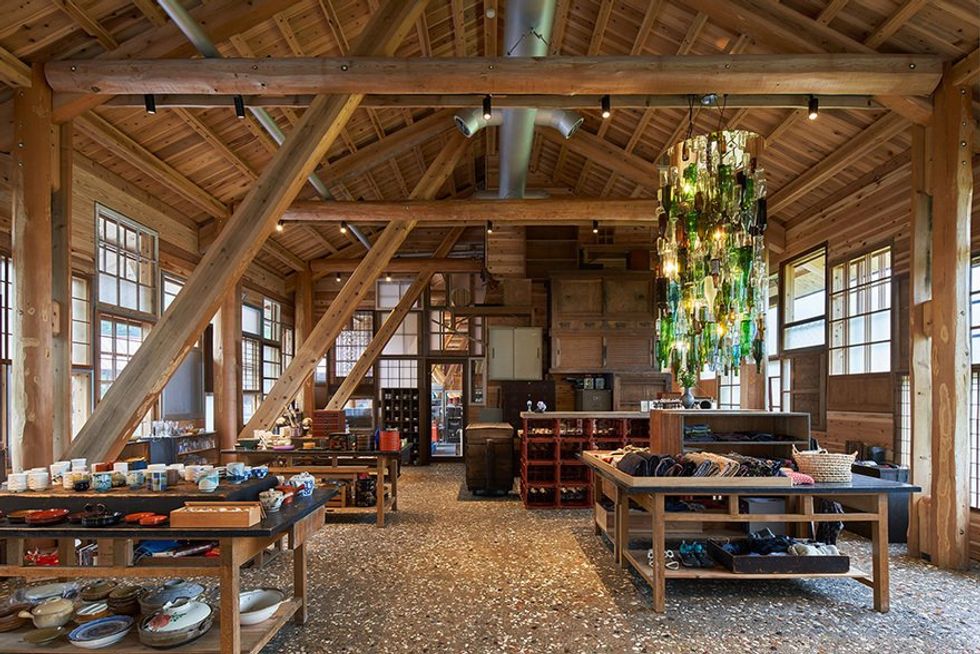  The inside of Kamikatsu's Zero Waste Center.
The inside of Kamikatsu's Zero Waste Center.  How to recycle boxes and other cardboard goods.
How to recycle boxes and other cardboard goods.  Give radical recycling a try.
Give radical recycling a try.  Raise that top dishwasher rack to the roof!
Photo by
Raise that top dishwasher rack to the roof!
Photo by  How it feels to learn you've been using your dishwasher wrong for yaers.
How it feels to learn you've been using your dishwasher wrong for yaers.