Semicolon tattoo: Here's what it means and why it matters.
They represent hope.
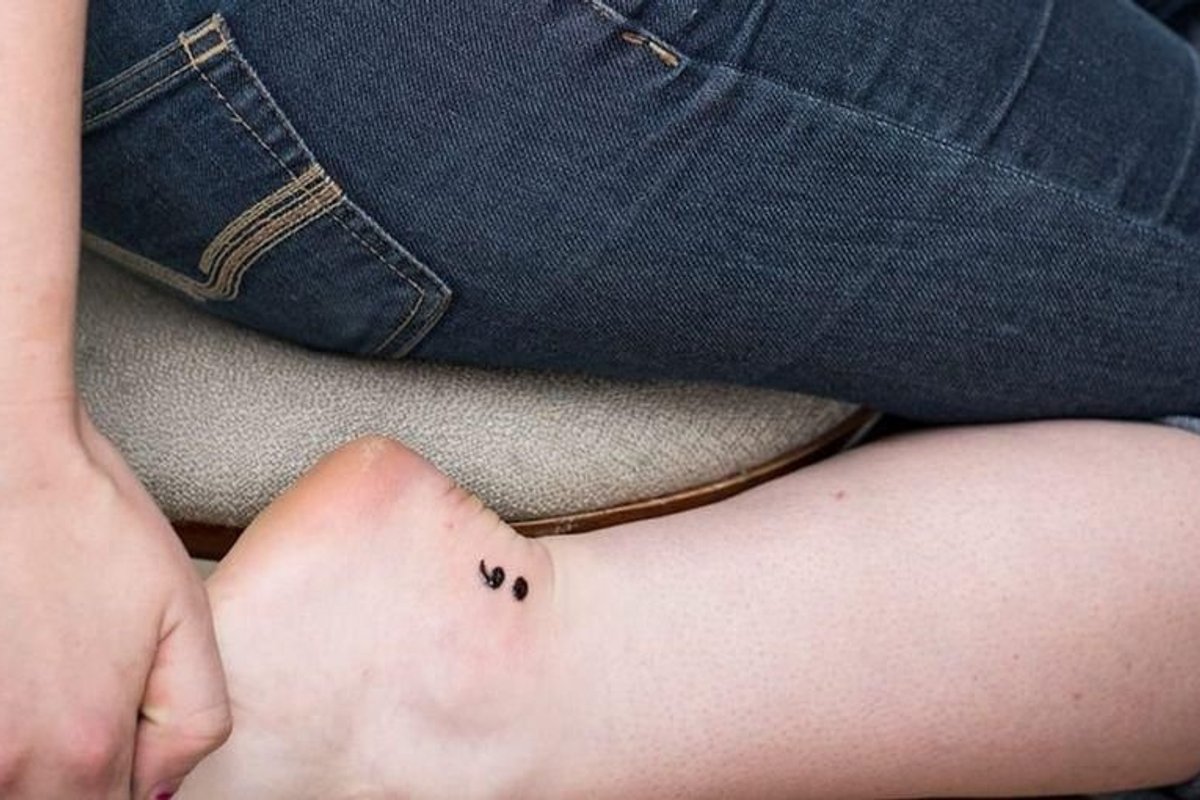

A semicolon tattoo
Have you seen anyone with a semicolon tattoo like the one above?
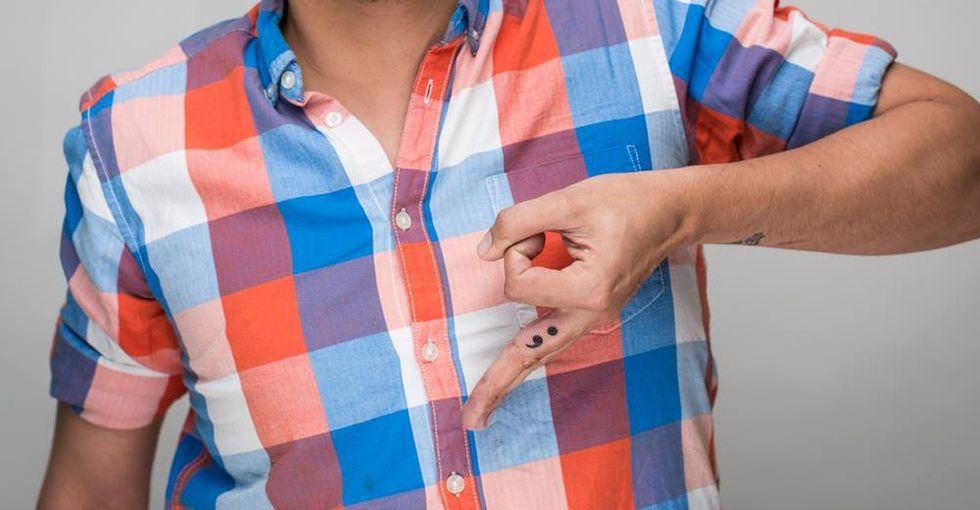

Photo by The Semicolon Tattoo Project.
That's right: the semicolon. It's a tattoo that has gained popularity in recent years, but unlike other random or mystifying trends, this one has a serious meaning behind it. (And no, it's not just the mark of a really committed grammar nerd.)
The semicolon tattoo represents mental health struggles and the importance of suicide prevention.
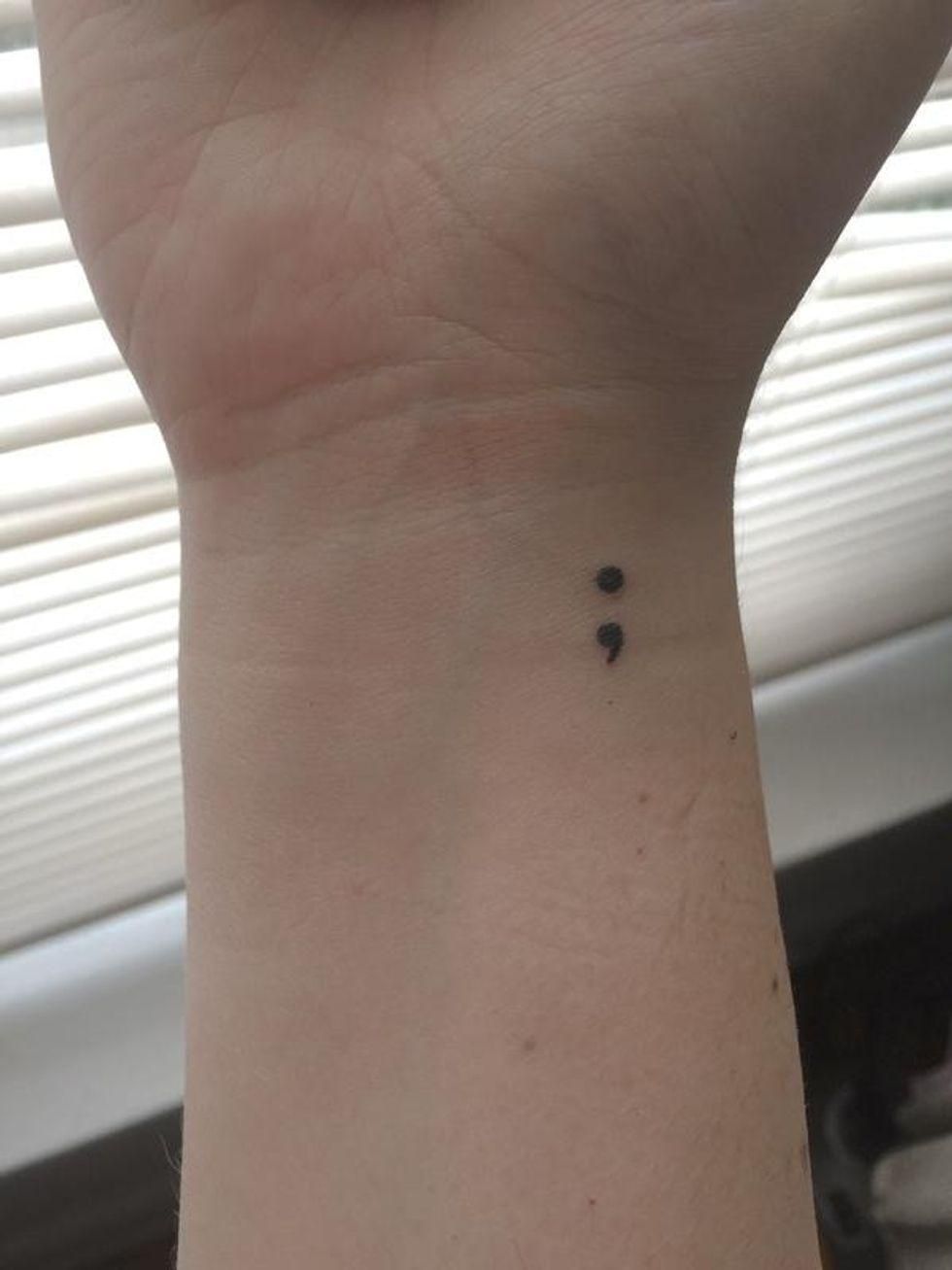

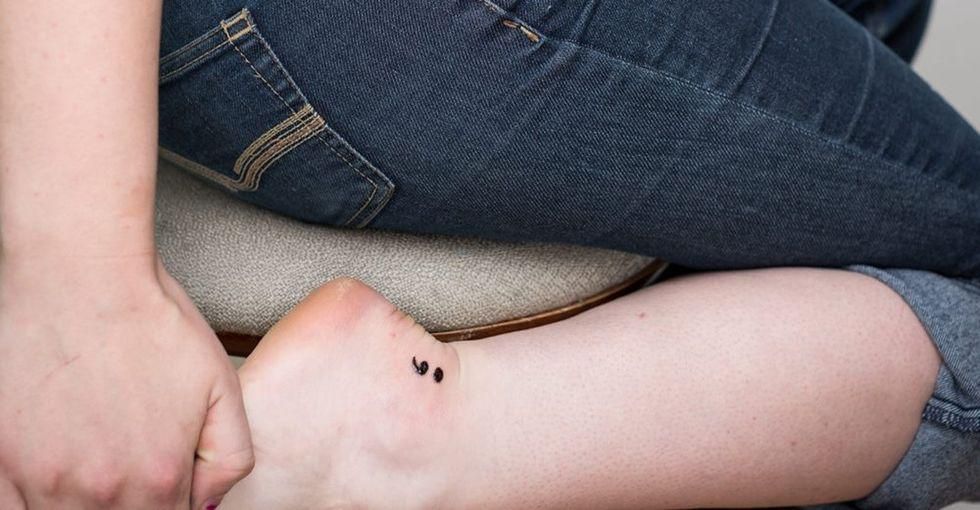
Photo by The Semicolon Tattoo Project.
Project Semicolon was born from a social media movement in 2013.
They describe themselves as a "movement dedicated to presenting hope and love to those who are struggling with depression, suicide, addiction, and self-injury. Project Semicolon exists to encourage, love, and inspire."
But why a semicolon?
"A semicolon is used when an author could've chosen to end their sentence, but chose not to. The author is you and the sentence is your life."
Originally created as a day where people were encouraged to draw a semicolon on their bodies and photograph it, it quickly grew into something greater and more permanent. Today, people all over the world are tattooing the mark as a reminder of their struggle, victory, and survival.
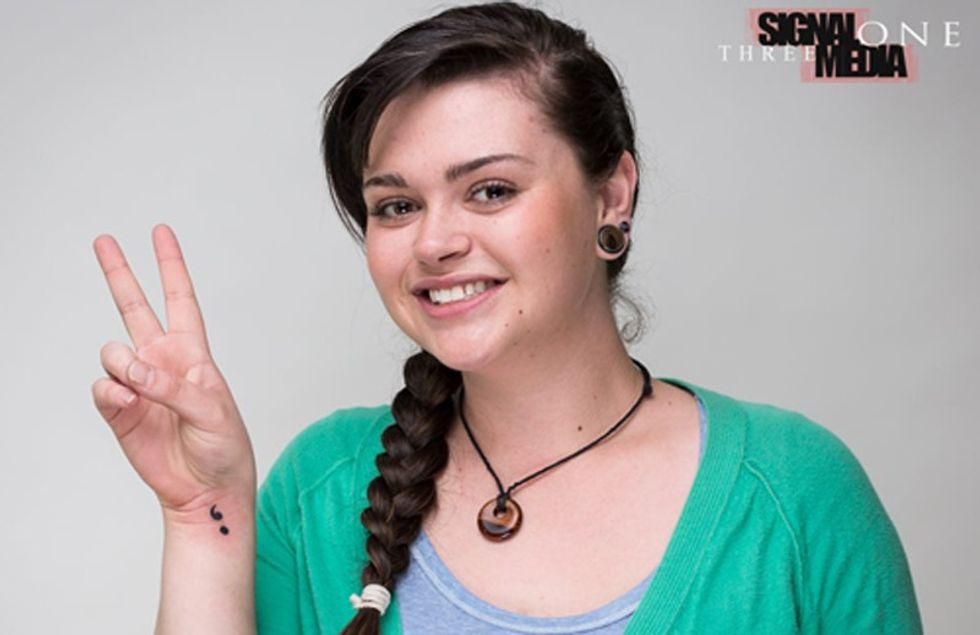
Photo by The Semicolon Tattoo Project.
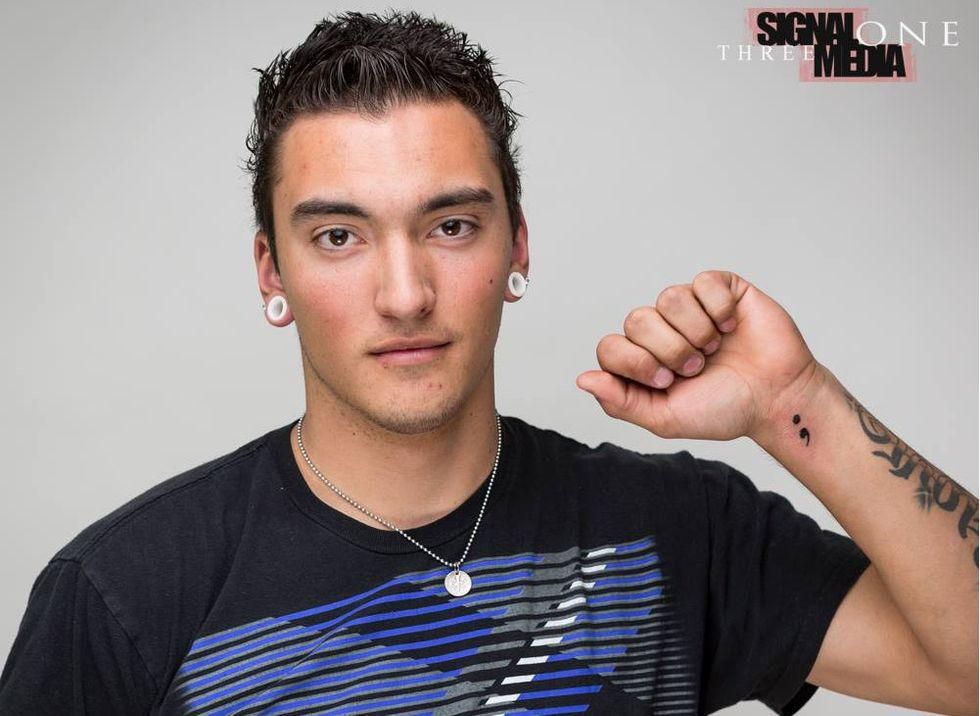
Photos by The Semicolon Tattoo Project.
I spoke with Jenn Brown and Jeremy Jaramillo of The Semicolon Tattoo Project, an organization inspired by the semicolon movement. Along with some friends, Jenn and Jeremy saw an opportunity to both help the community and reduce the stigma around mental illness.
In 2012, over 43 million Americans dealt with a mental illness. Mental illness is not uncommon, yet there is a stigma around it that prevents a lot of people from talking about it — and that's a barrier to getting help.
More conversations that lead to less stigma? Yes please.
"[The tattoo] is a conversation starter," explains Jenn. "People ask what it is and we get to tell them the purpose."
"I think if you see someone's tattoo that you're interested in, that's fair game to start a conversation with someone you don't know," adds Jeremy. "It provides a great opportunity to talk. Tattoos are interesting — marks we put on our bodies that are important to us."
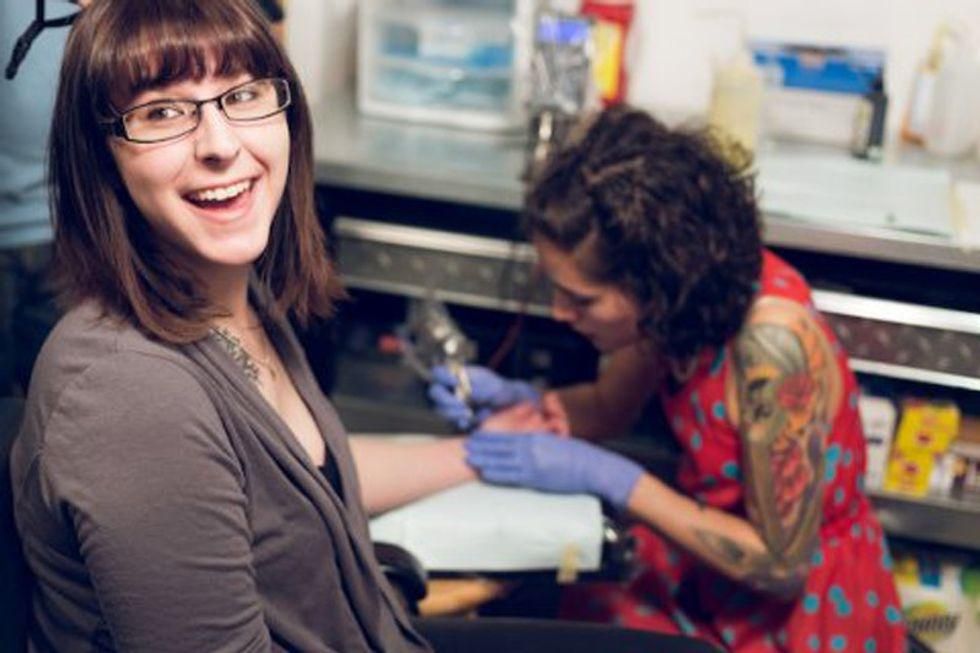
In 2014, The Semicolon Tattoo Project held an event at several tattoo shops where people could get a semicolon tattoo for a flat rate. "That money was a fundraiser for our crisis center," said Jenn. In total, over 400 people received semicolon tattoos in one day. Even better, what began as a local event has spread far and wide, and people all over the world are getting semicolon tattoos.
And it's not just about the conversation — it's about providing tangible support and help too.
Jenn and Jeremy work with the Agora Crisis Center. Founded in 1970, it's one of the oldest crisis centers in the country. Through The Semicolon Tattoo Project, they've been able to connect even more people with the help they need during times of crisis. (If you need someone to talk to, scroll to the end of the article for the center's contact information.)
So next time you see this small punctuation tattoo, remember the words of Upworthy writer Parker Molloy:
"I recently decided to get a semicolon tattoo. Not because it's trendy (though, it certainly seems to be at the moment), but because it's a reminder of the things I've overcome in my life. I've dealt with anxiety, depression, and gender dysphoria for the better part of my life, and at times, that led me down a path that included self-harm and suicide attempts.
But here I am, years later, finally fitting the pieces of my life together in a way I never thought they could before. The semicolon (and the message that goes along with it) is a reminder that I've faced dark times, but I'm still here."
No matter how we get there, the end result is so important: help and support for more people to also be able to say " I'm still here."
If you want to see more incredible semicolon tattoos, check out nine photos and stories that our readers shared with us!
This article was written by Laura Willard and originally appeared 10 years ago.
- If anyone's ever told you that you'll regret your tattoo, they should ... ›
- A woman in hospice care gets a tattoo she always wanted - Upworthy ›
- Semicolon tattoo: Here's what it means and why it matters. - Upworthy ›
- A tattoo artist is giving people free 'nipple tattoos' to help cancer survivors - Upworthy ›
- A tattoo artist is giving people free 'nipple tattoos' to help cancer survivors - Upworthy ›
- Writer Joel L. Daniels shares his powerful story of how the Suicide Prevention Lifeline saved his life - Upworthy ›
- Rep. Jamie Raskin's beautiful obituary for his son is an important message about mental health - Upworthy ›
- Woman shares her pre-pandemic tattoo as worst case of 'bad timing' in the history of body art - Upworthy ›
- What you shouldn't say to someone who is suicidal - Upworthy ›
- What you shouldn't say to someone who is suicidal - Upworthy ›
- Bumper sticker saves someone's life - Upworthy ›
- Megan Montgomery's tragic story - Upworthy ›
- Bumper sticker saves someone's life - Upworthy ›
- Trapper Keeper inventor dies - Upworthy ›
- Woman shares her pre-pandemic tattoo as worst case of 'bad timing' in the history of body art - Upworthy ›
- Megan Montgomery's tragic story - Upworthy ›
- 6 ways to help a friend or loved one who may be suicidal. - Upworthy ›
- 'This is the face of domestic violence.' The tragedy of Megan Montgomery happens far too often. - Upworthy ›





 Potted plants and herbs can thrive in a container garden.
Potted plants and herbs can thrive in a container garden. Freshly harvested potatoes are so satisfying.
Freshly harvested potatoes are so satisfying. Do you see a box or do you see a planter?
Do you see a box or do you see a planter? Where did the mood ring come from?
Photo by
Where did the mood ring come from?
Photo by  If only Wenick had patented the mood ring...
If only Wenick had patented the mood ring... Crystals encased in quartz or glass change color according to body temperature.
Crystals encased in quartz or glass change color according to body temperature.  Unfortunately, mood rings are not backed by the power of science.
Unfortunately, mood rings are not backed by the power of science.  CEO Rob Dance holds up a whipe board with his culture philosophy.
CEO Rob Dance holds up a whipe board with his culture philosophy.  A woman enjoying a plate of pasta.via
A woman enjoying a plate of pasta.via  A muscular man with some baskets of vegetables.via
A muscular man with some baskets of vegetables.via  Pooch smooches are sweet if they're not too slobbery.
Pooch smooches are sweet if they're not too slobbery. Many dogs will lick you if you give them the chance.
Many dogs will lick you if you give them the chance.  puppy love kiss GIF by Pickler & Ben
puppy love kiss GIF by Pickler & Ben Keep your dog's mouth clean with regular teeth brushing.
Keep your dog's mouth clean with regular teeth brushing.