Gen Xers and boomers open up about whether life was really safer when they were young
Perception is everything.

Were the good old days really that good?
Sometimes we hear wistful tales of a bygone era when life was simpler and people felt safer. Kids could go out and run around the neighborhood. Parents didn't worry about child trafficking or online sextortion or whether their kids would make it through the school day without being shot.
But was life really safer back then? The elders are often the ones who romanticize the olden days, but according to Gen Xers and boomers who were asked, the good old days may not have been as rosy as those rose-colored glasses make them appear.
Someone asked the AskOldPeople channel on Reddit, "Hey elders! I often talk to my grandmother and she states that the world was better back then — she could send her kids out to play for hours with no worries about them. I’m wondering: was life really safer back then?"
Of course, there are always a few people who reminisce about never locking their doors, but for the most part the answers were surprisingly and consistently "no," but for many different reasons.
Life before antibiotics and vaccines
Most of these tragic disease stories are from Gen Xers and boomers' parents and grandparents, but still, we're only a generation or two removed from communicable illnesses wiping out entire families.
"My grandmother had 7 children on a tuesday in 1936. One of them caught diphtheria. By saturday she had one living child. so..."
"It was typhus for my great grandparents. Lost kids 3 of 5 in one week. In Chicago."
"There's a cemetery on my property from the late 1800s, there were 6 kids in the family who all died within a calendar year due to a diphtheria epidemic. Newborn to 17 year old, all gone."
"This is doubly tragic because diphtheria antitoxin (which protected people who had the disease) was widely available by 1910, and diphtheria vaccine was manufactured by 1930."
"My grandmother was born in 1897. Her mother had 8 children but half her siblings died of Whooping Cough."
"My grandfather was only 1 of 6 that survived. The rest buried out back. Yea, so much better."
"I went to my local cemetery. There were three children from the same family. All under age five. Time of death was the early 1900's. We don't realize how good we have it nowadays."
"This is why vaccinations are so important. People forget that entire families were wiped out by illness."
"My dad’s sister got polio and recovered. Then she got it again and died at age 7, right before the vaccine was available. My grandma was never the same after that."
"That's why the Salk vaccine was such a huge thing in the 50s."
Food regulations, too
People like to complain about government regulations, but there's no question they've made a difference in food and packaging safety.
"A similar story in my family: in the late 1920s some cousins of my father bought ice cream from a street vendor. Three of the four of them died of botulism. They tried to sue, but the lawyers for Bad Ice Cream only accused them of bad parenting. They got nothing."
"I read a book about poverty in New York City in the 1920’s. It mentioned that the city gave away potted meat ( whatever that is) and a lot of children died after eating it. The parents couldn’t sue the city because it was considered a charitable act, the city meant well, and therefore they had immunity from the crime. Can you imagine?"
Rape and sexual assault happened a lot, people just didn't report it
Young folks today may not fully appreciate what life was like for the generations before the Me Too Movement. It's still hard to report and be believed, but it wasn't that long ago that nobody reported anything and swept it all under the rug.
"Particularly pedophilia. It was not spoken about so people did not know to be careful with their children."
"They were really good at sweeping it under the carpet."
"Yep rape, pedophelia, child and spousal abuse all grossly under reported. Even murder was - lynchings weren’t classified as murder and neither were the murders of 'undesirables' (eg prostitutes)."
"Unfortunately, most people who hurt children are not the 'random in the neighborhood.' It's a family member or trusted family friend (baseball coach, Boy Scout master, church leaders, etc). People often covered this up for the shame of the family and a misguided idea that it was 'protecting the victim.' Children were definitely not better protected from this behavior in the past."
"I'm from Boston. A ton of my own elder neighbors and their families were harmed by the priests in our neighborhood. They knew. Plenty of them absolutely knew. Sometimes mom would try to go to a higher up about it on behalf of her kid, and she'd get bullied/manipulated into not saying anything (hanging the threat of going to hell over her), and then they'd just move the priest onto some other church to hurt more kids. Families that were deeply involved in the religion were most susceptible to the hush up tactics."
"In our town, it was the Boy Scouts (late 60s-early 70s). As my age group grew up, it became known amongst the guys that the Scoutmaster REALLY, REALLY liked boys... It made me feel a lot better about not having joined up."
"Exactly. My mum was abused by an uncle as a kid. No consequences. We were all heavily abused for years by her second husband. Police wouldn't even respond. It was well known they had zero interest in "domestics." It wasn't safer, it just wasn't acknowledged."
More drunk drivers, less safe cars
Just the invention of back-up cameras and airbags alone has changed car accident mortality rates drastically. Car seat safety, seat belts, so many safety features we didn't have back then. Plus a lot more drunk driving awareness (though cell phone distraction has probably replaced a lot of those deaths).
"Cars were very unsafe back then. I knew one person personally, and several more indirectly that died in car wrecks. That really doesn't seem to happen so much anymore. No crumple zones, no collapsible steering columns, lots of angular metal hard surfaces, no anti-lock brakes. And, people didn't use seat belts very much back then."
"When I was in high school in the 80s, every yearbook had 2-4 "in memoriam" pages for the kids who died that year. It was car wrecks every year I was there. My own children went to the same high school. Classes of 2016 and 2019. During their 7 years at that school (with almost twice as many students) one child died in a freak accident."
"Growing up, there were several kids in my rural area who died. Car accident were the biggest killer."
"The cars we drove or rode in fifty years ago could not be sold as new cars today. Roads are safer. There is less drunk driving."
"The cars point is a big one and just one example of product safety. Products are a million times safer now than they used to be. And then the medical care if you do get hurt is likewise worlds better."
Survivor bias is a thing
There's a reason things have gotten safer besides just increased anxiety due to the internet. We also learned from our mistakes.
"Most of the many (many, many) children for whom being a kid back then was a nightmare of malnutrition, crippling disease, brutality, abuse, torture, and an early grave didn't get a chance to grow up to be grandmothers complaining about how much better the past was. So you're only going to get part of the story."
"It's called 'survivor bias.' You see it in all the boomer posts: 'We didn't wear seat belts (or whatever else), and we lived to tell about it!'
But some of their peers DIDN'T live to tell about it. Enough of them were seriously injured or killed that it was worth passing laws about seatbelts and car seats and not riding around in the back of pickups, etc.
Enough of their peers were kidnapped/r*ped/killed, that 'stranger danger' became a thing and parents realized that it might not be a great idea to let young children wander unsupervised for 12 hours a day.
In short, all the 'snowflake' safety measures we have in place today are thanks to previous generations being idiots and the prime example of what NOT to do."
"There's more than a little survivor bias at play when you hear stuff like 'we played with lawn darts and we're fine' or 'we didn't need helmets for our bicycles' or 'we didn't have life-threatening allergies like today.' Things weren't safer then but people weren't as aware of the dangers they were avoiding as we are now."
It's all in the perception
The internet may have been a mistake, at least when it comes to the flood of news and information we're bombarded with that makes it seem like terrible things are happening all around us all the time.
"It was less safe but the PERCEPTION of safety was higher. Just like how now it’s actually incredibly safe but the perception of danger is high."
"Statistically, it was less safe. But you only heard about issues in your local area, not the whole country, and news was something that for most only came in the form of the daily newspaper, and the evening news. So the perception was that it was safer."
"So true. Bad things happened but weren't blasted around the world in nano-seconds. I don't think it's any safer due to kids being micromanaged though. Technology and 'stranger danger' awareness have certainly had a positive impact on response times and prevention."
"Yes, this is the correct answer. I grew up in a very safe small town, where everyone assumed bad things didn't happen, but the internet age has shown us that not only do bad things happen everywhere, but they always did."
"We also weren't warned about things. Not like now. I recall in 1st grade one of my classmate - tallest girl in my class - suddenly didn't come back to school anymore. Our teacher told us it was because "a bad man did something bad to her so she will not coming back." And that was it. I never did find out what happened but I got the feeling later on that she was raped. A 6 year old."
"Exactly. The reason everyone feels less safe today is because of our news. 24 hours/7 days a week of it and good news doesn't sell. So you don't get much of that.
Violent crime in the US peaked in 1992. With the exception of some bumps, it's been going down since."
"This exactly. Before the internet and cable news you just didn't hear about things that happened outside of your town or even less so outside of your state. There was no 24 hour news, and therefore no need to constantly feed the outrage/fear machine to generate ad dollars like there is now. There has always been crime and there always will be, but crime was in fact much worse when I was a kid than it is now."




 A father does his daughter's hair
A father does his daughter's hair A father plays chess with his daughter
A father plays chess with his daughter A dad hula hoops with his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad hula hoops with his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. A dad talks to his daughter while working at his deskAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad talks to his daughter while working at his deskAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. A dad performs a puppet show for his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad performs a puppet show for his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. A dad walks with his daughter on his backAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad walks with his daughter on his backAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. a dad carries a suitcase that his daughter holds onto
a dad carries a suitcase that his daughter holds onto A dad holds his sleeping daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad holds his sleeping daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. A superhero dad looks over his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A superhero dad looks over his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.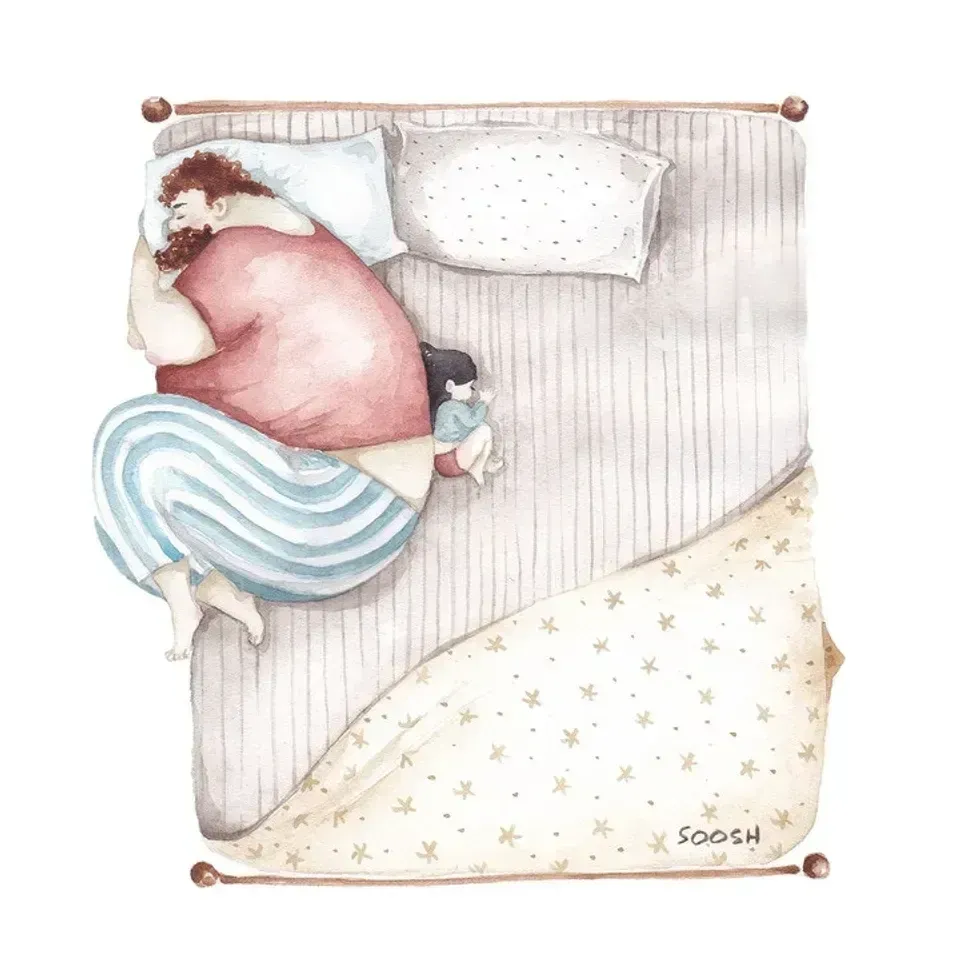 A dad takes the small corner of the bed with his dauthterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad takes the small corner of the bed with his dauthterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. Season 8 Nbc GIF by The Office
Season 8 Nbc GIF by The Office Figuring out our finances may be getting easier.
Photo by
Figuring out our finances may be getting easier.
Photo by  Plumbing Plumber GIF by Family Guy
Plumbing Plumber GIF by Family Guy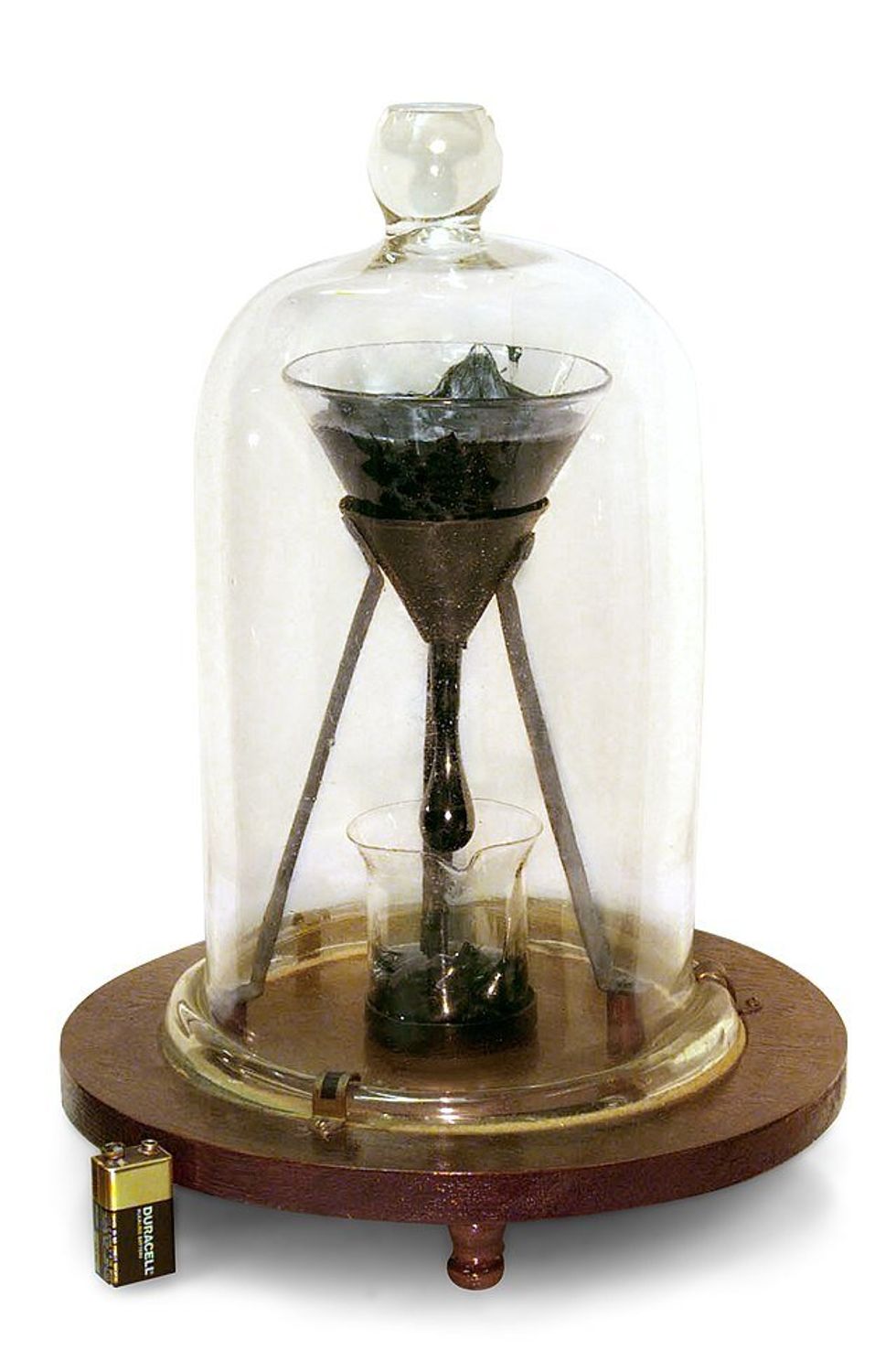 Pitch moves so slowly it can't be seen to be moving with the naked eye until it prepares to drop. Battery for size reference.
Pitch moves so slowly it can't be seen to be moving with the naked eye until it prepares to drop. Battery for size reference.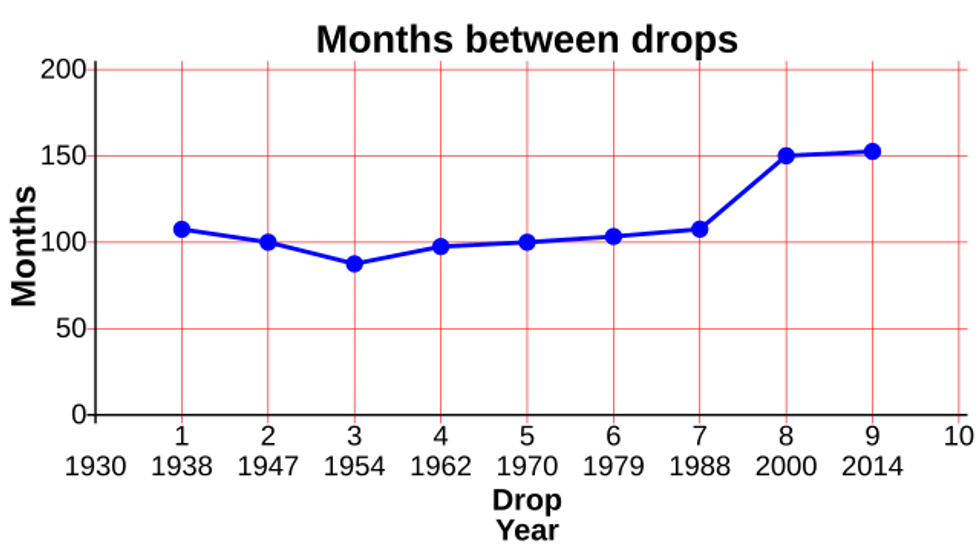 The first seven drops fell around 8 years apart. Then the building got air conditioning and the intervals changed to around 13 years.
The first seven drops fell around 8 years apart. Then the building got air conditioning and the intervals changed to around 13 years.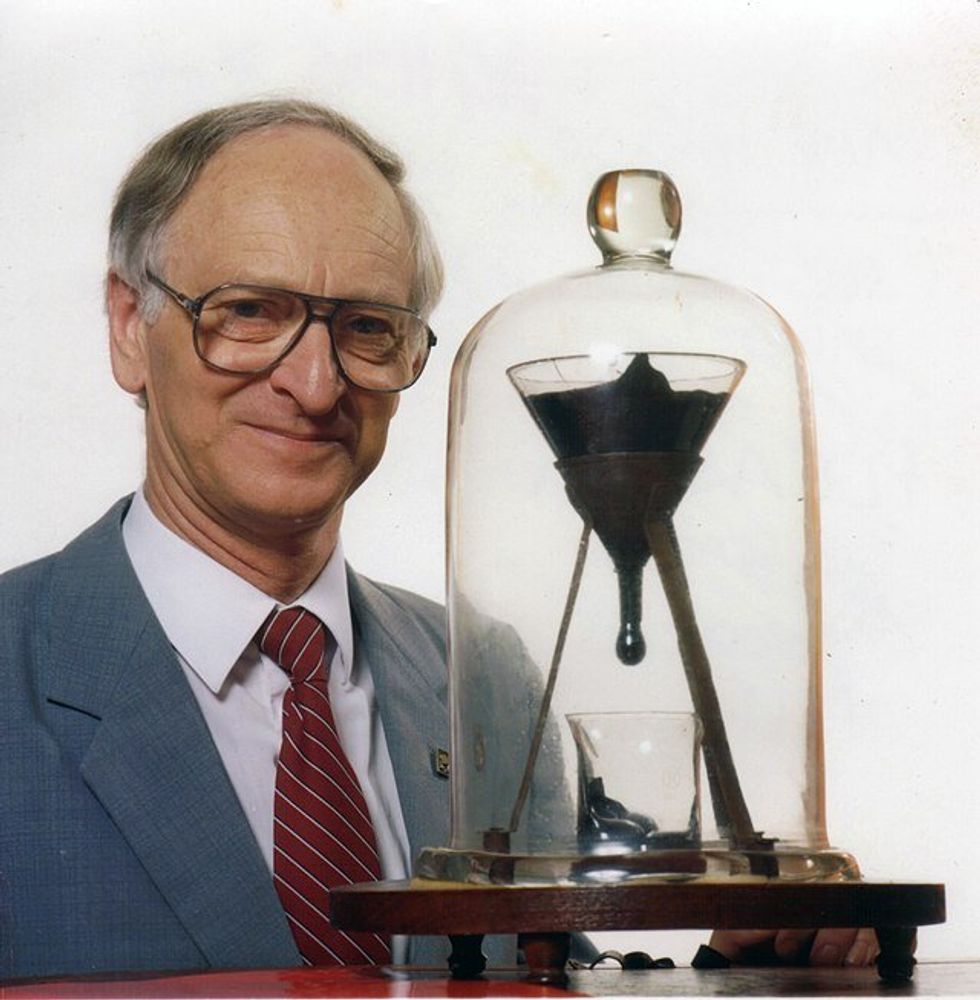 John Mainstone, the second custodian of the Pitch Drop Experiment, with the funnel in 1990.
John Mainstone, the second custodian of the Pitch Drop Experiment, with the funnel in 1990. The Alhambra sits atop a plateau overlooking Granada, Spain.
The Alhambra sits atop a plateau overlooking Granada, Spain.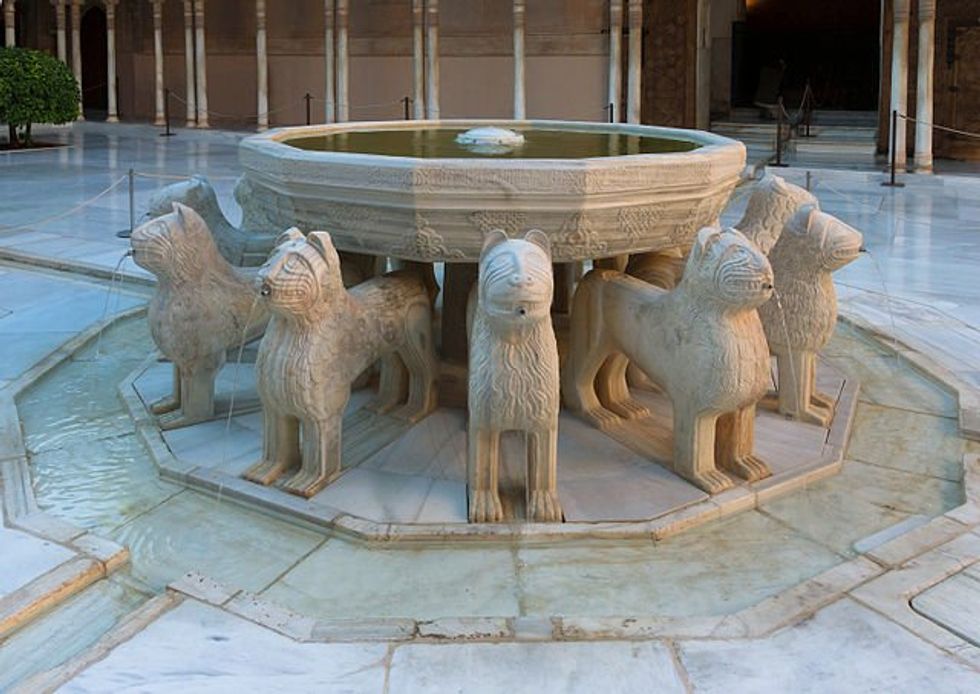 Fountain of the Lions at the Alhambra, Granada
Fountain of the Lions at the Alhambra, Granada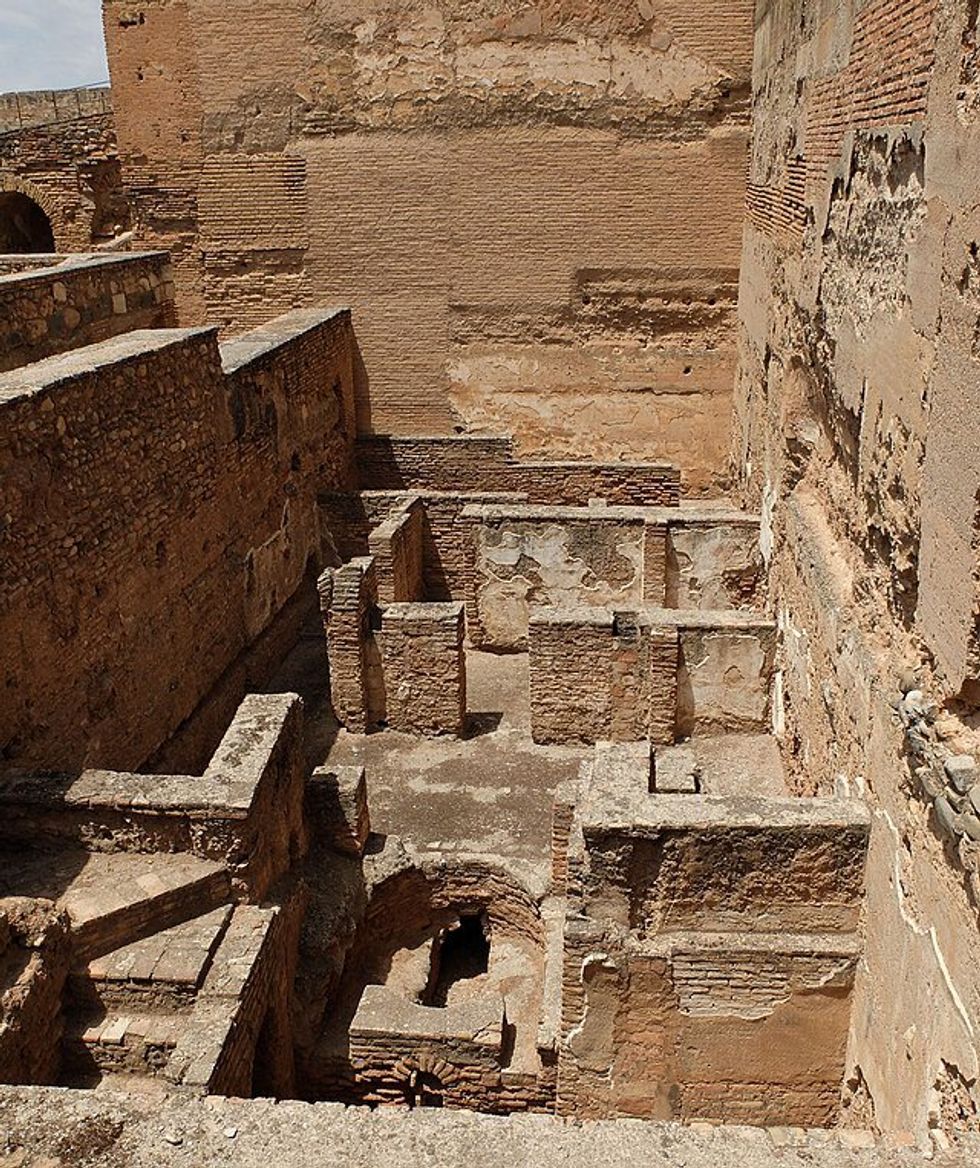 Remains of baths inside the Alhambra Alcazaba
Remains of baths inside the Alhambra Alcazaba