Female bonobos shut down violent males. Here's what humans can learn from them.
Who run the bonobos world? GIRLS!
Hey ladies, you know that uncomfortable moment when you're at a bar with your girlfriends and some sketchy dude comes over to hit on one of you?
Maybe this dude elbows his way into your conversation or maybe he leans too close and tries to buy a round of drinks. Then maybe he not-so-subtly drapes a sweaty hand on one of your shoulders? Yeah, it sucks.
Image via iStock
If that sounds familiar to you, then you'll probably recognize what happens next because it's kind of awesome: Your friends close ranks and block the dude's unwanted approach.
Even more awesome? This behavior isn't limited to humans.
Scientists at the Primate Research Institute at Kyoto University have observed female bonobos employing similar behaviors when a female in their group feels threatened by a male.
In fact, according to a four-year study on bonobos (cousins to chimpanzees) conducted in the Congo, female bonobos purposely form all-female groups to keep aggressive males at bay.
Females of all ages from different families would come together in these groups, with the older bonobos looking out for the younger ones by keeping them in the center of a protective circle. Researchers even found that female bonobos from different families were incredibly tolerant of one another, and that female-on-female bonobo aggression was surprisingly rare.
Bonobos females holding each other. Photo via Georges Gobet/Getty Images.
Nahoko Tokuyama, the leader of the study, believes this ability to get along is the key to female dominance in the bonobo population.
In species that display what humans might call "stereotypically gendered behavior," males are more often observed using aggressive tactics to coerce copulation and/or acquire higher social status. This could be anything from a male trying to mate with a female to a male bonobo feeding on a tree that a female bonobo has claimed as hers.
Sound familiar? Yeah.
But in the Kyoto University study, researchers noticed female bonobo grouping together to prevent this kind of male aggression. They called these groups "female coalitions," but you or I might describe them as "deep female friendships."
If there's one thing males in pretty much every species know, it's not to mess with a group of angry women. Photo by Mark Dumont/Flickr.
If one female in a coalition attacked a male for any reason, the rest would follow suit and come to her aid.
According to Tokuyama, 69% of these female coalitions were observed forming after or during an incident of aggressive male behavior.
What's more, female coalitions rarely (if ever) lose to a male aggressor, and because the male bonobos know they can't win, they're less prone to acting out with aggression or violence in the first place.
"Males frequently direct display and charge toward females, but they seldom attack females physically, even though males are bigger," Tokuyama told Upworthy.
A coalition of female bonobos attacking an offending male. GIF via animal coalition/YouTube.
Of course, meeting aggression with aggression might not sound like the best approach to conflict resolution. And this isn't to say that bonobos of all genders are inherently violent either. But these female coalitions have been so effective that they've virtually eliminated violent outbreaks in the bonobo population.
GIF from "Game of Thrones."
Another reason researchers think bonobo groups are less aggressive than their chimp cousins? Sex. Lots of it.
Researchers have observed bonobos engaging in all kinds of sexual acts — not just heterosexual intercourse. They're down with everything from same-sex sex to masturbation to oral sex to group sex and also, uhhh, rubbing each others' genitals as a form of casual greeting when a new group comes into the area.
We humans might be inclined to call that "kinky." But to them, it's just a very, very friendly way of saying, "Hello, how are you today?"
Self-explanatory. Photo by Jaume F. Lalana/Flickr.
Of course, we can't know for certain whether bonobos are actually engaging in this behavior for pleasure.
But whatever the reason, it has helped to decrease the number of tense confrontations between individuals and groups. When everybody's gettin' it on on the reg — for pleasure, not for force — then the whole group is generally calmer and less violent.
Contrast this to the observed behavior of their chimpanzee cousins. They have plenty of sex, but theirs appears to be more about power and dominance than personal or shared pleasure. They're known to engage in rape, murder, and infanticide, and they are more likely to have violent interactions with newcomers.
(Again: sound familiar?)
Anthropological data analyzed by neuropsychologist James Prescott suggests societies that are more sexually open are also less likely to be violent. The key to understanding this correlation, however, is that it's the society as a whole that is more sexually open and not just a small percentage of individuals.
Photo by Ted/Flickr.
So, to bring it back to that guy approaching a group of women at the bar: is there anything we as humans can learn from bonobos?
It's pretty clear the combination of female coalitions of bonobos defending their own, and bonobos of all genders engaging in casual sex seems to have resulted in a less violent ape society. (In this case, let's assume that "sex" means "pleasure and fulfillment.)
While bonobos' behavior doesn't exactly translate to modern human society, it is an important reminder that if humans work to ensure that everyone has the opportunity to feel fulfilled and to feel pleasure on a regular basis, we may find ourselves living in a less violent, less aggressive society.
It's really as simple as that.





 Imposter syndrome is very common.
Imposter syndrome is very common.  Self-doubt is normal.
Self-doubt is normal.  Use imposter syndrome to assess your strengths and weaknesses.
Use imposter syndrome to assess your strengths and weaknesses. 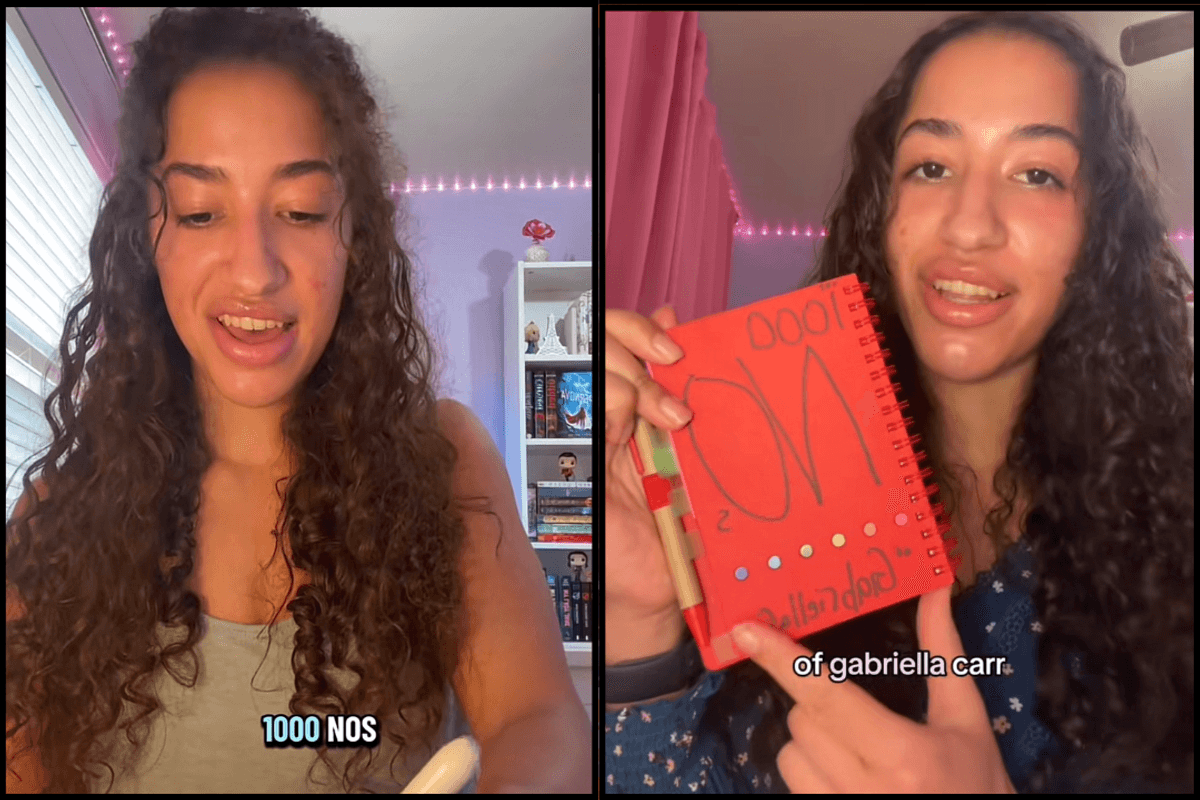
 This is where Gabrielle tracks her rejection journey.
This is where Gabrielle tracks her rejection journey. Social rejection feels just like physical pain to the brain.
Social rejection feels just like physical pain to the brain.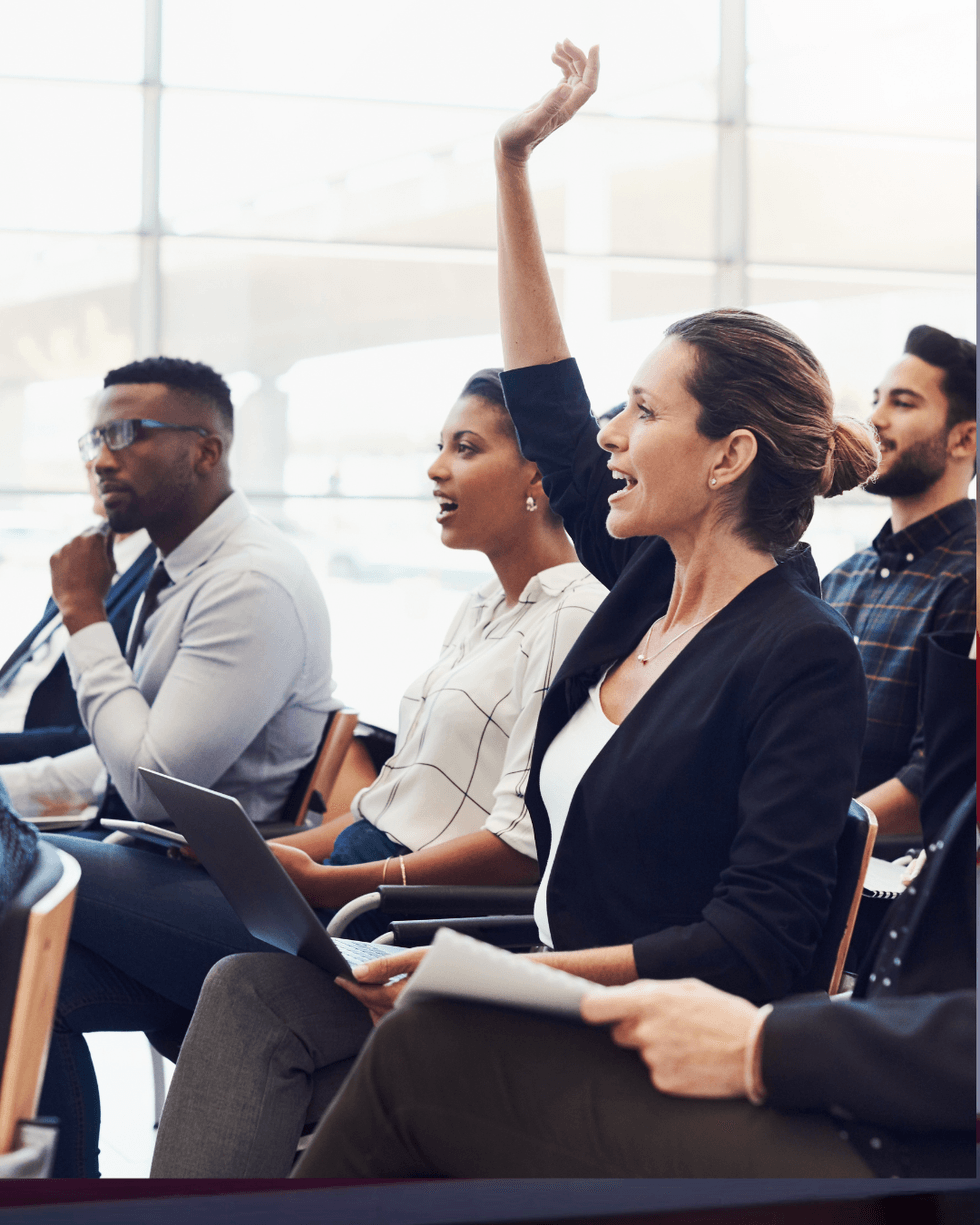 Asking questions can be a form of bravery.
Asking questions can be a form of bravery.
 a man sitting at a desk with his head on his arms Photo by
a man sitting at a desk with his head on his arms Photo by  Can a warm cup of tea help you sleep better? If you believe it, then yes. Photo by
Can a warm cup of tea help you sleep better? If you believe it, then yes. Photo by 
 Woman working, productively.
Woman working, productively.
 An exhausted mom and her baby.
An exhausted mom and her baby. A mom yawns while feeding her baby.
A mom yawns while feeding her baby.