Across the country, millions of people are in an uproar about racism in policing and law enforcement as a whole – however one of the more sinister and overlooked aspects of racism in policing is found in the very place where human bias is supposed to be notably absent.
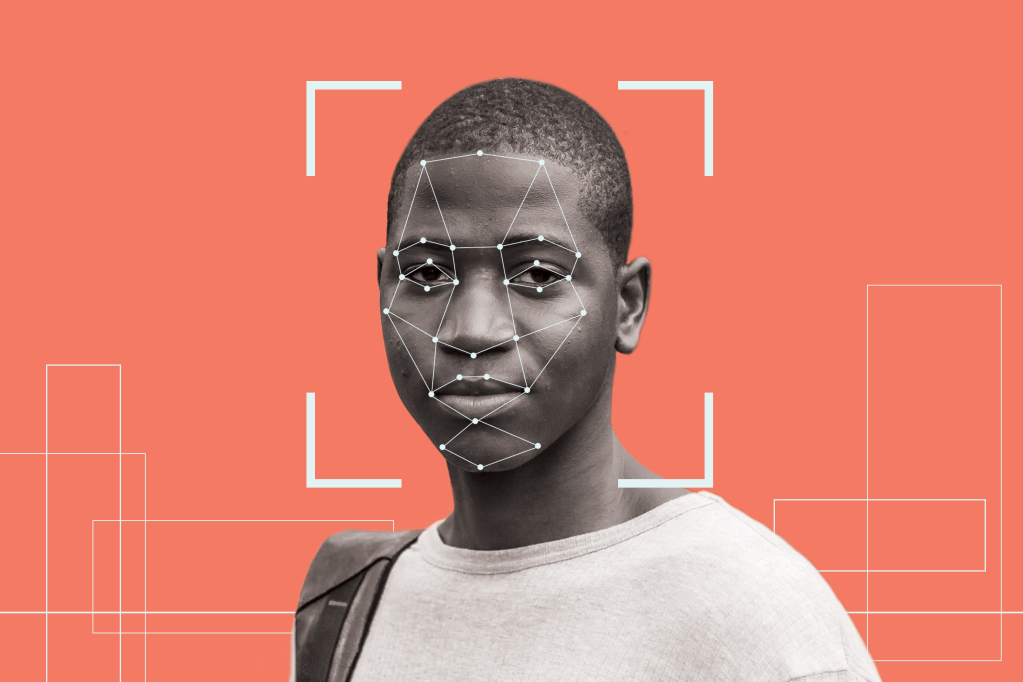
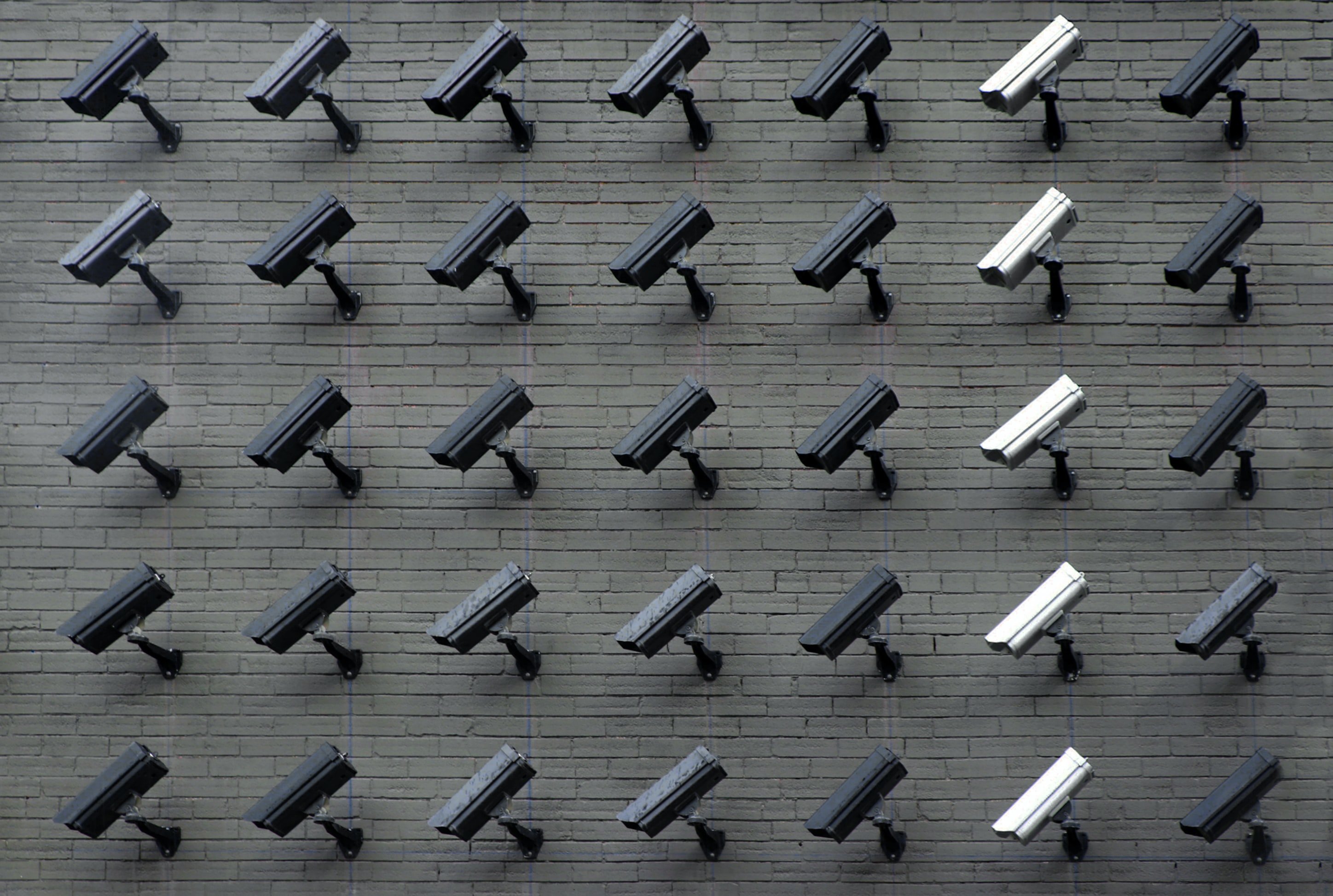
Facial recognition, the technology used for surveillance in many communities nationwide, has now become a major point of discussion for many who are deeply concerned that the inherent bias of its algorithm is not racially impartial.
Used for observation, tracking, and in many cases prosecution – facial recognition has been in use by many agencies for well over 20 years. There’s just one glaring error – it is mostly accurate when it is profiling white men.
Studies by M.I.T. and NIST have found that because of a lack of diversity in the databases the technology uses as a baseline, the systems are flawed from the start. Having a broken database to work from, the rates of misidentification are in danger of destroying countless lives due to a computing bias that doesn’t have a large enough reference pool from which to analyze data.
This month, Microsoft, Amazon, and IBM announced they would stop or pause their facial recognition offerings for law enforcement. However, many of the technology companies that law enforcement utilize aren’t as recognizable as Amazon. Some of them are lesser known outfits like Clearview AI, Cognitec, NEC, and Vigilant Solutions.

The fact that the protests have reignited the conversation regarding facial recognition is an interesting development, as protests themselves are a main source of data-gathering for the systems themselves. Protests, along with general collection points (social media, phone unlocking, security camera capture, image scraping).
Joy Buolamwini, a Ghanaian-American computer scientist and digital activist based at the MIT Media Lab, founded the Algorithmic Justice League to “create a world with more ethical and inclusive technology”. Her work over the past few years has helped to bring attention to the issue of the racial bias in the system.
Speaking to The Guardian, Buolamwini explains, “When I was a computer science undergraduate I was working on social robotics – the robots use computer vision to detect the humans they socialize with. I discovered I had a hard time being detected by the robot compared to lighter-skinned people. At the time I thought this was a one-off thing and that people would fix this. Later I was in Hong Kong for an entrepreneur event where I tried out another social robot and ran into similar problems. I asked about the code that they used and it turned out we’d used the same open-source code for face detection – this is where I started to get a sense that unconscious bias might feed into the technology that we create. But again I assumed people would fix this. So I was very surprised to come to the Media Lab about half a decade later as a graduate student, and run into the same problem. I found wearing a white mask worked better than using my actual face.
Buolamwini continues, “This is when I thought, you’ve known about this for some time, maybe it’s time to speak up … Within the facial recognition community you have benchmark data sets which are meant to show the performance of various algorithms so you can compare them. There is an assumption that if you do well on the benchmarks then you’re doing well overall. But we haven’t questioned the representativeness of the benchmarks, so if we do well on that benchmark we give ourselves a false notion of progress.”
Many have raised this concern in the past, however it has taken a wave of demonstrations nationally to bring the issue back into conversation for tech companies reexamining their relationships with how they build and distribute products – especially as it relates to law enforcement.
Another early whistleblower concerning racial bias in AI was Calypso AI, a software company that “builds software products that solve complex AI risks for national security and highly-regulated industries”.
Speaking with Davey Gibian, Chief Business Officer at Calypso AI, he revealed that Calypso had already been working on a comprehensive anti-bias tool for their systems over the past few months that is launching imminently.
Describing the overall issues related to facial recognition bias, Gibian explains, “There are two primary issues when it comes to racial profiling and police specific bias, one is data collection and data availability. The data available is based on things that have already happened – so police are looking for criminals by looking at data of who has already been booked. However, because police primarily target minority communities, that creates an inherent data bias model that predicts minorities will commit the most crime. The second primary issue is that even if you are aware of bias – simply stripping out race alone doesn’t help. You actually have to address the other elements related to the race data. For example, the geo-coordinates, the context of the capture, mugshots, the neighborhoods where people live, and other indicators from open source data, like spending habits, articles of clothing associated with minority and marginalized communities. All of these factors contribute to bias models, which leads police to use preexisting bias to designate criminals. So, because these are feedback loops in AI – it’s going to over-index racial bias.”
Put simply, he says, “Existing police data is biased because police are biased – models trained on that bias will be biased. Bias begets bias.”
When planning their approach to combat this deeply rooted issue in the system, Calypso decided to go for transparency instead of the murky steps many other outfits have opted for.
Speaking matter-of-factly, Gibian continues, “There aren’t enough tools to ensure that correlated indicators of race are stripped out of models. Our entire mission is to accelerate trusted AI into societal benefit – basically, we want to use AI for good. A massive barrier is the ethical and non-technical impact of AI and bias is one of the largest concerns we have. Because of this we’ve baked in an automated bias-detection tool into our software to ensure that any organization deploying a model can check for inherent bias, and can know not only if the data is biased, but how to mitigate against that. We believe that these bias scores should be shared with the public anytime AI is used in a public sector.”
As the Black Lives Matter protests continue and the movement moves from the streets to policy change, what remains to be seen is whether the large corporations that are publicly pledging support will follow the example of smaller companies like Calypso AI, Arthur AI, Fiddler, Modzy and others who are looking into bias in AI systems – and whether they will implement permanent solutions that make facial recognition a truly impartial, unbiased tool for the future.
It is worth noting that the Department of Defense recently released new guidance that explicitly requires that any AI used must not be biased.
Despite these positive movements towards a better technology overall, Gibian warns, “There’s a huge amount of benefit that AI can bring to make a more equitable society – but there are also pitfalls as a result of the original human bias. If we don’t avoid that – AI could accelerate a less equitable and more disenfranchised future.”