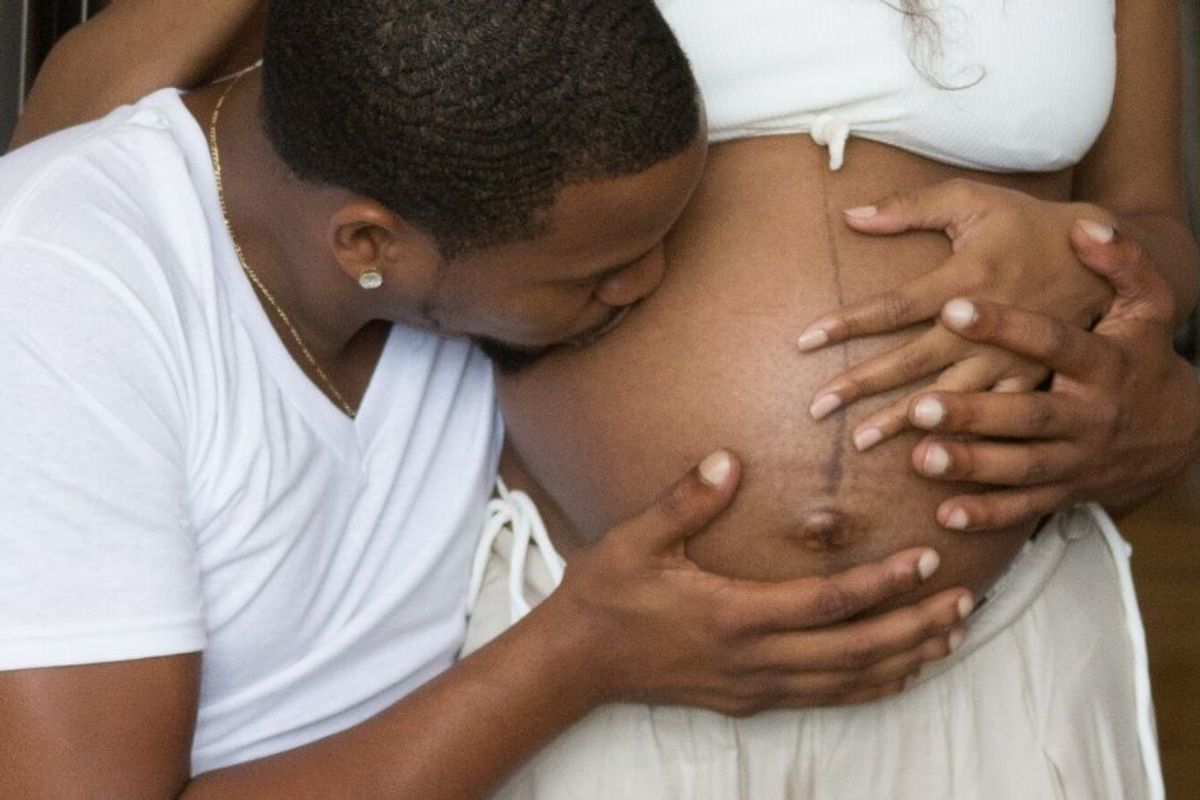
COVID-19 has made the overlooked Black maternal health crisis even more vital to address

"New normal." That's the phrase ushered in by the novel coronavirus and the devastating scourge of death from COVID-19. "New normal" is the only way we as a collective can explain our current way of life: Social distancing, face mask wearing, working and teaching from home, constantly conferencing over Zoom and scheduling telehealth appointments instead of physically seeing a doctor unless absolutely necessary.
However, not all characteristics of "normal" life are easily converted to digital expression. Specifically, giving birth.
Right now as the United States grapples with more than 100,000 COVID-19 deaths, a resurgence of the virus in a dozen states, and massive demonstrations over the most recent murders of unarmed Black men and women, there is one crisis that is not getting the same attention, a crisis that has been allowed to linger and fester in this country for decades: The glaring disparity in the maternal death rate and infant mortality rate for Black mothers and their newborns.
Pre-pandemic numbers show that Black women are three to four times more likely to die during childbirth than are white women, and Black infants are twice as likely to die at birth or immediately after than are white infants.
"The thought of losing a child that didn't even get a chance to live life is truly terrifying," says Rebecca Merriweather, who recently gave birth to a baby girl.
Merriweather wasn't aware of the statistics surrounding Black maternal health and infant mortality when she learned she was pregnant, but already had concerns of her own: "Preeclampsia and possible complications during labor and how to avoid them." Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and is 60% more common in Black women compared to white women.
"Oftentimes women take very good care of themselves," said Certified Nurse Midwife Marsha E. Jackson CNM, MSN, FACNM. "They're often knowledgeable, they're eating right, they're doing all the right things, and they start running into problems with their blood pressure creeping up and things like that and it stems back to our whole healthcare system and all of the hurts we as Black people have experienced for centuries."
To help stave off some of those complications, Dr. Chandra Adams, M.D. has had to find new ways to keep up with her patients health while also providing them the best care.
"We're doing telehealth visits, which works pretty well, but we had to work out getting blood pressure cuffs, encouraging people to buy them, that way if they aren't coming to the office we can keep up with their vital signs," Dr. Adams said.
In the midst of the pandemic some Black women have been taking their birth experience into their own hands, looking for alternatives to decrease their risks and exposure to the coronavirus and any complications that could impose on their pregnancy, labor, and delivery. Those alternatives include midwifery care.
"More Black women go to the hospital to have their babies, but I think with this pandemic we have had an increase in women seeking our services," Jackson said. Jackson is the owner, co-founder, and director of BirthCare & Women's Health, Ltd. based in Alexandria, Virginia, a midwifery practice that caters to clients who have births in their homes or in the BirthCare birth center.
Dr. Adams, The Owner of Full Circle Jax in Jacksonville, Florida runs a private practice with doctors and midwives on staff. While she believes in the midwifery and birth center model, she cautions that it is not for everyone.
"I'm not opposed to out of hospital birth, but I don't think any decisions about birth should be made out of fear . . . You shouldn't run from a hospital because of a perceived danger without understanding what the risks are of delivering outside of the hospital."
Tecoya Harris, currently pregnant with her first child, admits to having mixed feelings about giving birth.
"I feel anxious about delivery due to the fact that I can't anticipate how it will feel," Harris said. "At the same time, my faith is high so I have to trust that God has brought me to this moment because I am ready. Having resources, a strong partner, and a doula also helps bring down some of those anxieties."
Dr. Adams strongly advocates for her moms to have a doula, and also encourages pregnant women to use their voice to advocate for themselves.
"I've been hearing women saying [about health problems] 'I've never brought it up again because I was afraid of what a doctor would say to me,' and so they just stopped talking about their problem. Don't stop talking about your problem! Go find somebody who's going to listen to you, and treat you like someone who respects you, and will find out what's wrong. That's our job. That's literally our job!"
While that may be the job, history shows the healthcare industry has a negative track record when it comes to listening and believing Black women when they say something is wrong.
"The system has done a terrible job of listening to Black women," Dr. Adams said.
Tennis superstar Serena Williams and Olympic-gold medal winner Allyson Felix have both been vocal about their birth experiences, the complications they faced, and how they had to fight to be heard to get well. Yet their stories, though cautionary, still end with a positive outcome. The same cannot be said for Charles Johnson IV who lost his wife Kira in 2015 when she bled to death after the birth of their second child.
"They [were] under the care of a physician, and basically they just let her die," Jackson said, recounting hearing Charles Johnson IV tell his family's story during the 2020 virtual conference of the American College of Nurse Midwives.
Jackson and Dr. Adams believe some of the blame for the Black maternal health crisis lies with ever expanding physician practices.
"One of the biggest problems was when hospitals started to employ physicians," Dr. Adams said. "Physicians, before, when we started we'd hang our shingle and open solo practices. You had the personal care because in the similar fashion of the mom-and-pop shop you were responsible for the level of customer service, and that is how you kept your 'customers' coming back."
Now, many physicians are employed by hospitals or large doctor groups who are more focused on productivity. Dr. Adams said that has led to a decrease in time doctors have with their patients, which can lead to a decrease in care. Because of this, Dr. Adams and Marsha Jackson both say Black women need to educate themselves in every way.
"You have to do research in the beginning. You want to find out what kind of options are available," Jackson said.
"But you're not going to go to medical school," Dr. Adams added. "There's a certain amount that you can't just get from Googling or reading on your own . . . but if you gather enough information about people you'll find what you're looking for."
This advice applied before the pandemic hit. Now, the country's response to COVID-19 has made it all the more important for pregnant Black women to do their research, assess their risks, and have the hard conversations with their doctors.
On her birth experience, Merriweather said, "The labor and delivery ward where I had my child was very meticulous in keeping the section of the hospital cut off from the rest to protect the lives of the mother and baby from the virus. Each doctor and nurse was only allowed to work in that division of the hospital and had to be tested before being allowed in while wearing masks."
For Harris, hearing of positive birth experiences from friends and loved ones has helped to keep her spirits up, even in the face of the pandemic and Black maternal health crises.
"Although it is scary, seeing that other women have had healthy babies and deliveries give me hope," Harris said. "Our bodies were made to do this and we are already amazing moms with every decision we make during pregnancy."
Pandemic or no pandemic, Dr. Adams—who has been focused on the Black maternal health crisis for over a decade—says while this discussion isn't new, people are finally being heard and there is responsibility for doctors and Black women.
"What is unfortunate in the healthcare system is that Black women are not listened to, we are not treated with respect, and we are not believed when we present valid complaints," she said. "[But] what is actually physically killing us is hypertension and hemorrhage. We are not dying from people not being nice to us. We are disenfranchised and we're not receiving the appropriate amount of preventative care, and sometimes responsive care, because of that."
In early March, U.S. Representatives Lauren Underwood, Alma S. Adams, and Senator Kamala Harris introduced the Black Maternal Health Momnibus Act of 2020. The legislation is a package of nine individual bills aimed at "comprehensively addressing every dimension of the Black maternal health crisis." However, the package has received little exposure due to COVID. Once again, Black women, mothers, and their children are left to fend for themselves at a time when Black people are twice as likely to die from COVID than their white peers.
With the future passability of the Black Maternal Health Momnibus Act unknown, and the expected resurgence of COVID-19 in the fall (or until there is a vaccine) the onus remains on Black women to educate and advocate for themselves and their unborn children, and perhaps to seek a collaborative model of care where available.
"Cooperative care between midwives and physicians is essential," Dr. Adams said. "You have to have a midlevel to understand what is normal. [Someone] who has been trained enough to see enough to know what is abnormal and to appropriately refer to someone to handle when something is abnormal."
- It's Black Breastfeeding Week. Wondering why? One gut-punching ... ›
- Black teens experience racial discrimination five times a day on ... ›
- Public health experts share open letter defending anti-racism ... ›
- A Black woman came out of surgery with more braids than before. Here's why that matters. - Upworthy ›
- People are sharing the lessons of COVID-19 ›
- People are sharing the lessons of COVID-19 - Upworthy ›
- Moms say they'd choose their life over their child's in birth - Upworthy ›
- People help support grandmother raising 12 grandchildren - Upworthy ›
- OB-GYN breaks down shoulder dystocia after tragedy in Atlanta - Upworthy ›
- Death doula shares the big lesson she's learned form the dying - Upworthy ›

 A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
 An office kitchen.via
An office kitchen.via  An angry man eating spaghetti.via
An angry man eating spaghetti.via 



An Irish woman went to the doctor for a routine eye exam. She left with bright neon green eyes.
It's not easy seeing green.
Did she get superpowers?
Going to the eye doctor can be a hassle and a pain. It's not just the routine issues and inconveniences that come along when making a doctor appointment, but sometimes the various devices being used to check your eyes' health feel invasive and uncomfortable. But at least at the end of the appointment, most of us don't look like we're turning into The Incredible Hulk. That wasn't the case for one Irish woman.
Photographer Margerita B. Wargola was just going in for a routine eye exam at the hospital but ended up leaving with her eyes a shocking, bright neon green.
At the doctor's office, the nurse practitioner was prepping Wargola for a test with a machine that Wargola had experienced before. Before the test started, Wargola presumed the nurse had dropped some saline into her eyes, as they were feeling dry. After she blinked, everything went yellow.
Wargola and the nurse initially panicked. Neither knew what was going on as Wargola suddenly had yellow vision and radioactive-looking green eyes. After the initial shock, both realized the issue: the nurse forgot to ask Wargola to remove her contact lenses before putting contrast drops in her eyes for the exam. Wargola and the nurse quickly removed the lenses from her eyes and washed them thoroughly with saline. Fortunately, Wargola's eyes were unharmed. Unfortunately, her contacts were permanently stained and she didn't bring a spare pair.
- YouTube youtube.com
Since she has poor vision, Wargola was forced to drive herself home after the eye exam wearing the neon-green contact lenses that make her look like a member of the Green Lantern Corps. She couldn't help but laugh at her predicament and recorded a video explaining it all on social media. Since then, her video has sparked a couple Reddit threads and collected a bunch of comments on Instagram:
“But the REAL question is: do you now have X-Ray vision?”
“You can just say you're a superhero.”
“I would make a few stops on the way home just to freak some people out!”
“I would have lived it up! Grab a coffee, do grocery shopping, walk around a shopping center.”
“This one would pair well with that girl who ate something with turmeric with her invisalign on and walked around Paris smiling at people with seemingly BRIGHT YELLOW TEETH.”
“I would save those for fancy special occasions! WOW!”
“Every time I'd stop I'd turn slowly and stare at the person in the car next to me.”
“Keep them. Tell people what to do. They’ll do your bidding.”
In a follow-up Instagram video, Wargola showed her followers that she was safe at home with normal eyes, showing that the damaged contact lenses were so stained that they turned the saline solution in her contacts case into a bright Gatorade yellow. She wasn't mad at the nurse and, in fact, plans on keeping the lenses to wear on St. Patrick's Day or some other special occasion.
While no harm was done and a good laugh was had, it's still best for doctors, nurses, and patients alike to double-check and ask or tell if contact lenses are being worn before each eye test. If not, there might be more than ultra-green eyes to worry about.