'13th' wasn't around to watch in your history class. 13 reasons to watch it now.
If you see only one Oscar-nominated film this year, make it "13th."
Directed by Ava DuVernay, the stirring documentary explores America's long history of overpolicing and imprisoning black and brown people since the passing of the 13th Amendment. DuVernay sat down with scholars, educators, elected leaders, authors, and activists to tell this troubling but necessary story.
DuVernay (left) interviews scholar and activist Angela Davis for "13th." Image via Netflix.
While these issues are difficult, we need to talk about them and, better yet, do something about them. "13th" truly couldn't have come at a better time.
Here are 13 lessons everyone should learn from this from powerful must-see film.
1. The 13th Amendment had so much promise ... almost.
Section 1 of the 13th Amendment reads:
"Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction."
The clause, "except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted," was included so farmers and landowners could essentially continue a form of slavery to support their businesses — so long as the black men and women were deemed criminals. There's no such thing as a throwaway clause in the Constitution. This is an intentional legal loophole.
A political cartoon from 1865 featuring President Lincoln and an amended U.S. constitution. Photo by Hulton Archive/Getty Images.
2. The legal loophole in the 13th Amendment led to mass arrests and incarceration during the late 19th century.
It was the United States' first prison boom.
Black people were arrested en masse for petty crimes, like loitering or vagrancy, and incarcerated. Once labeled criminals, landowners and farmers could "lease" convicts from the state in exchange for full control of their lives.
These convicts were leased to harvest timber. Photo circa 1915, via World Digital Library/State Library and Archives of Florida.
3. While black men filled prisons, popular culture stoked fears.
Black men were portrayed in films as menacing, evil, and in relentless pursuit of white women.
In the 1915 film, "Birth of a Nation," which is essentially three hours of racist propaganda masking as a historical film, a white woman throws herself off a rocky cliff to save herself from being assaulted by a black man. Critics raved, drowning out mounting protests.
As a result of the popular film, membership in the Ku Klux Klan boomed.
Still image from "Birth of a Nation," (1915). Image via "Birth of a Nation"/Wikimedia Commons.
4. As the KKK grew, black people were terrorized and murdered.
Lynchings were used to reinforce white supremacy while traumatizing and terrorizing black people. There was a disgusting entertainment aspect to it, as mobs of white people — including elected officials and community leaders — gathered to watch victims get beaten, shot, and tortured. Picture postcards were made of the swinging, mutilated bodies.
More than 4,000 lynchings occurred between 1877 and 1950 across Texas and the American South.
A large crowd watches the lynching of 18-year-old Jesse Washington in Waco, Texas. Photo via Library of Congress.
5. The murder of Emmett Till kickstarted the Civil Rights movement.
14-year-old Emmett Till was brutally beaten and murdered by a group of white men for allegedly whistling at and flirting with a white woman in 1955. (The woman recently admitted she fabricated at least part of her testimony.) Photos from his open casket funeral and the face of Till's weeping mother sent shockwaves around the country, galvanizing black people and their allies in the fight for equality.
6. But then the War on Drugs started an unrelenting wave of mass incarceration.
Crime started to increase in the early 1960s, and many in power quickly blamed the uptick on the end of segregation. Before long, the word "crime" was a stand-in for the word "race."
Nixon appealed to southern Democrats with thinly-veiled racism and promises to clean up the streets. His rhetorical "War on Drugs" became very real in the 1980s under President Reagan, who threw money, resources, and the full weight of the executive branch behind the issue. A wide swath of an entire generation was essentially removed from the narrative.
President Ronald Reagan and his wife Nancy wave to supporters in November 1984. Photo by Don Rypka/AFP/Getty Images.
7. The numbers are astonishing. Full stop.
In 1970, there were 196,429 sentenced prisoners in state and federal prisons. In 1980, there were 329,821 people in state and federal prisons, and by 1990, that number more than doubled to 771,243.
Today, the American criminal justice system holds 2.3 million people. This is not normal. It is not OK.
Data from the Bureau of Justice Statistics; graph via Smallman12q/Wikimedia Commons.
8. Republicans are not solely to blame for this crisis. President Clinton did his part too.
In the wake of President Reagan and President George H.W. Bush, appearing "soft on crime" wasn't an option for President Bill Clinton. In 1994, he signed the Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act. It expanded the list of death penalty eligible offenses and included a "three strikes" provision, which meant mandatory life sentences for people convicted of their third felony. It also funded new prisons and provided the budget for 100,000 police officers.
President Bill Clinton. Photo by Paul Richards/AFP/Getty Images.
9. Sadly, there's a lot of money to be made off mass incarceration.
Private correctional facilities made a reported $629 million in profits in 2014, and that's just scratching the surface. From the corporations building and maintaining prison facilities, to the food vendors, health care providers, and equipment and textile manufacturers who keep them running, many companies have a lot to gain from maintaining the status quo.
An inmate stands with handcuffs in San Quentin State Prison. Photo by Justin Sullivan/Getty Images.
10. As mass incarceration starts to get a bad rap, the winds are shifting — and not necessarily for the better.
As mass incarceration and America's prison problem take center stage, legislators and businesses are looking for new ways to redefine the narrative while still making money. What does that look like? For starters, monetizing bail, probation, parole, and house arrest.
Photo by iStock.
11. We can't forget the people and families caught in the struggle.
In 2010, 16-year-old Kalief Browder was arrested for a robbery he insisted he did not commit. Browder was thrown into an adult correctional facility where he would spend nearly three years awaiting trial and almost two years in solitary confinement. In 2013, the district attorney dismissed the case against Browder, and he went home a free — but forever changed — young man.
After many attempts, Browder died by suicide in May 2015.
Browder's story is far too common. Many poor people, especially poor people of color, are locked up for years either awaiting trial or because they cannot afford bail.
ABC News' Juju Chang, Venida Browder, mother of Kalief Browder, and civil rights attorney Paul V. Prestia discuss Kalief Browder's life and death. Photo by Slaven Vlasic/Getty Images.
12. American prisons are intended to punish, but former felons continue to suffer after they have served their time.
Former felons are stripped of voting rights, have difficulty securing employment, applying for aid, and finding housing.
"Ban the box" campaigns that seek to end asking about felony convictions on job and aid applications are popping up across the country, and for many, these initiatives can't come soon enough.
Outreach materials at a press conference for a Ban the Box Petition Delivery to The White House in 2015. Photo by Larry French/Getty Images for ColorOfChange.org.
13. As President Trump settles into office, many are worried about his next moves — and rightfully so.
He repeatedly refers to parts of Chicago as lawless, dangerous, and worse than parts of the war-torn Middle East. He's threatened the city with federal intervention to get the "carnage" under control. His repeated calls to arrest and deport undocumented immigrants tend to include gross mischaracterizations of immigrants as gang members, rapists, or drug dealers.
His "law and order" catchphrase is the same dog whistle Nixon used to kickstart the War on Drugs. His comments about Chicago and other inner cities are stoking fears and playing to the imaginations of his base, much like the horrifying scenes in "Birth of a Nation."
Photo by Mario Tama/Getty Images.
These facts are alarming, but here's what you can do about it.
Use your privilege for good. Pass the mic to voices that may go unheard. Help others register to vote. Support Ban the Box initiatives and organizations that help people with criminal records land on their feet.
Ask to see the numbers. Plenty of police data is publicly available. Check out the numbers in your community. Look at the demographics of people being stopped, arrested, or convicted. Numbers don't lie. Hold your leaders accountable and make them answer for racial disparities.
Stay active in schools. Overpolicing and the criminalization of black people doesn't begin and end with police officers. Black children are nearly four times as likely to be suspended as white children. Ask tough questions of your child's teachers and administrators. Attend school board meetings.
Photo by iStock.
This is no ordinary crisis and it will require extraordinary solutions.
Watch the film, do your part. Let's get to work.





 a man sitting at a desk with his head on his arms Photo by
a man sitting at a desk with his head on his arms Photo by  Can a warm cup of tea help you sleep better? If you believe it, then yes. Photo by
Can a warm cup of tea help you sleep better? If you believe it, then yes. Photo by 
 A woman is getting angry at her coworker.via
A woman is getting angry at her coworker.via  A man with tape over his mouth.via
A man with tape over his mouth.via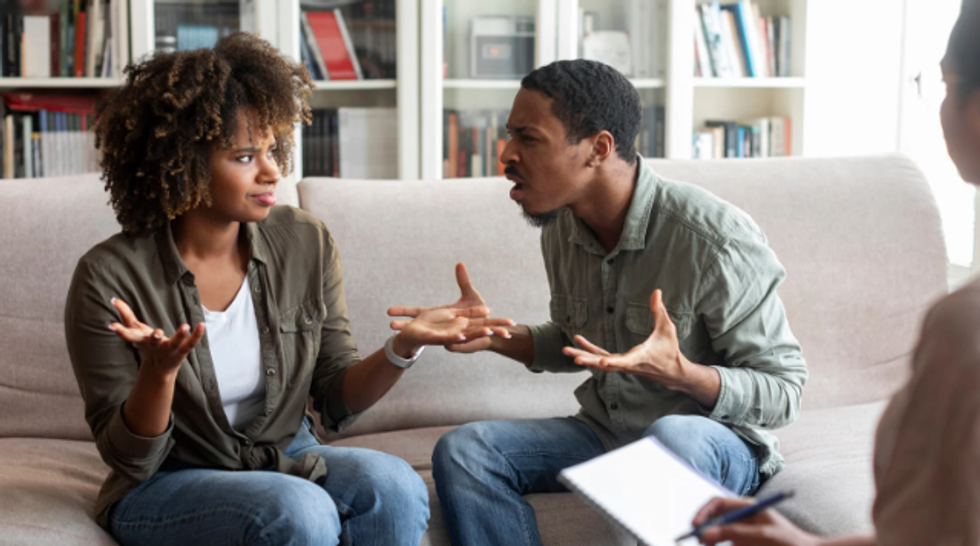  A husband is angry with his wife. via
A husband is angry with his wife. via 
 Three women sit on a blanket in the park.
Three women sit on a blanket in the park. 
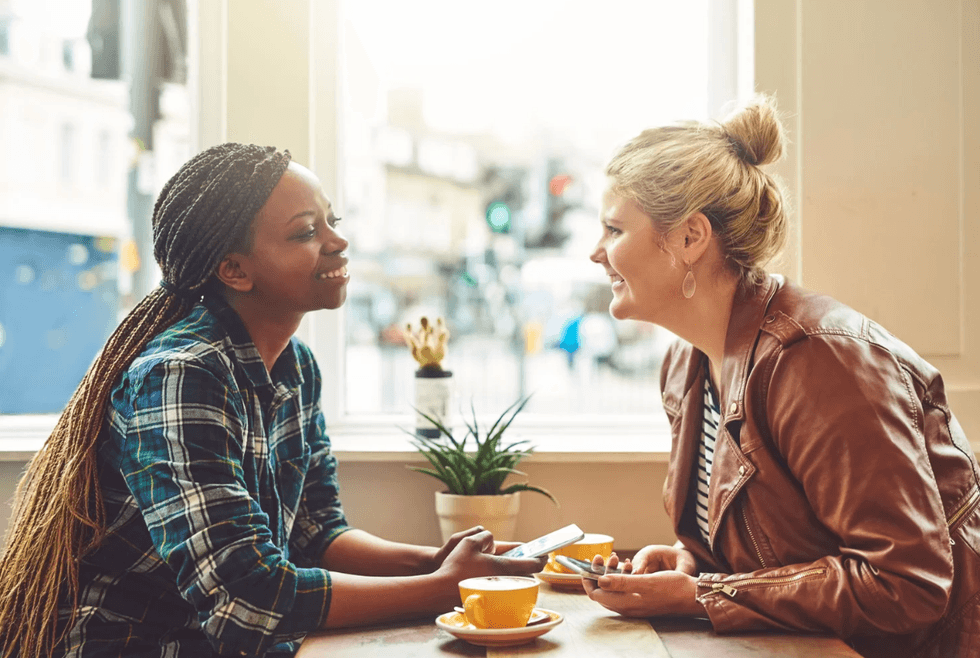 Two women engaging in a pleasant conversation inside a coffee shop
Two women engaging in a pleasant conversation inside a coffee shop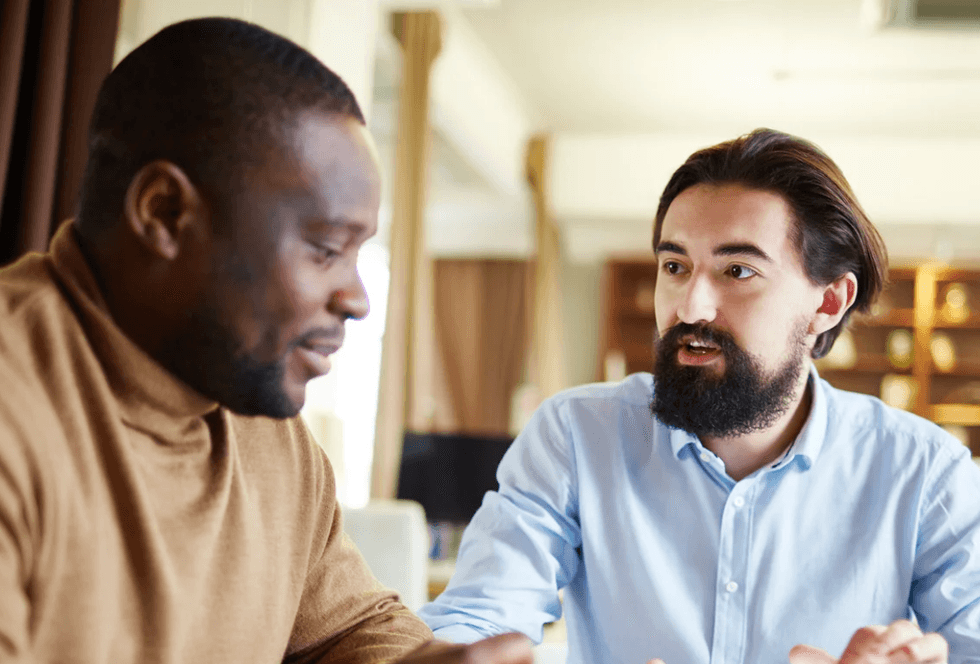 Two men engaging in a peaceful disagreement.
Two men engaging in a peaceful disagreement.
Resurfaced video of French skier's groin incident has people giving the announcer a gold medal
"The boys took a beating on that one."
Downhill skiing is a sport rife with injuries, but not usually this kind.
A good commentator can make all the difference when watching sports, even when an event goes smoothly. But it's when something goes wrong that great announcers rise to the top. There's no better example of a great announcer in a surprise moment than when French skier Yannick Bertrand took a gate to the groin in a 2007 super-G race.
Competitive skiers fly down runs at incredible speeds, often exceeding 60 mph. Hitting something hard at that speed would definitely hurt, but hitting something hard with a particularly sensitive part of your body would be excruciating. So when Bertrand slammed right into a gate family-jewels-first, his high-pitched scream was unsurprising. What was surprising was the perfect commentary that immediately followed.
This is a clip you really just have to see and hear to fully appreciate:
- YouTube youtu.be
It's unclear who the announcer is, even after multiple Google inquiries, which is unfortunate because that gentleman deserves a medal. The commentary gets better with each repeated viewing, with highlights like:
"The gate the groin for Yannick Bertrand, and you could hear it. And if you're a man, you could feel it."
"Oh, the Frenchman. Oh-ho, monsieurrrrrr."
"The boys took a beating on that one."
"That guy needs a hug."
"Those are the moments that change your life if you're a man, I tell you what."
"When you crash through a gate, when you do it at high rate of speed, it's gonna hurt and it's going to leave a mark in most cases. And in this particular case, not the area where you want to leave a mark."
Imagine watching a man take a hit to the privates at 60 mph and having to make impromptu commentary straddling the line between professionalism and acknowledging the universal reality of what just happened. There are certain things you can't say on network television that you might feel compelled to say. There's a visceral element to this scenario that could easily be taken too far in the commentary, and the inherent humor element could be seen as insensitive and offensive if not handled just right.
The announcer nailed it. 10/10. No notes.
The clip frequently resurfaces during the Winter Olympic Games, though the incident didn't happen during an Olympic event. Yannick Bertrand was competing at the FIS World Cup super-G race in Kvitfjell, Norway in 2007, when the unfortunate accident occurred. Bertrand had competed at the Turin Olympics the year before, however, coming in 24th in the downhill and super-G events.
As painful as the gate to the groin clearly as, Bertrand did not appear to suffer any damage that kept him from the sport. In fact, he continued competing in international downhill and super-G races until 2014.
According to a 2018 study, Alpine skiing is a notoriously dangerous sport with a reported injury rate of 36.7 per 100 World Cup athletes per season. Of course, it's the knees and not the coin purse that are the most common casualty of ski racing, which we saw clearly in U.S. skier Lindsey Vonn's harrowing experiences at the 2026 Olympics. Vonn was competing with a torn ACL and ended up being helicoptered off of the mountain after an ugly crash that did additional damage to her legs, requiring multiple surgeries (though what caused the crash was reportedly unrelated to her ACL tear). Still, she says she has no regrets.
As Bertrand's return to the slopes shows, the risk of injury doesn't stop those who live for the thrill of victory, even when the agony of defeat hits them right in the rocks.