You're probably already a manatee fan. If not, here are 22 reasons to become one.
Manatees are awesome.
Roly-poly pacifists, tropical underwater munch-machines, they look like something a kid would make out of Play-Doh. But there's a lot of cool stuff about them you might not know.
In the name of sea cows everywhere, here are 22 interesting facts about manatees.
1. There are three different species of manatee (and one dugong).
Image from psyberartist/Flickr.
There's the Amazonian manatee, the West Indian manatee, and the West African manatee. No points for guessing where each of them lives. They also have a single cousin, the dugong, which lives in the Indian and western Pacific oceans.
2. Their closest living relatives are elephants and hyraxes.
What a weird family. Images from U.S. Geological Survey, Oliver Wright, and Josski/Wikimedia Commons.
They split off over 50 million years ago though, so don't expect to see them all at the same family reunion.
3. Manatees love the tropics.
Image from pelican/Wikimedia Commons.
Though they look chubby, they don't have all that much fat, so they prefer swimming in warm water.
4. They've got big bellies...
Image from NASA/Wikimedia Commons.
Manatees are plant eaters, like horses, so their stomach and guts have evolved to digest tough plant matter. Up to 20% of their weight can come from their bellies alone.
5. ...and even bigger appetites.
Image from Eric Kilby/Flickr.
Open the buffet! Manatees chow down on about 10% of their body weight a day. That means a 1,000-pound manatee will eat about 100 pounds of plants every day!
6. They never have to visit a dentist, either.
OK, technically this one is a dugong. You got me. Image from Julien Willem/Wikimedia Commons.
Manatees replace their teeth throughout their lives. Their diet is pretty tough on their teeth (partly because they end up chewing on a lot of sand as they eat), so as their molars get worn down, new ones grow up behind them. It's like a conveyor belt of teeth.
7. Their pregnancies last a pretty long time.
This lil' baby is getting a drink. Manatee teats are located behind their arms. Image from USFWS/Wikimedia Commons.
A manatee is pregnant for about 12 months — that's not quite as long as the 22-month pregnancy of their distant relatives, the elephants, but it's longer than a human's nine! Their babies usually stick around for a year or two after the mom gives birth.
8. Once upon a time, people may have thought manatees were mermaids.
Image from U.S. Geological Survey/Wikimedia Commons.
Might be hard to believe, but it's true! Even people on Columbus' journey to North America got confused:
"On the previous day [Jan. 8, 1493], when the Admiral went to the Rio del Oro [in Haiti], he said he quite distinctly saw three mermaids, which rose well out of the sea; but they are not so beautiful as they are said to be, for their faces had some masculine traits."
— "Voyages of Columbus," page 218
The name for their scientific order — Sirenia — even comes from the sirens of Greek mythology who are sometimes described as mermaids.
9. They may also be named after breasts. Yes, breasts.
Image from U.S. Fish and Wildlife Endangered Animals/Flickr.
When Columbus got to the Caribbean, he found the Taíno people already living there. Their word for breast – manatí – is probably the origin of the animal's English name.
10. They're pretty slow...
Image from Jim Reid/Wikimedia Commons.
Manatees usually plod along at about 3-5 mph, although they can get up to 20 mph if they really try.
11. ...and they can get pretty old...
Snooty getting a birthday "cake" made of fruits and vegetables. Image from Netweave/Wikimedia Commons.
Snooty the manatee, who lives in the South Florida Museum's Parker Manatee Aquarium, is a venerable 67 years old.
12. ...but they're not dumb.
A curious young manatee inspects a kayak. Image from mwanner/Wikimedia Commons.
Manatees have relatively small brains for their bodies, but some scientists actually think it's the other way around — they have huge bodies for their brains! And some research has shown that they might be as good at experimental tasks as dolphins. They just look kind of dumb because they're a lot slower.
13. They used to have huge cousins.
Image from Biodiversity Heritage Library/Wikimedia Commons.
In the 18th century, explorers scouting around Alaska found 30-foot-long dugongs living in the Arctic waters. Known as Steller's sea cows, they ate the kelp that grew in the icy water.
Unfortunately, they went extinct soon afterward. Sailors discovered that, in addition to being huge, they were also delicious. And it wasn't just Europeans — there's evidence that Native Americans hunted them too.
14. They have no natural predators.
Image from Tanjila Ahmed/Flickr.
No other wild animal eats them. Good for them!
15. But that doesn't mean they're not in danger.
Whut? Image from Hans Stieglitz/Wikimedia Commons.
Though manatees are awesome, their populations have historically been dropping.
16. Humans are their biggest threat.
This manatee survived a run-in with a motor boat but bears the scars of its encounter. Image from Robert K. Bond/Wikimedia Commons.
Habitat loss is a big problem for manatees, as are run-ins with human objects or vehicles. Manatees can get stuck in fishing gear or accidentally eat fishing line. Motor boats are especially problematic, as manatees are too slow to get out of the way of their sharp propeller blades.
17. That's why the U.S. government protects them.
The Crystal River National Wildlife Refuge is home to many manatees. Image from U.S. Fish and Wildlife Endangered Species/Flickr.
Three different laws help protect them: the Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972, the Endangered Species Act of 1973, and the Florida Manatee Sanctuary Act of 1978.
These laws make it illegal to kill or hurt a manatee in the United States.
18. Boating speed limits help too.
Image from Jim Reid/Wikimedia Commons.
Many waterways in manatee habitats now come with speed limits to give manatees time to get out of the way of propellers. People have also made manatee sanctuaries to make sure they have a home.
19. And there's good news: All those protections are starting to pay off.
Image from PublicDomainImages/Pixabay.
20. While there's still more work to be done, the number of manatees in the U.S. is starting to rise again.
Image from satemkemet/Flickr.
21. In fact, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service just proposed that the West Indian manatee should be moved to "Threatened" from "Endangered."
Image from NOAA's National Ocean Service/Flickr.
"The manatee's recovery is incredibly encouraging and a great testament to the conservation actions of many," Fish and Wildlife Service Southeast Regional Director Cindy Dohner said at a Miami Seaquarium event.
And don't worry – the manatees won't lose any of their protections.
22. They're a conservation success story!
Image from U.S. Fish and Wildlife Endangered Species/Flickr.
Now that's something to smile about!
They're living, breathing (and not to mention adorable) proof that we can make a difference for our friends in need.
Of course, it's not over yet. By spreading the word, we can help raise awareness about them, the other manatee species, and all the other animals who need our protection! Hopefully, all of them can continue their successful rebound — just like the West Indian manatee.
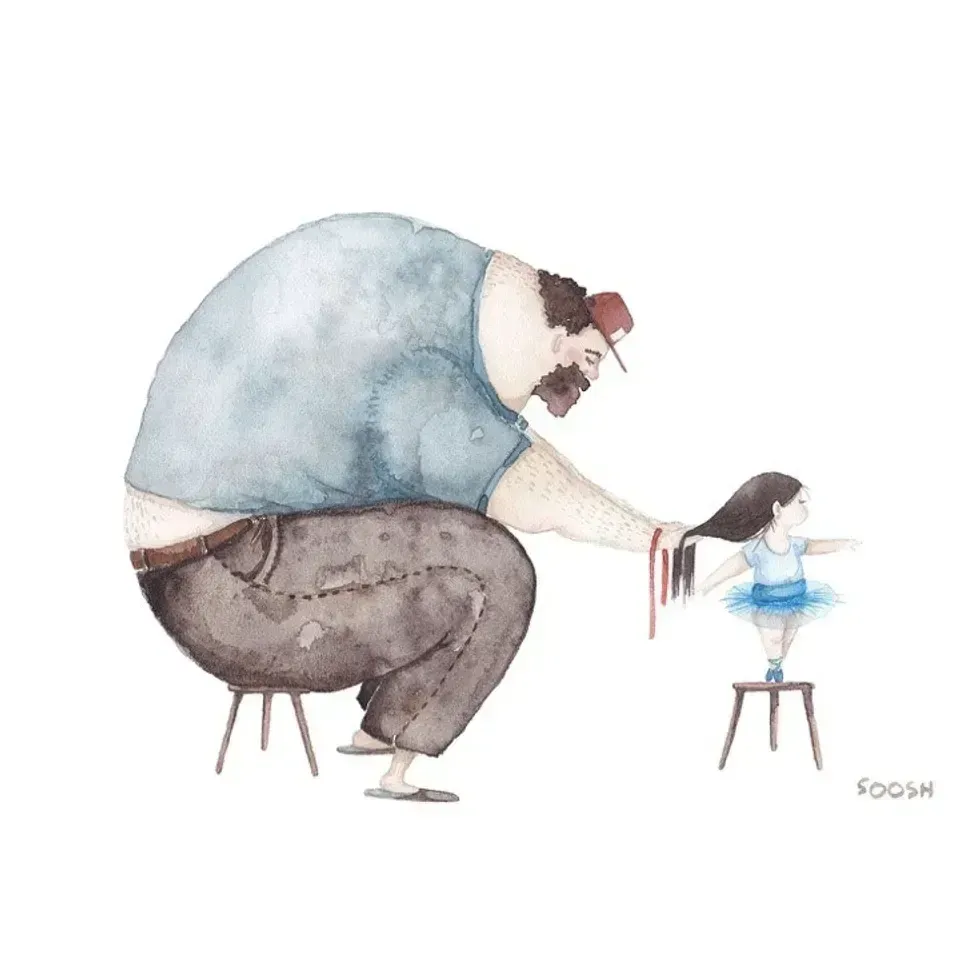




 A father does his daughter's hair
A father does his daughter's hair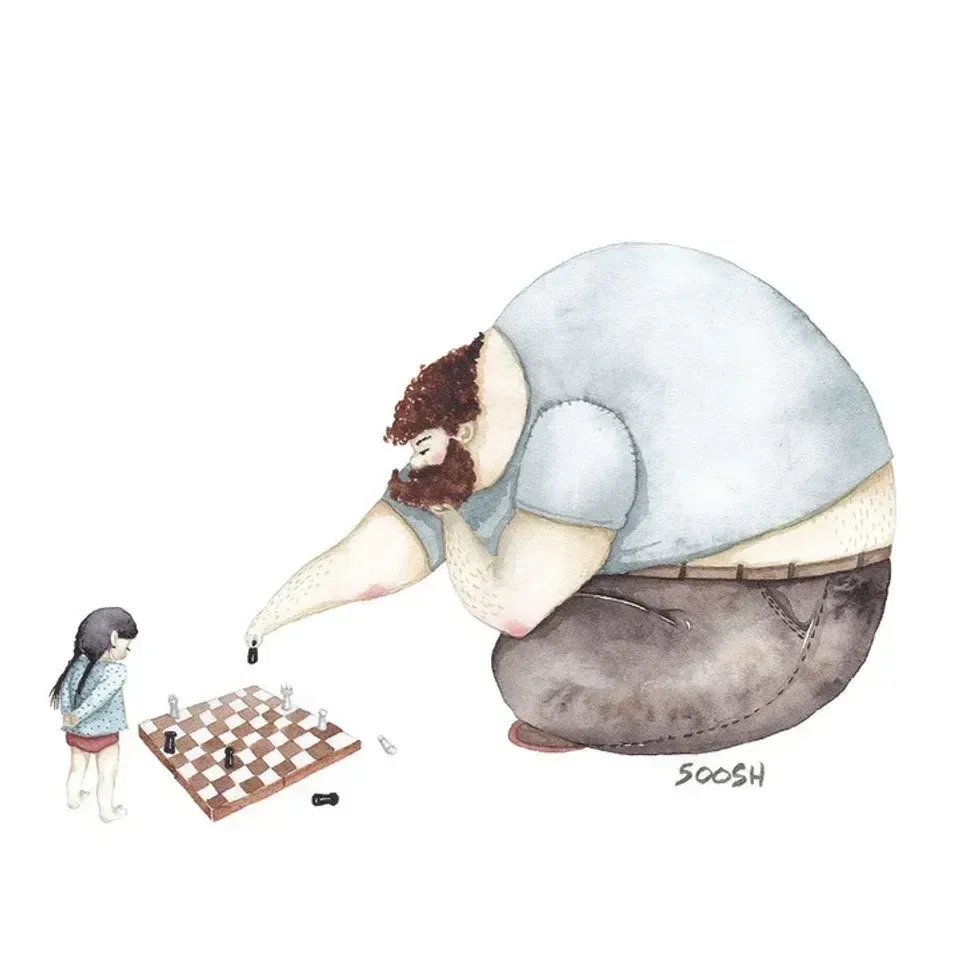 A father plays chess with his daughter
A father plays chess with his daughter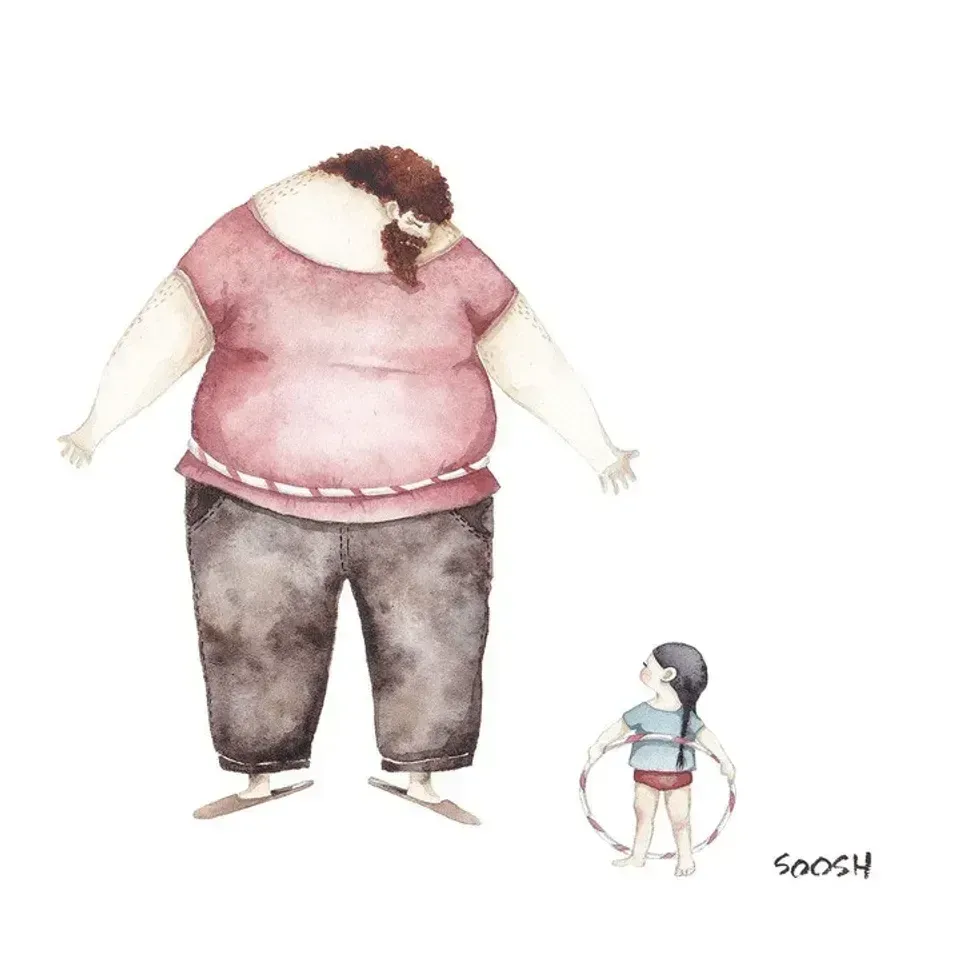 A dad hula hoops with his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad hula hoops with his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. A dad talks to his daughter while working at his deskAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad talks to his daughter while working at his deskAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. A dad performs a puppet show for his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad performs a puppet show for his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.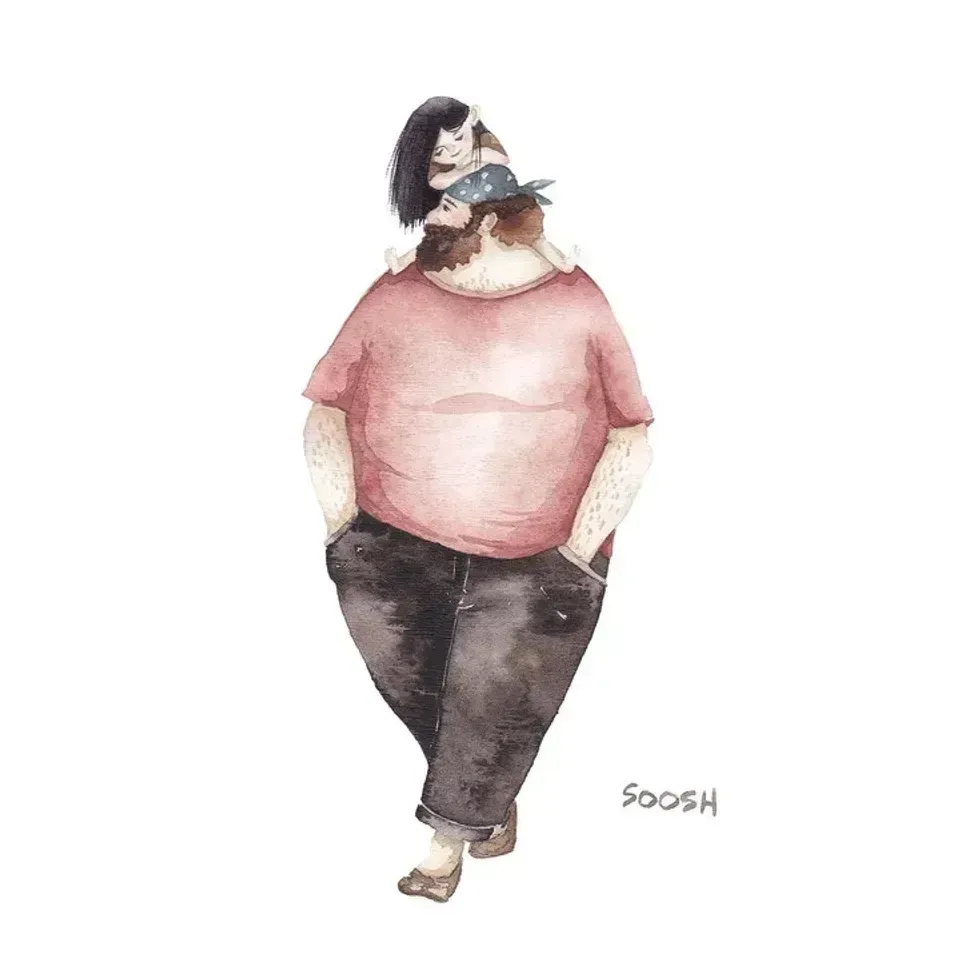 A dad walks with his daughter on his backAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad walks with his daughter on his backAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.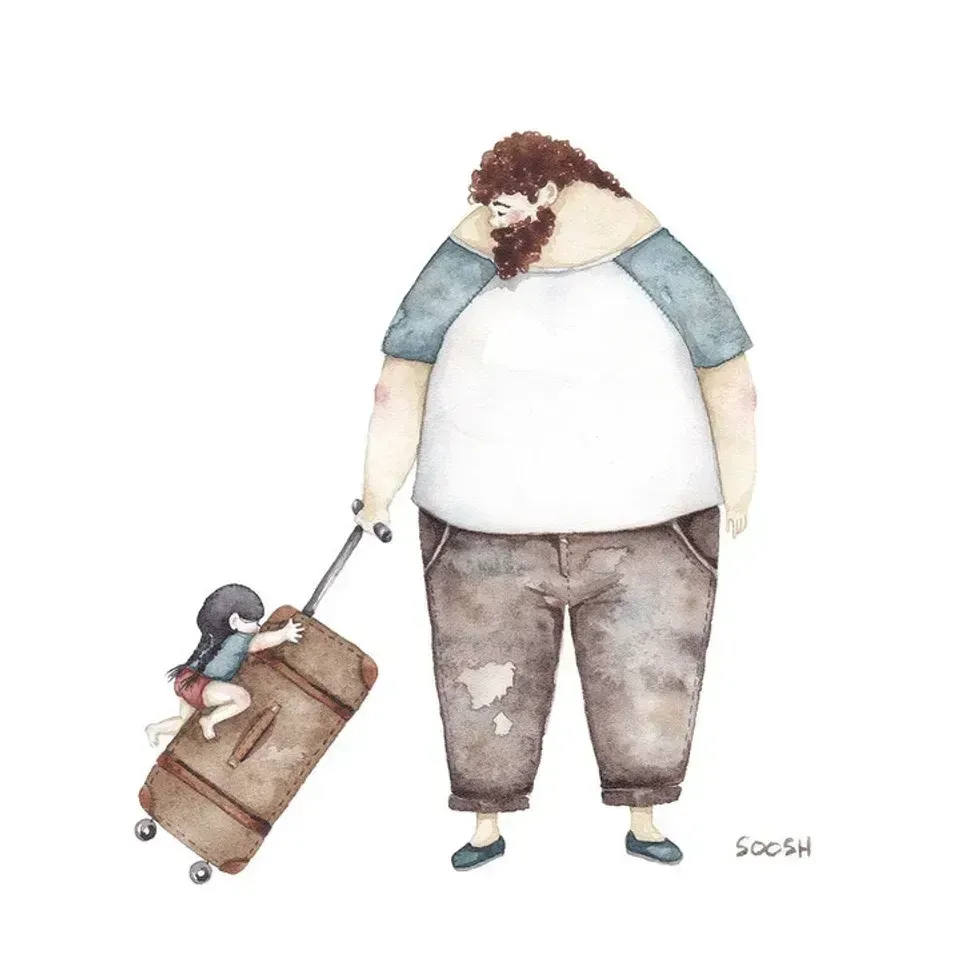 a dad carries a suitcase that his daughter holds onto
a dad carries a suitcase that his daughter holds onto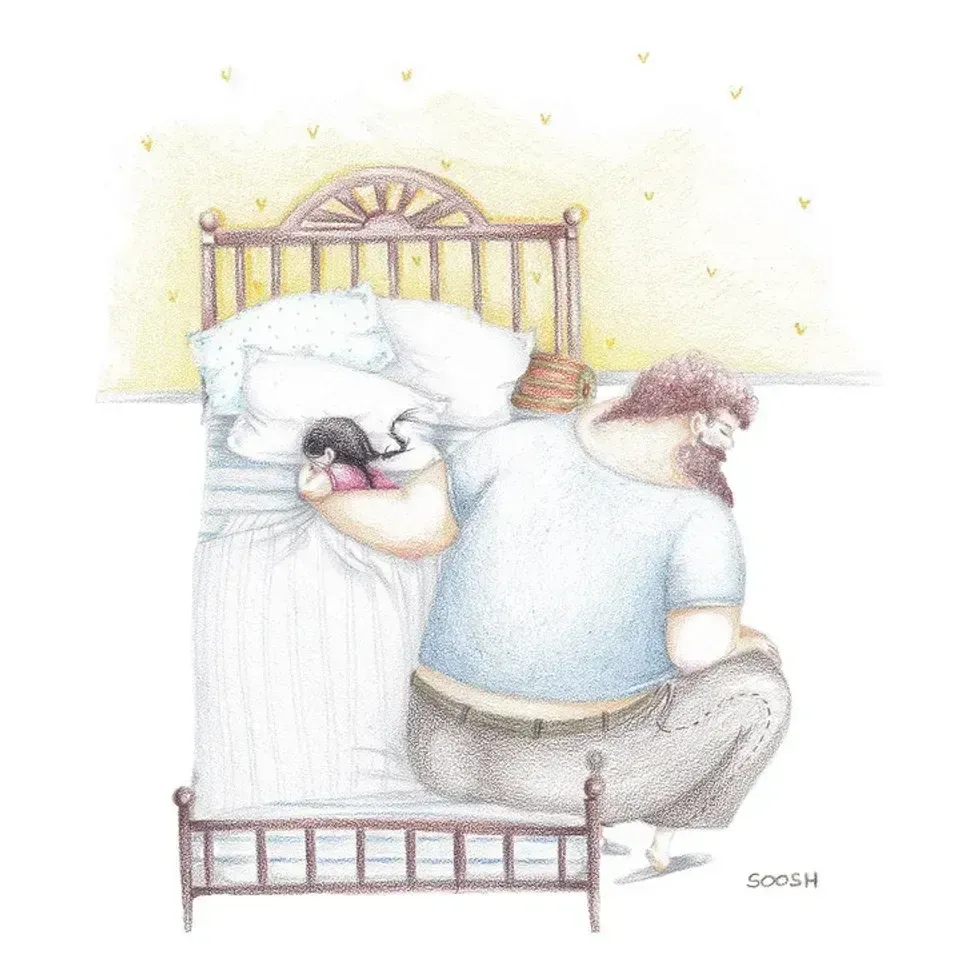 A dad holds his sleeping daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad holds his sleeping daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.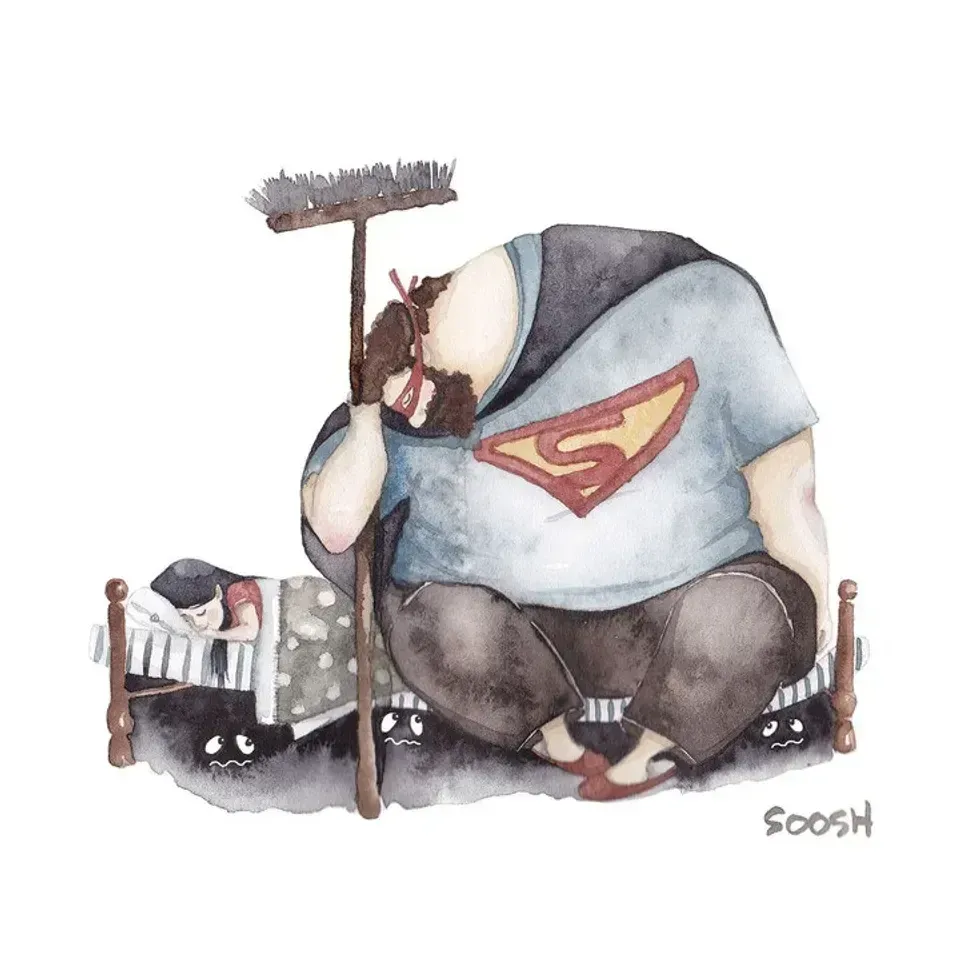 A superhero dad looks over his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A superhero dad looks over his daughterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.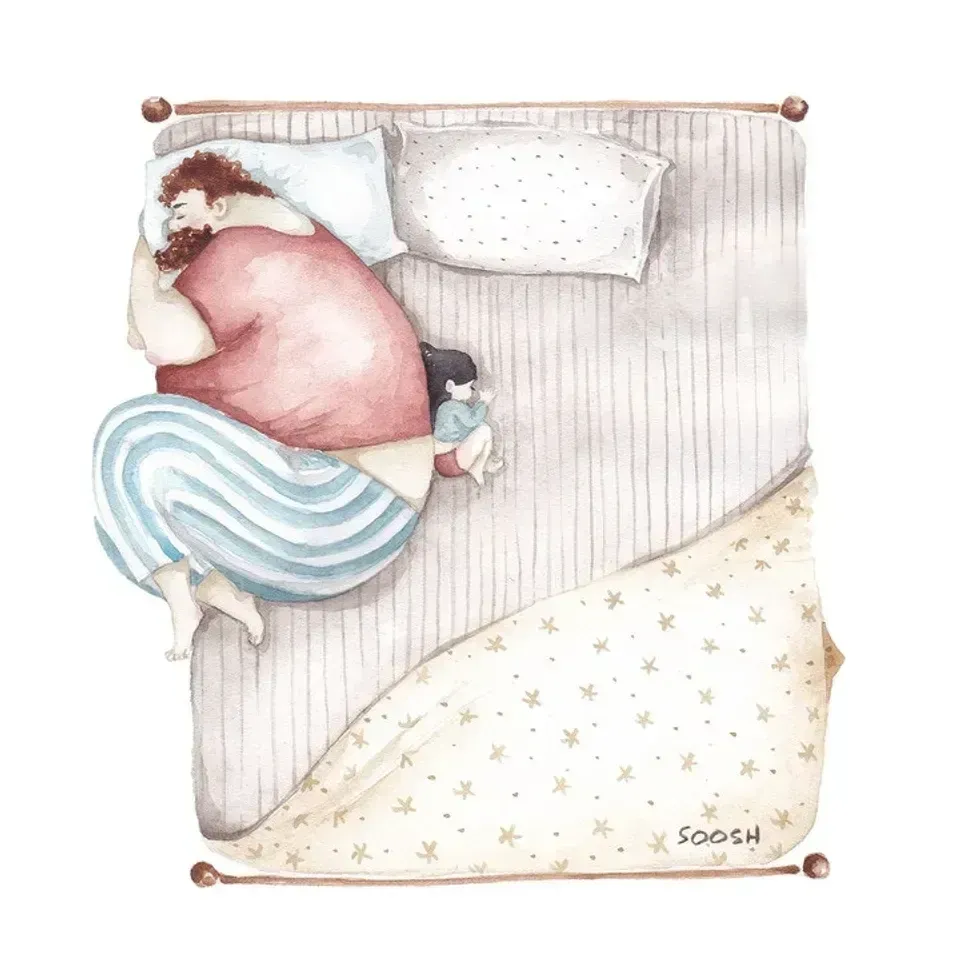 A dad takes the small corner of the bed with his dauthterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission.
A dad takes the small corner of the bed with his dauthterAll illustrations are provided by Soosh and used with permission. Season 8 Nbc GIF by The Office
Season 8 Nbc GIF by The Office Figuring out our finances may be getting easier.
Photo by
Figuring out our finances may be getting easier.
Photo by  Plumbing Plumber GIF by Family Guy
Plumbing Plumber GIF by Family Guy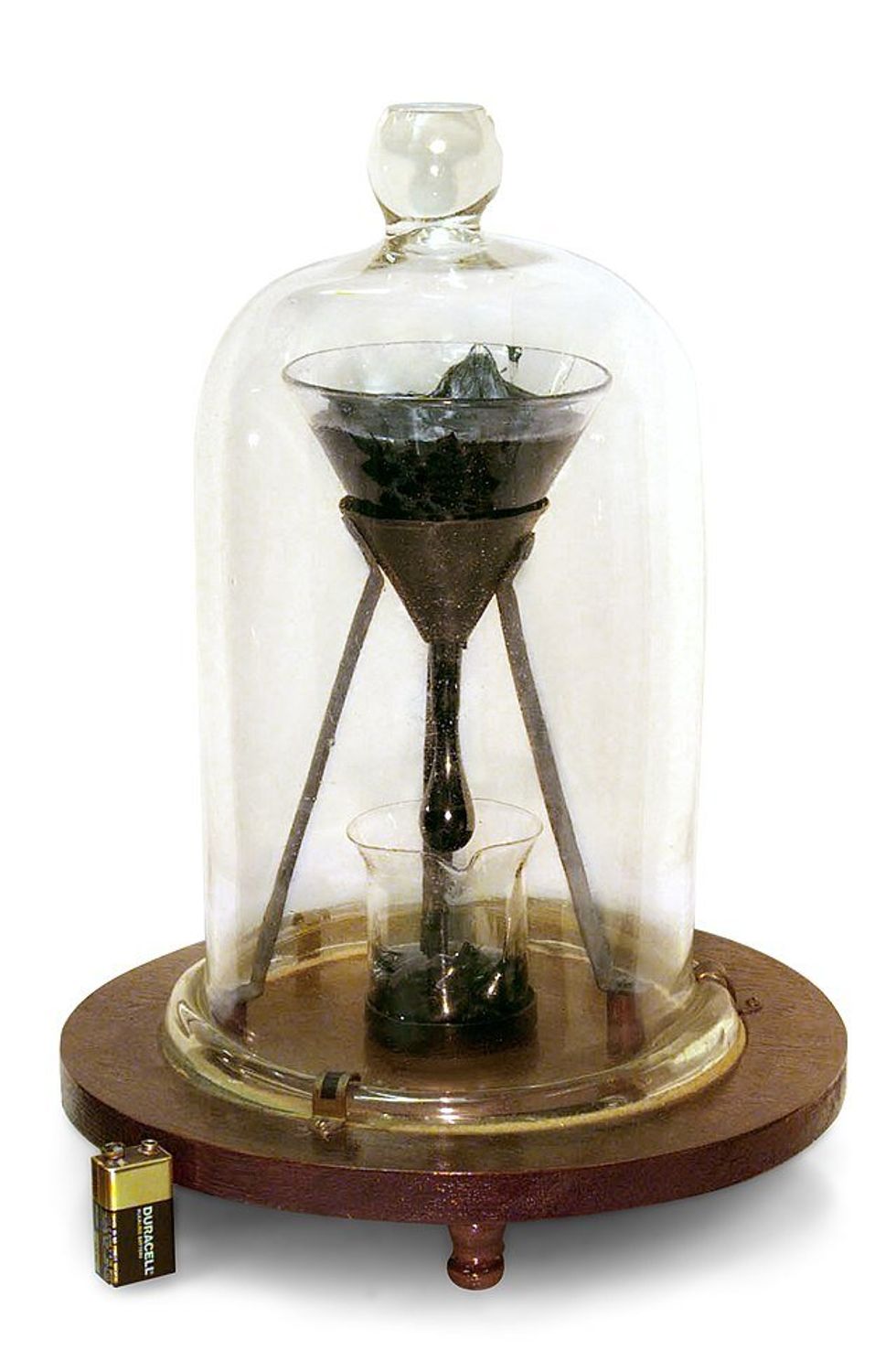 Pitch moves so slowly it can't be seen to be moving with the naked eye until it prepares to drop. Battery for size reference.
Pitch moves so slowly it can't be seen to be moving with the naked eye until it prepares to drop. Battery for size reference.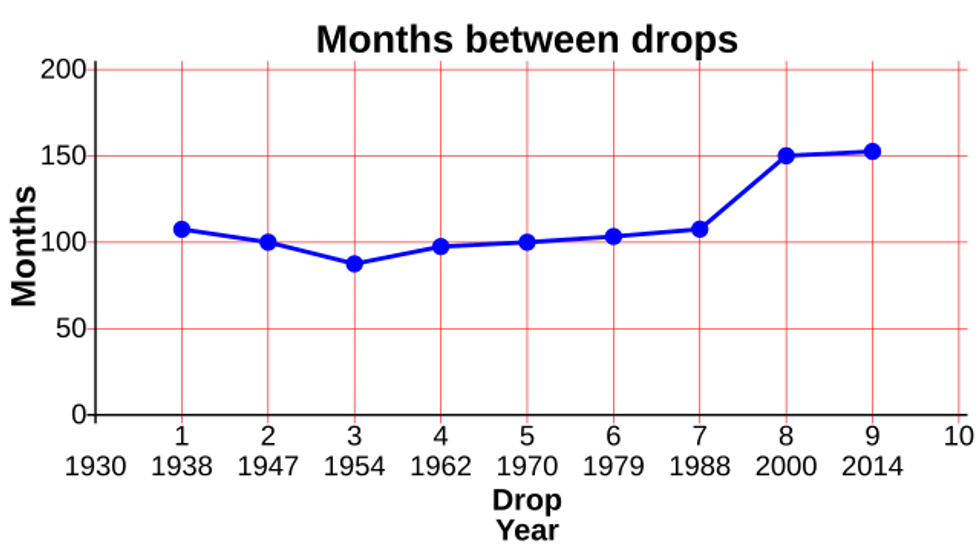 The first seven drops fell around 8 years apart. Then the building got air conditioning and the intervals changed to around 13 years.
The first seven drops fell around 8 years apart. Then the building got air conditioning and the intervals changed to around 13 years.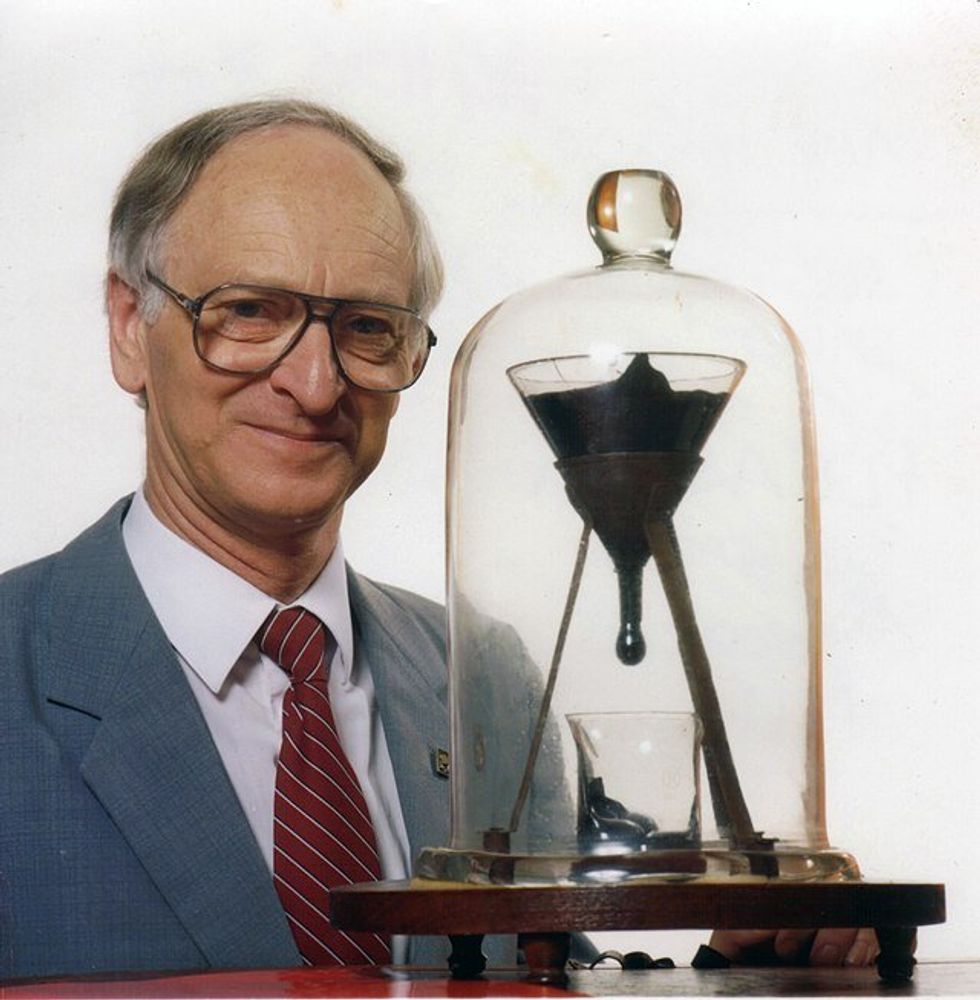 John Mainstone, the second custodian of the Pitch Drop Experiment, with the funnel in 1990.
John Mainstone, the second custodian of the Pitch Drop Experiment, with the funnel in 1990. The Alhambra sits atop a plateau overlooking Granada, Spain.
The Alhambra sits atop a plateau overlooking Granada, Spain.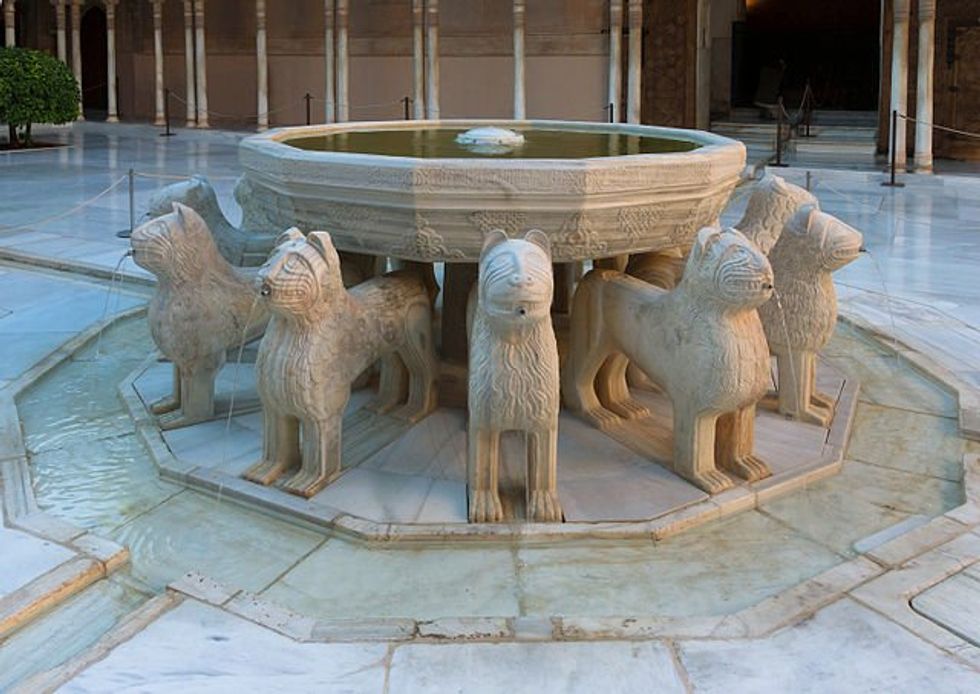 Fountain of the Lions at the Alhambra, Granada
Fountain of the Lions at the Alhambra, Granada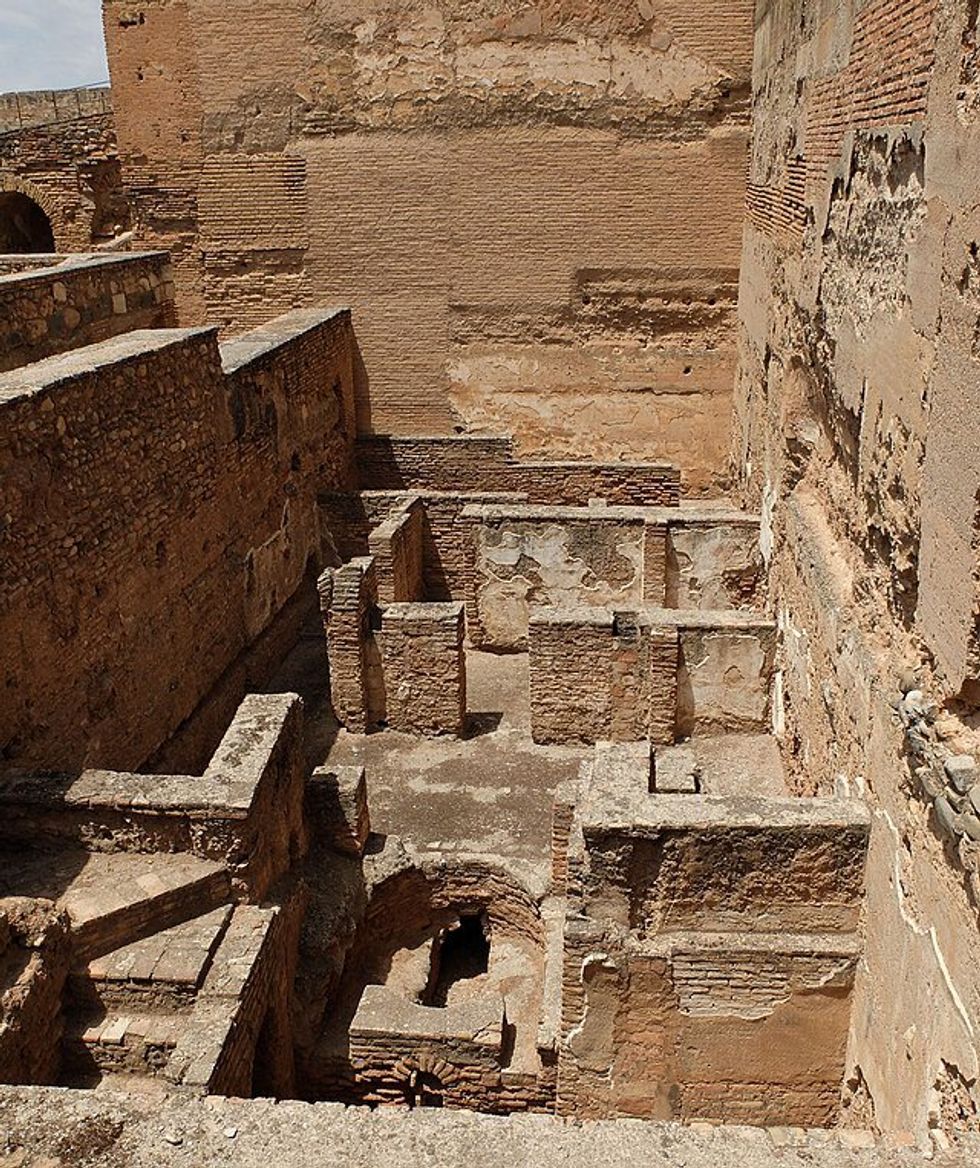 Remains of baths inside the Alhambra Alcazaba
Remains of baths inside the Alhambra Alcazaba