More
Barack Obama should hire this guy to attack Mitt Romney.
We have everything Mitt Romney has ever said that was contradictory in one video. EVERYTHING. (As of today, but there will be more soon).
08.07.12
Facebook is critical to our success and we could use your help. It will only take a few clicks on your device. But it would mean the world to us.
Here’s the link . Once there, hit the Follow button. Hit the Follow button again and choose Favorites. That’s it!

If you’d like to know why this is so important for us, you can read more about it here .
"I love my mom dearly, but I'm surprised at how little effort she puts in."
A stressed mom and her happy, busy parents.
As far as generational stereotypes go, baby boomers (1946 to 1964) have often been accused of being a self-absorbed generation that has had no problem hoarding wealth, disregarding the environment, and prioritizing their own interests over their families. After all, they’re the generation that predominantly raised Gen X (1965 to 1980) and older millennials ('80s babies), also known as Gen Goonie, who were the least parented group of people in decades.
It’s unfair to paint an entire generation with the same brush. Still, the people who were once called the “Me Generation” are developing a reputation for being less involved in their grandchildren’s lives than their parents. The different grandparenting styles have been attributed to the fact that boomers worked longer and therefore want to enjoy their retirement. They also have more money than their parents to enjoy traveling and pursuing their hobbies. Those looking to take shots at boomers claim that they didn’t put a lot of effort into raising their kids, so why would they be any different with their grandkids?

A mother of one, who goes by TheCalmQuail on Mumsnet (a UK-based mothers' forum), made a controversial post, calling out a significant double standard when it comes to boomers. They had no problem having their parents help raise their kids, but they don’t want to extend the same courtesy to their children.
“It's come up in a few conversations with other parents recently about how little time their parents spend with their children, especially in comparison to when they were younger and at their grandparents' daily,” CalmQuail wrote. “Myself included, I avoided nursery completely when my mother went back to work because free daily childcare from a relative, and some of my happiest regular memories are spending regular one-on-one time with my Nana.”
“I realise grandparents are entitled to their own lives, but the lack of help does seem like double standards, when a large majority have seemingly had so much help themselves,” she continued.

CalmQuail added that her mother lives up the road from her but still finds excuses not to help our child or even spend time with her kid. “It often feels like she's an extra toddler, as I have to suggest stuff to tempt her to do anything together; I manage the logistics, drive her there, etc. She will be there for emergency childcare requests when possible,” she continued. At the end of her post, she asked whether she was being unreasonable for thinking that her parents should put as much effort into raising their grandchildren as they had put into raising their parents.
The verdict: 68% thought she was NOT being unreasonable, and 32% felt that she was being unreasonable. Therefore, a majority of parents on the forum believe that Baby Boomers have the same responsibility to their grandchildren as the Silent Generation (1928 to 1945) did to theirs.
Many parents on the forum have experienced similar situations with their boomer parents and have given them a little grace by acknowledging that their grandparents didn’t have many resources or retirement expectations, so they dedicated their energy to their families.

“I know this will turn into a boomer bashing thread but my experience is my parents and their friends are early retirees with a fair bit of cash and feel they’ve earnt a nice easy long comfortable retirement (they have worked hard but only the same as us except we can’t afford a nanny, cleaner etc like they did…).so they’re busy on holidays, golfing, socialising,” a commenter wrote. “My grandparents were typical of their generation—very hard working, modest life, and incredibly family orientated, they had us every holiday.”
“I don’t think my grandparents had much in the way of expectations of retirement,” another commenter added. “They retired relatively early by today’s standards, and lived far longer than they expected. There wasn’t much of a sense of ‘enjoying your retirement’ by jetting off around the world or pursuing personal hobbies - they were always there and available.”
Ultimately, there’s nothing wrong with baby boomers enjoying their retirement, but their children have a right to feel a bit miffed by the shift in grandparenting priorities. As times change, so do expectations, but why does it feel like younger people are always getting the short end of the stick when it comes to life's necessities, such as childcare and the cost of living? Unfortunately, so many younger people feel like they have to go it alone. However, kudos to the boomer grandparents who do help out with childcare, just as their parents did. As they say, it takes a village to raise a child, and these days, our villages need to be growing instead of shrinking.
They may have uncovered the secrets of our final moments.
A doctor is analyzing brain scans.
Death remains one of the greatest mysteries of life. It’s impossible to know what happens as a person passes and whether there’s anything afterward because no one has ever been able to report what happens from beyond the grave. Of course, if you ask those with a keen interest in the supernatural, they may say otherwise.
However, in 2021, researcher Dr. Raul Vicente and his colleagues at the University of Tartu, Estonia, became the first people ever to record the brainwaves of someone in the process of dying, and what they’ve come to realize should be very comforting to everyone. “We measured 900 seconds of brain activity around the time of death and set a specific focus to investigate what happened in the 30 seconds before and after the heart stopped beating,” Dr. Ajmal Zemmar, a neurosurgeon at the University of Louisville, US, who organized the study, told Frontiers.
The patient who died while having his brain waves measured was 87 years old and had epilepsy. While researchers were studying his brain to learn more about the condition, they had a heart attack and passed away. “Just before and after the heart stopped working, we saw changes in a specific band of neural oscillations, so-called gamma oscillations, but also in others such as delta, theta, alpha, and beta oscillations,” Zemmar said.
The different types of brain oscillations that occurred in the patient before and after the heart attack were associated with high cognitive functions, including dreaming, concentrating, memory retrieval, and memory flashbacks. Therefore, it’s possible that as the patient was dying, they had their life flash before their eyes. What an amazing and comforting experience right before leaving this mortal coil.
“Through generating oscillations involved in memory retrieval, the brain may be playing a last recall of important life events just before we die, similar to the ones reported in near-death experiences,” Zemmar speculated. “These findings challenge our understanding of when exactly life ends and generate important subsequent questions, such as those related to the timing of organ donation.”
Science has found that people can remain conscious up to 20 seconds after they are declared dead. Even after the heart and breathing have stopped, the cerebral cortex can hang on for a while without oxygen. So, some people may experience the moment when they hear themselves declared dead, but they aren’t able to move or react to the news. In cases where someone performs CPR on the deceased person, the blood pumped by the compressions can temporarily keep the brain alive as well.
Although the experience of death will probably always remain a mystery, we should take solace in the idea that, in many cases, it may not necessarily be a miserable experience but an ecstatic final burst of consciousness that welcomes us into the great beyond. “Something we may learn from this research is: although our loved ones have their eyes closed and are ready to leave us to rest, their brains may be replaying some of the nicest moments they experienced in their lives,” Zemmar concludes.
This article originally appeared in February
It takes nearly a decade for one drop of this liquid to fall.
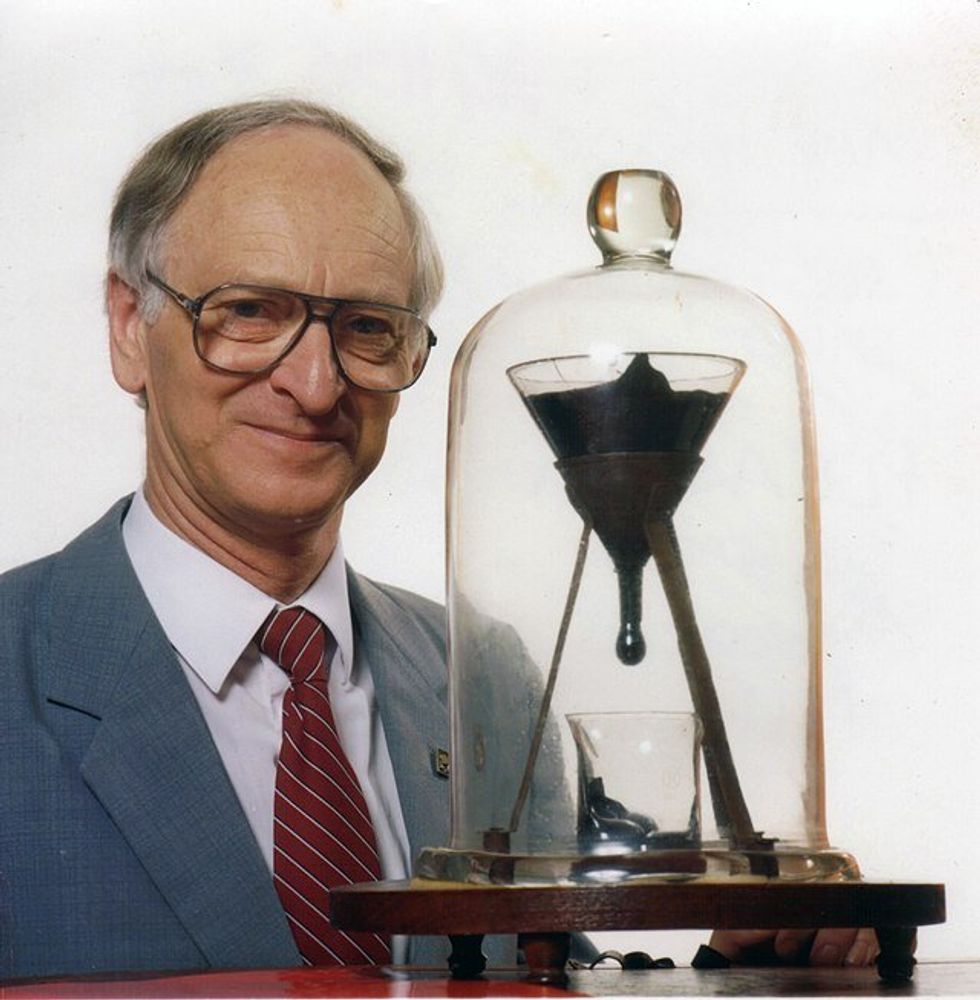
John Mainstone was the custodian of the Pitch Drop Experiment for 52 years.
Because we use water all the time, most of us have an intuitive sense of how long it takes a drop of water to form and fall. More viscous liquids, like oil or shampoo or honey, drop more slowly depending on how thick they are, which can vary depending on concentration, temperature and more. If you've ever tried pouring molasses, you know why it's used as a metaphor for something moving very slowly, but we can easily see a drop of any of those liquids form and fall in a matter of seconds.
But what about the most viscous substance in the world? How long does it take to form a falling drop? A few minutes? An hour? A day?
How about somewhere between 7 and 13 years?
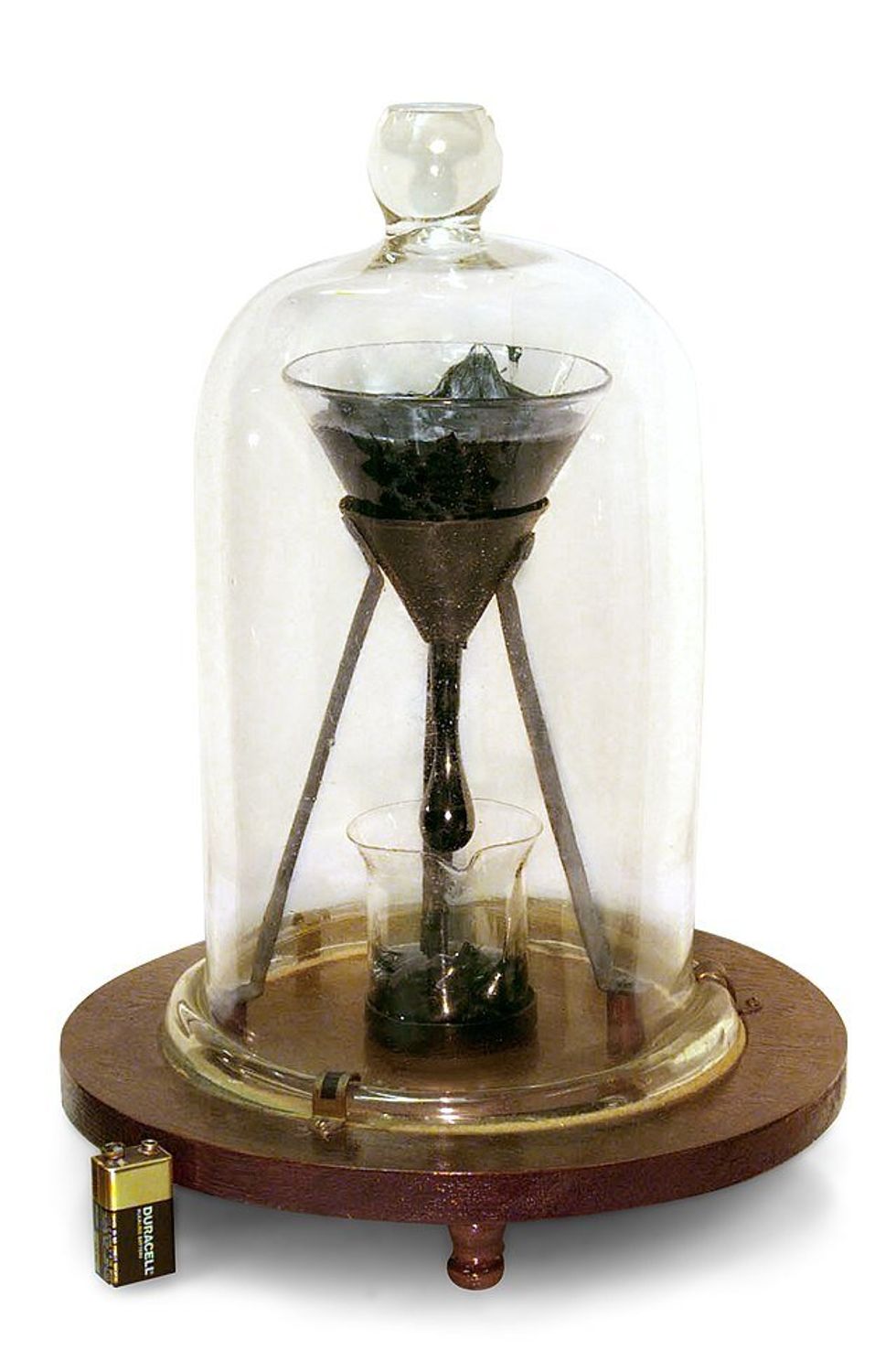

The Pitch Drop Experiment began in 1927 with a scientist who had a hunch. Thomas Parnell, a physicist at the University of Queensland in Australia, believed that tar pitch, which appears to be a solid and shatters like glass when hit with a hammer at room temperature, is actually a liquid. So he set up an experiment that would become the longest-running—and the world's slowest—experiment on Earth to test his hypothesis.
Parnell poured molten pitch it into a funnel shaped container, then let it settle and cool for three years. That was just to get the experiment set up so it could begin. Then he opened a hole at the bottom of the funnel to see how long it would take for the pitch to ooze through it, form a droplet, and drop from its source.
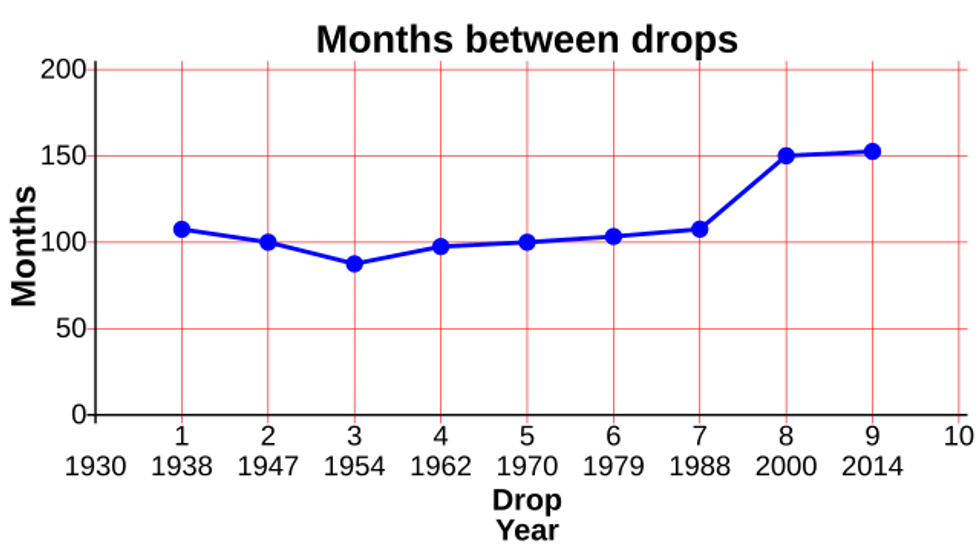
It took eight years for the first drop to fall. Nine years for the second. Those were the only two drops Parnell was alive for before he passed away in 1948.
- YouTubewww.youtube.com
In total, there have been nine pitch drops in the University of Queensland experiment. The first seven drops fell between 7 and 9 years apart, but when air conditioning was added to the building after the seventh drop, the amount of time between drops increased significantly. The drops in 2000 and 2014 happened approximately 13 years after the preceding one. (The funnel is set up as a demonstration with no special environmental controls, so the seasons and conditions of the building can easily affect the flow of the pitch.)
The next drop is anticipated to fall sometime in the 2020s.
Though Parnell proved his hypothesis well before the first drop even fell, the experiment continued to help scientists study and measure the viscosity of tar pitch. The thickest liquid substance in the world, pitch is estimated to be 2 million times more viscous than honey and 20 billion times the viscosity of water. No wonder it takes so ridiculously long to drop.
One of the most interesting parts of the Pitch Drop Experiment is that in the no one has ever actually witnessed one of the drops falling at the Queensland site. The drops, ironically, happen rather quickly when they do finally happen, and every time there was some odd circumstance that kept anyone from seeing them take place.
The Queensland pitch drop funnel is no longer the only one in existence, however. In 2013, Trinity College in Dublin, Ireland, managed to capture its own pitch drop on camera. You can see how it looks as if nothing is happening right up until the final seconds when it falls.
- YouTubewww.youtube.com
Today, however, with the internet and modern technology, it's likely that many people will be able to witness the next drop when it happens. The University of Queensland has set up a livestream of the Pitch Drop Experiment, which you can access here, though watching the pitch move more slowly than the naked eye can detect is about as exciting as watching paint dry.
But one day, within a matter of seconds, it will drop, hopefully with some amount of predictability as to the approximate day at least. How many people are going to be watching a livestream for years, waiting for it to happen?
PoorJohn Mainstone was the custodian of the experiment for 52 years, from 1961 to 2013. Sadly, he never got to witness any of the five drops that took place during his tenure. Neither did Parnell himself with the two that took place while he was alive.

Sometimes science is looks like an explosive chemical reaction and sometimes it's a long game of waiting and observing at the speed of nature. And when it comes to pitch dripping through a funnel, the speed of nature is about as slow as it gets.
So... when are we getting the matching 4-day work week?
When talking with other parents I know, it's hard not to sound like a grumpy old man when we get around to discussing school schedules. "Am I the only one who feels like kids have so many days off? I never got that many days off when I was a kid! And I had to go work in the coal mine after, too!" I know what I sound like, but I just can't help it.
In Georgia, where I live, we have a shorter summer break than some other parts of the country. But my kids have the entire week of Thanksgiving off, a week in September, two whole weeks at Christmas, a whole week off in February, and a weeklong spring break. They have asynchronous days (during which they complete assignments at home, which usually takes about 30 minutes) about once a month, and they have two or three half-day weeks throughout the year. Quite honestly, it feels like they're never in school for very long before they get another break, which makes it tough to get in a rhythm with work and career goals. Plus, we're constantly arranging day camps and other childcare options for all the time off. Actually, I just looked it up and I'm not losing my mind: American kids have fewer school days than most other major countries.
So it caught my attention in a major way when I read that Whitney Independent School District in Texas recently decided to enact a 4-day week heading into the 2025 school year. That makes it one of dozens of school districts in Texas to make the change and over 900 nationally.
The thought of having the kids home from school EVERY Friday or Monday makes me want to break out in stress hives. But this 4-day school week movement isn't designed to give parents a headache. It's meant to lure teachers back to work.
Yes, teachers are leaving the profession in droves and young graduates don't seem eager to replace them. Why? The pay is bad, for starters, but that's just the beginning. Teachers are burnt out, undermined and criticized relentlessly, held hostage by standardized testing, and more. It can be a grueling, demoralizing, and thankless job. The love and passion they have for shaping the youth of tomorrow can only take you so far when you feel like you're constantly getting the short end of the stick.
School districts want to pay their teachers more, in theory, but their hands are often tied. So they're getting creative to recruit the next generation of teachers into their schools — starting with an extra day off for planning, catch-up, or family time every week.

So far, the data shows that the truncated schedule perk is working. In these districts, job applications for teachers are up, retirements are down, and teachers are reporting better mental well-being. That's great news!
But these positive developments may be coming at the price of the working parents in the communities. Most early adopters of the 4-day week have been rural communities with a high prevalence of stay-at-home parents. As the idea starts to take hold in other parts of the country, it's getting more pushback. Discussions on Reddit, Facebook, and other social media are overrun with debate on how this is all going to shake up. Some parents, to be fair, like the idea! If they stay-at-home or have a lot of flexibility, they see it as an opportunity for more family time. But many are feeling anxious. Here's what's got those parents worried:
The effect on students' achievement is still unclear.
The execution of the 4-day week varies from district to district. Some schools extend the length of each of the four days, making the total instructional time the same. That makes for a really long day, and some teachers say the students are tired and more unruly by the late afternoon. Some districts are just going with less instruction time overall, which has parents concerned that their kids might fall behind.
4-day school weeks put parents in a childcare bind.
Having two working parents is becoming more common and necessary with the high cost of living. I know, I know — "school isn't daycare!" But it is the safe, reliable, and educational place we send our kids while we need to work.
Families with money and resources may be able to enroll their kids in more academics, extracurriculars, sports, or childcare, but a lot of normal families won't be able to afford that cost. Some schools running a 4-day week offer a paid childcare option for the day off, but that's an added expense and for families with multiple kids in the school system, it's just not possible.
This will inevitably end with some kids getting way more screentime.
With most parents still working 5-day weeks, and the cost of extra activities or childcare too high, a lot of kids are going to end up sitting around on the couch with their iPad on those days off. I'm no expert, and I'm certainly not against screentime, but adding another several hours of it to a child's week seems less than ideal.
Of course there are other options other than paid childcare and iPads. There are play dates, there's getting help from family and friends. All of these options are an enormous amount of work to arrange for parents who are already at capacity.
A Commissioner of Education from Missouri calls truncated schedules a "band-aid solution with diminishing returns." Having an extra planning day won't stop teachers from getting scapegoated by politicians or held to impossible curriculum standards, it won't keep them from having to buy their own supplies or deal with ever-worsening student behavior.
Some teachers and other experts have suggested having a modified 5-day school week, where one of the days gets set aside as a teacher planning day while students are still on-site participating in clubs, music, art — you know, all the stuff that's been getting cut in recent years. Something like that could work in some places.
As a dad, I don't mind the idea of my busy kids having an extra day off to unwind, pursue hobbies, see friends, catch up on projects, or spend time as a family. And I'm also very much in favor of anything that takes pressure off of overworked teachers. But until we adopt a 4-day work week as the standard, the 4-day school week is always going to feel a little out of place.
This article originally appeared in February
Things couldn't have been more different.
A young couple can't handle high prices and their dad says to save money.
One of the big talking points in the great American millennials versus baby boomers debate is whether the younger generation has knee-capped itself by its lavish spending habits that have prevented them from owning homes. If millennials stopped buying $14 avocado toast and $1,000 iPhones, would they be able to save enough for a down payment on a modest home?
Freddie Smith, 36, of Orlando, Florida, recently went viral on TikTok for a video in which he challenged the boomer argument with statistics from the Bureau of Labor, Federal Reserve, and the U.S. Census Bureau. Smith believes that the older generations misunderstand millennial finances because their concept of luxury is based on 1980s economics. Smith says that for baby boomers, essentials such as rent and child care were much more affordable, but items considered luxuries (TVs, CD players, computers) were much more expensive.
"The main shift is that core essentials—housing, education, healthcare, and even food—have become more expensive," Smith said. "Housing and rent, for instance, now outpace wage growth, making homeownership feel unattainable for many. The cost of childcare has also skyrocketed, and food prices have increased.”
"As a result, I think older generations have a different perspective on luxury versus necessity,” Smith continued. “They grew up in a time when hard work typically led to financial stability, whereas today, even with hard work, many people struggle with the high costs of housing, rent and medical expenses. Basic survival used to be far more affordable, allowing people more financial room to build a stable life."
Smith’s numbers don’t lie. For a person in the '80s to own three TVs, a CD player, a cellphone, a microwave, and a computer, it would cost them 3.5 years of rent or a 20% downpayment on the average home. So, it was irresponsible for someone in that period to purchase all of what was known then as luxuries. However, these days, for a Millennial to have the average apartment and the equivalent amount of "luxuries" would only cost a little over one month's rent.

"But if you skip that daily $6 Starbucks drink, you’ll have enough for the downpayment in 29.22 years," Yokahana joked in the comments. "I hate that housing and transportation have become luxuries," Molly added. "Imagine spending 3x your rent on a microwave," Donutdisaster wrote.
The price of manufactured goods has steadily fallen over the last few decades due to technological improvements and trade policies that have allowed the U.S. to import goods from places where labor costs are cheaper. "International, global competition lowers prices directly from lower-cost imported goods, and indirectly by forcing U.S. manufacturers to behave more competitively, with lower prices, higher quality, better service, et cetera," Sociologist Joseph Cohen of Queens University said, according to Providence Journal.
Housing prices in the US have soared due to the low inventory caused by the Great Recession, mortgage rates, and zoning laws that make building more challenging. Rents have increased considerably since the pandemic due to low inventory, inflation, barriers to home ownership, and the fact that more people want to live alone than with a roommate or romantic partner.
Smith’s breakdown of the economic changes over the past two generations makes a strong case for the idea that millennial financial troubles have more to do with systemic problems than spending habits. The boomers got a bad deal regarding luxury items, and the millennials with necessities. Wouldn’t living in a world where both were affordable in the same era be great?
This article originally appeared in February


